Jute geotextiles offer superior biodegradability and cost-effectiveness compared to coir geotextiles, making them ideal for temporary erosion control and soil stabilization projects. Coir geotextiles provide greater durability and water retention, which enhances plant growth and long-term slope reinforcement. Choosing between jute and coir depends on project duration, environmental conditions, and required mechanical strength.
Table of Comparison
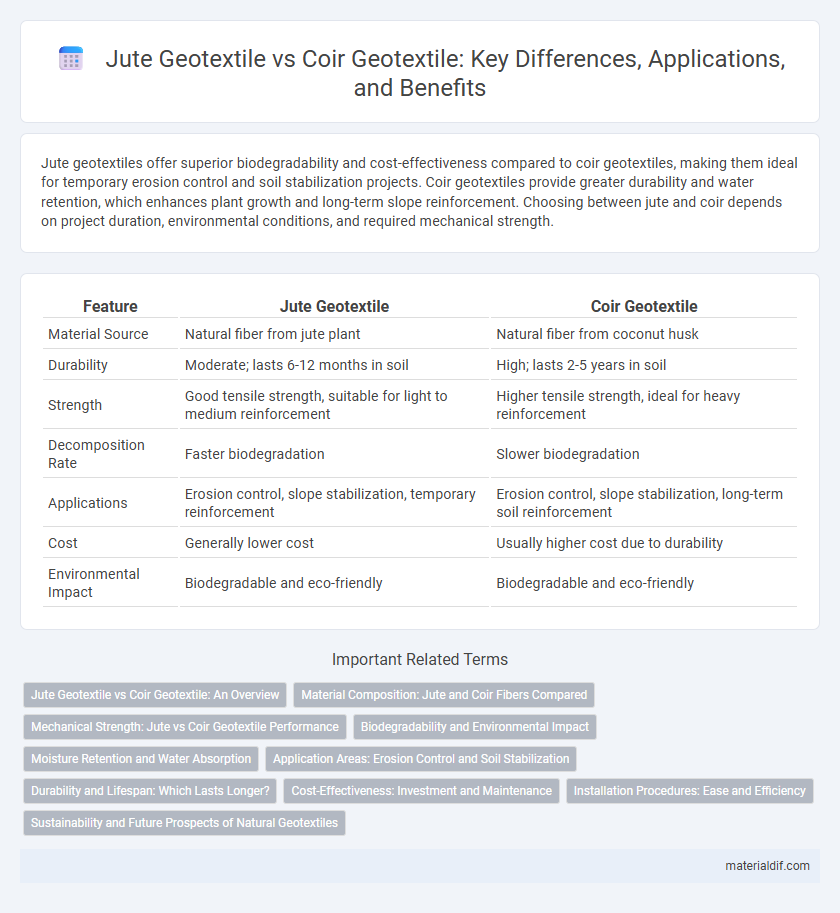
| Feature | Jute Geotextile | Coir Geotextile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural fiber from jute plant | Natural fiber from coconut husk |
| Durability | Moderate; lasts 6-12 months in soil | High; lasts 2-5 years in soil |
| Strength | Good tensile strength, suitable for light to medium reinforcement | Higher tensile strength, ideal for heavy reinforcement |
| Decomposition Rate | Faster biodegradation | Slower biodegradation |
| Applications | Erosion control, slope stabilization, temporary reinforcement | Erosion control, slope stabilization, long-term soil reinforcement |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost due to durability |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Biodegradable and eco-friendly |
Jute Geotextile vs Coir Geotextile: An Overview
Jute geotextile offers superior tensile strength and biodegradability compared to coir geotextile, making it ideal for soil erosion control and agricultural applications. Coir geotextile, derived from coconut husks, excels in water retention and is preferred for landscaping and horticulture projects requiring moisture conservation. The choice between jute and coir geotextiles depends on project-specific needs such as durability requirements, environmental conditions, and cost efficiency.
Material Composition: Jute and Coir Fibers Compared
Jute geotextiles are composed primarily of soft, long jute fibers known for their high tensile strength and biodegradability, making them suitable for erosion control and soil stabilization. In contrast, coir geotextiles consist of coarse, stiff coir fibers derived from coconut husks, offering superior durability and resistance to microbial degradation in harsh environmental conditions. The material composition differences influence their performance, with jute providing better flexibility and coir delivering enhanced abrasion resistance in geotextile applications.
Mechanical Strength: Jute vs Coir Geotextile Performance
Jute geotextiles exhibit higher tensile strength and better elongation at break compared to coir geotextiles, enhancing their mechanical performance in soil reinforcement applications. Coir geotextiles provide moderate mechanical strength but excel in flexibility and resilience, making them suitable for erosion control on uneven terrains. The superior mechanical strength of jute geotextiles ensures greater durability and load-bearing capacity in heavy-duty geotechnical projects.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
Jute geotextiles exhibit superior biodegradability, breaking down within 6 to 12 months, thereby minimizing long-term environmental impact in soil stabilization and erosion control projects. In comparison, coir geotextiles, derived from coconut husks, degrade more slowly over 12 to 36 months, offering prolonged soil reinforcement but with a longer environmental footprint. Both natural fibers promote sustainability, yet jute's faster decomposition aligns better with eco-friendly objectives by reducing residual material in ecosystems.
Moisture Retention and Water Absorption
Jute geotextiles exhibit superior moisture retention due to their dense fiber structure, allowing them to hold water efficiently and support plant growth in erosion control applications. Coir geotextiles possess high water absorption capacity, absorbing and retaining more water than jute, which aids in stabilizing soil moisture over extended periods. The choice between jute and coir geotextile depends on specific project needs, with jute favored for quick moisture retention and coir for prolonged water absorption.
Application Areas: Erosion Control and Soil Stabilization
Jute geotextile exhibits superior biodegradability and tensile strength, making it ideal for erosion control on slopes, riverbanks, and highways by promoting vegetation growth and soil retention. Coir geotextile offers enhanced water retention and cushioning properties, making it effective for soil stabilization in wetland restoration, embankments, and coastal erosion protection. Both materials are environmentally friendly, but jute is preferred in areas requiring faster decomposition, while coir suits applications needing prolonged structural support.
Durability and Lifespan: Which Lasts Longer?
Jute geotextiles generally offer higher tensile strength and better resistance to microbial degradation, resulting in a longer lifespan of up to two years in soil stabilization applications compared to coir geotextiles, which typically last around one year. The durability of jute is enhanced by its tight fiber structure, making it more suitable for projects requiring extended erosion control and reinforcement. Conversely, coir geotextiles, derived from coconut husks, provide excellent water retention and biodegradability but degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness: Investment and Maintenance
Jute geotextiles generally offer a more cost-effective investment compared to coir geotextiles due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Maintenance costs for jute geotextiles tend to be minimal as they degrade naturally without requiring chemical treatments, unlike coir which may need additional preservation measures. Long-term durability combined with affordability makes jute geotextiles a preferred choice for budget-sensitive erosion control and soil stabilization projects.
Installation Procedures: Ease and Efficiency
Jute geotextile installation benefits from its lightweight and flexible nature, allowing easy handling and faster deployment over large areas with minimal labor. Coir geotextiles, while durable and robust, often require more careful positioning due to their thicker and rougher texture, which can slow down the installation process. Overall, jute offers higher efficiency in installation, particularly in projects demanding swift soil stabilization and erosion control.
Sustainability and Future Prospects of Natural Geotextiles
Jute geotextiles exhibit superior biodegradability and higher tensile strength compared to coir geotextiles, making them more sustainable for soil erosion control and agricultural applications. Coir geotextiles excel in water retention and resistance to microbial degradation, offering longevity in tropical climates. The future of natural geotextiles hinges on integrating these materials into eco-friendly infrastructure projects, driven by increasing demand for renewable resources and government incentives promoting sustainable construction practices.
Jute Geotextile vs Coir Geotextile Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com