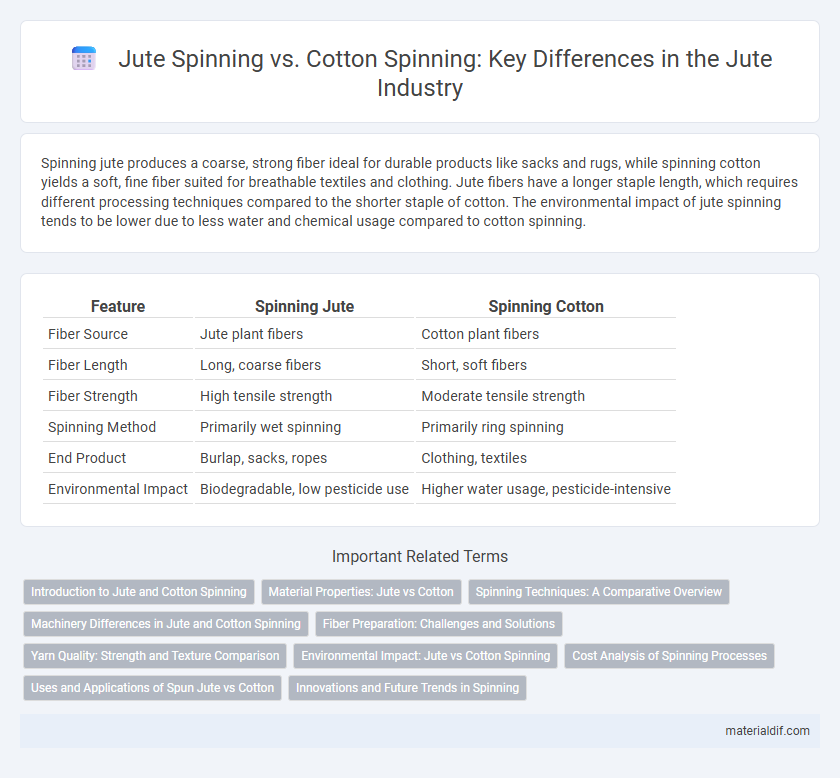
Spinning jute produces a coarse, strong fiber ideal for durable products like sacks and rugs, while spinning cotton yields a soft, fine fiber suited for breathable textiles and clothing. Jute fibers have a longer staple length, which requires different processing techniques compared to the shorter staple of cotton. The environmental impact of jute spinning tends to be lower due to less water and chemical usage compared to cotton spinning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spinning Jute | Spinning Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Source | Jute plant fibers | Cotton plant fibers |
| Fiber Length | Long, coarse fibers | Short, soft fibers |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Spinning Method | Primarily wet spinning | Primarily ring spinning |
| End Product | Burlap, sacks, ropes | Clothing, textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low pesticide use | Higher water usage, pesticide-intensive |
Introduction to Jute and Cotton Spinning
Jute spinning involves coarse, long fibers derived from the stem of the jute plant, producing strong, biodegradable yarn used primarily in sacks, mats, and ropes. Cotton spinning utilizes shorter, soft fibers harvested from cotton plants, resulting in fine, breathable yarn ideal for textiles and apparel. The fundamental difference lies in fiber length and texture, influencing machinery settings and the final product's application in the textile industry.
Material Properties: Jute vs Cotton
Jute fibers are coarse, strong, and have high lignin content, making them more rigid and less elastic compared to the softer, more flexible cotton fibers with lower lignin and higher cellulose content. The natural moisture absorbency of cotton enhances breathability, whereas jute's rough texture and lower moisture absorption make it suitable for durable sacks and ropes. Jute's higher tensile strength supports heavy-duty use, while cotton's fine fibers enable smoother, softer textiles ideal for apparel and home furnishings.
Spinning Techniques: A Comparative Overview
Spinning jute involves coarse, long fibers requiring wet spinning techniques to enhance fiber strength and cohesion, whereas cotton spinning typically uses dry spinning methods suited for shorter, finer fibers. Jute spinning demands specific machinery adjustments to manage its stiff texture, contrasting with the finer, more flexible cotton fibers that allow high-speed ring spinning. These technical differences influence yarn quality, durability, and end-use applications, making jute ideal for heavy-duty products and cotton preferred for soft textiles.
Machinery Differences in Jute and Cotton Spinning
Spinning jute requires specialized machinery designed to handle its coarse, stiff fibers, including roving frames with stronger rollers and heavier draft systems compared to those used in cotton spinning. Cotton spinning machines feature finer spindles and faster speeds to accommodate the softer, shorter fibers, enabling higher yarn uniformity and finer thread counts. Differences in carding and combing equipment are also prominent, as jute processing focuses on fiber alignment and impurity removal suited to its rough texture, while cotton machines emphasize fiber separation and parallelization for smooth yarn production.
Fiber Preparation: Challenges and Solutions
Spinning jute involves more complex fiber preparation than spinning cotton due to its coarse texture and high lignin content, which requires extensive retting and decortication processes to separate fibers. Unlike cotton, which undergoes standard ginning and carding, jute fibers demand additional steps such as washing and drying to improve pliability and reduce impurities. Innovations like enzymatic treatment and advanced combing machines enhance fiber softness and alignment, addressing challenges in jute spinning for smoother yarn production.
Yarn Quality: Strength and Texture Comparison
Spinning jute produces yarn with high tensile strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like sacks and ropes, whereas cotton yarn offers a softer texture suited for apparel and fine textiles. Jute fibers are coarse, resulting in a rougher yarn surface, while cotton fibers yield smoother, finer yarns with greater flexibility. The difference in fiber structure directly influences the durability and feel of the final yarn, with jute excelling in strength and cotton preferred for softness.
Environmental Impact: Jute vs Cotton Spinning
Jute spinning has a significantly lower environmental impact compared to cotton spinning due to its minimal water and pesticide requirements. While cotton cultivation consumes approximately 20,000 liters of water per kilogram, jute requires only about 1,200 liters, drastically reducing water scarcity issues. Furthermore, jute's natural biodegradability and lower chemical input contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly fiber production process.
Cost Analysis of Spinning Processes
Spinning jute generally incurs lower raw material costs compared to cotton due to jute's abundant availability and faster growth cycle. However, jute spinning requires specialized machinery and additional processing steps to soften the fibers, which can increase operational expenses relative to cotton. Overall, while jute offers cost advantages in raw materials, cotton spinning benefits from more streamlined and widely established processes, affecting the total cost dynamics in textile manufacturing.
Uses and Applications of Spun Jute vs Cotton
Spun jute is primarily used in eco-friendly packaging, carpets, geotextiles, and home furnishings due to its coarse texture and biodegradability, making it ideal for sustainable products. In contrast, spun cotton's fine, soft fibers suit apparel, bed linens, and medical textiles, offering comfort and breathability for everyday wear and hygiene applications. Jute's strength and roughness favor industrial and agricultural applications, while cotton dominates the fashion and household fabric markets with its versatility and softness.
Innovations and Future Trends in Spinning
Innovations in spinning jute focus on enhancing fiber strength and flexibility through enzymatic treatments and modified spinning techniques, aiming to improve yarn quality and durability compared to traditional cotton spinning. Future trends indicate increased automation and integration of sustainable processes, such as bio-based lubricants and digital monitoring systems, to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact in jute yarn production. Emerging hybrid spinning technologies also seek to combine jute with synthetic fibers, expanding applications in textiles and composites while maintaining eco-friendly attributes.
Spinning Jute vs Spinning Cotton Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com