Jute insulation offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to mineral wool insulation, providing excellent thermal and acoustic properties while being non-toxic and safe to handle without protective gear. Unlike mineral wool, which is made from rock or slag and can irritate skin and lungs, jute insulation is derived from natural plant fibers, promoting eco-friendly building practices. Both materials effectively reduce heat transfer, but jute insulation supports healthier indoor air quality and reduces environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
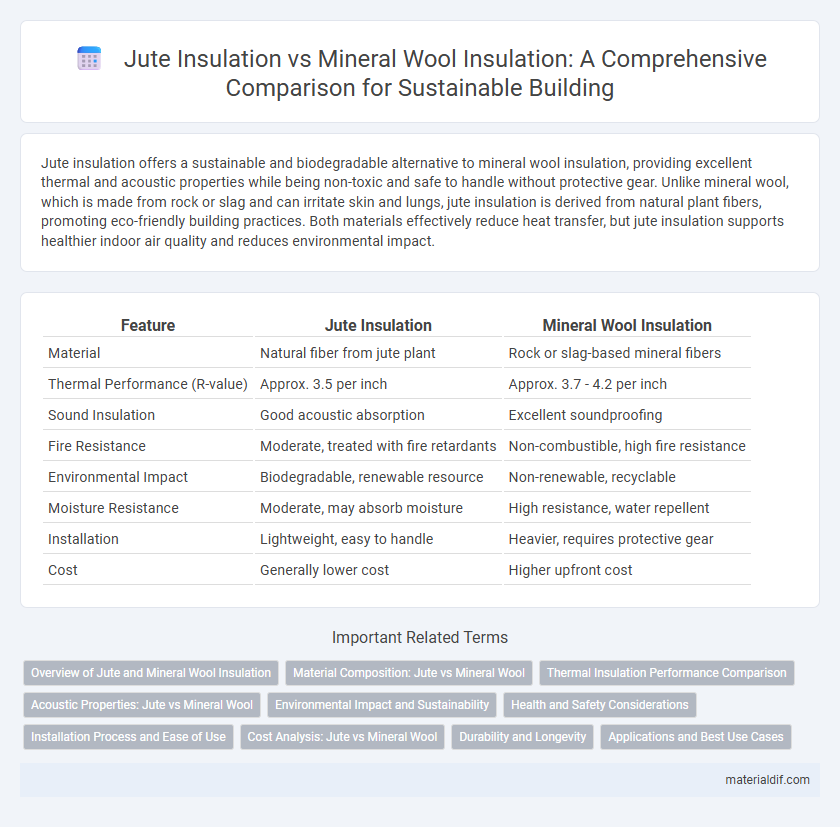
| Feature | Jute Insulation | Mineral Wool Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural fiber from jute plant | Rock or slag-based mineral fibers |
| Thermal Performance (R-value) | Approx. 3.5 per inch | Approx. 3.7 - 4.2 per inch |
| Sound Insulation | Good acoustic absorption | Excellent soundproofing |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate, treated with fire retardants | Non-combustible, high fire resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Non-renewable, recyclable |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, may absorb moisture | High resistance, water repellent |
| Installation | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier, requires protective gear |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher upfront cost |
Overview of Jute and Mineral Wool Insulation
Jute insulation, derived from natural jute fibers, offers excellent thermal and acoustic properties while being biodegradable and environmentally friendly. Mineral wool insulation, composed of molten rock or slag spun into fibers, provides superior fire resistance, soundproofing, and moisture resistance. Both materials serve as effective insulators but differ significantly in sustainability and chemical composition.
Material Composition: Jute vs Mineral Wool
Jute insulation is derived from natural plant fibers harvested from the jute plant, providing a renewable and biodegradable alternative characterized by its lightweight and moisture-regulating properties. Mineral wool insulation, composed primarily of basalt rock and recycled slag, offers fire resistance and high thermal performance due to its dense, fibrous structure formed through a high-temperature melting process. The organic nature of jute contrasts with the inorganic mineral composition of mineral wool, influencing factors such as sustainability, moisture absorption, and installation handling.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Jute insulation offers a thermal conductivity typically around 0.038 to 0.042 W/m*K, providing effective thermal resistance while ensuring sustainability and biodegradability. Mineral wool insulation has a slightly lower thermal conductivity, generally between 0.035 to 0.040 W/m*K, delivering superior thermal performance and enhanced fire resistance. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency, but mineral wool often outperforms jute in colder climates due to its higher thermal insulating capabilities.
Acoustic Properties: Jute vs Mineral Wool
Jute insulation offers natural sound absorption by dampening airborne noise and reducing echo, making it effective in enhancing acoustic comfort in residential spaces. Mineral wool insulation provides superior acoustic performance due to its dense, fibrous structure that traps and dissipates sound waves across a broader frequency range. While mineral wool excels in noise reduction, jute's eco-friendly properties combined with moderate acoustic benefits present a sustainable alternative for sound insulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Jute insulation offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative to mineral wool insulation, significantly reducing environmental impact due to its natural fiber composition and lower energy consumption during production. Mineral wool, derived from volcanic rock and slag, has a higher carbon footprint and involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Jute's sustainability is enhanced by its ability to sequester carbon during growth and its end-of-life compostability, making it a preferable choice for eco-conscious building projects.
Health and Safety Considerations
Jute insulation offers a natural, non-toxic alternative to mineral wool, reducing the risk of respiratory irritation and skin allergies commonly associated with mineral fibers. Its biodegradability and absence of chemical binders enhance indoor air quality, making it safer for occupants and installers alike. Mineral wool, while fire-resistant, requires protective gear during installation to prevent irritation, highlighting jute's advantage in health and safety with minimal protective measures needed.
Installation Process and Ease of Use
Jute insulation offers a lightweight and flexible installation process, allowing for easy cutting and fitting around irregular spaces without specialized tools. Mineral wool insulation, while fire-resistant and sound-absorbing, typically requires protective gear due to its fibrous nature and can be more time-consuming to handle and install. The natural properties of jute reduce irritation risks, making it more user-friendly during application compared to mineral wool.
Cost Analysis: Jute vs Mineral Wool
Jute insulation typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to mineral wool insulation, making it a budget-friendly option for eco-conscious building projects. Mineral wool, while more expensive initially, provides superior fire resistance and soundproofing that may reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating the total cost of ownership involves considering both material price and performance benefits specific to each insulation type.
Durability and Longevity
Jute insulation offers natural resistance to moisture and pests, contributing to its durability in moderate climates, whereas mineral wool insulation excels with superior fire resistance and moisture resilience, enhancing its lifespan in harsher environments. Mineral wool's inorganic composition prevents mold growth and degradation over time, making it a more durable option for long-term use. Jute insulation requires careful maintenance to maximize longevity, while mineral wool generally provides consistent performance under a wider range of conditions.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Jute insulation is ideal for eco-friendly construction projects, offering natural thermal and acoustic properties suitable for residential buildings, especially in sustainable homes and passive houses. Mineral wool insulation excels in commercial and industrial applications requiring superior fire resistance and soundproofing, making it best for mechanical rooms, high-temperature environments, and sound-sensitive spaces. Both materials provide effective thermal insulation, but jute is preferred for green building certifications, while mineral wool is favored for its durability and safety in demanding conditions.
Jute Insulation vs Mineral Wool Insulation Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com