Jute fabric is a soft, flexible material commonly used for bags, upholstery, and clothing, valued for its breathability and eco-friendliness. In contrast, jute matting is a thicker, coarser product designed for floor coverings, erosion control, and garden landscaping, offering durability and moisture resistance. Both products leverage jute's natural strength and biodegradability but serve distinctly different functional purposes.
Table of Comparison
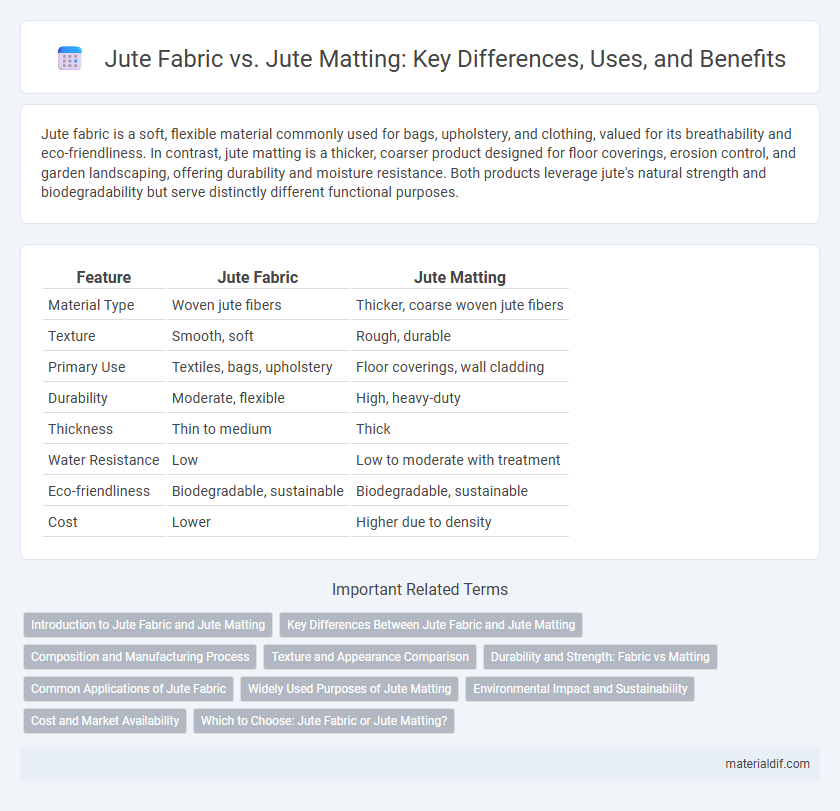
| Feature | Jute Fabric | Jute Matting |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Woven jute fibers | Thicker, coarse woven jute fibers |
| Texture | Smooth, soft | Rough, durable |
| Primary Use | Textiles, bags, upholstery | Floor coverings, wall cladding |
| Durability | Moderate, flexible | High, heavy-duty |
| Thickness | Thin to medium | Thick |
| Water Resistance | Low | Low to moderate with treatment |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable | Biodegradable, sustainable |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to density |
Introduction to Jute Fabric and Jute Matting
Jute fabric is a natural fiber textile known for its softness, strength, and biodegradability, commonly used in making sacks, bags, and upholstery. Jute matting, on the other hand, is woven from jute fibers into coarse mats primarily used for soil erosion control, landscaping, and geotextile applications. Both jute fabric and jute matting leverage the eco-friendly and durable properties of jute, but differ significantly in texture, weave density, and functional uses across industrial and agricultural sectors.
Key Differences Between Jute Fabric and Jute Matting
Jute fabric is a soft, woven material primarily used in making bags, upholstery, and garments, offering flexibility and breathability. Jute matting, on the other hand, is a coarser, thicker product designed for geotextile applications, erosion control, and floor coverings due to its durability and structural strength. While jute fabric emphasizes aesthetic appeal and comfort, jute matting prioritizes functionality and protection in industrial and environmental settings.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Jute fabric is composed of natural jute fibers woven into a dense, flexible textile primarily used in clothing and upholstery, while jute matting consists of loose, coarser fibers bound together to create a sturdy, rigid surface for flooring and erosion control. The manufacturing process of jute fabric involves spinning raw jute fibers into yarns followed by weaving on looms, whereas jute matting is produced by entangling fibers to form thick mats which are then stitched or laminated for added strength. Both products utilize retted jute fibers; however, fabric emphasizes fine yarn quality and tight weaving, contrasting with matting's focus on fiber density and durability.
Texture and Appearance Comparison
Jute fabric features a finer, softer texture with a more uniform weave, making it ideal for clothing and upholstery applications. In contrast, jute matting exhibits a coarser, rougher texture with thicker fibers and an uneven weave, providing durability and a rustic appearance suited for floor coverings and industrial use. The visual difference is evident as jute fabric has a smoother, cleaner look, while jute matting offers a rugged, natural aesthetic.
Durability and Strength: Fabric vs Matting
Jute fabric offers greater tensile strength and durability due to its tightly woven structure, making it ideal for applications requiring resistance to wear and tear. In contrast, jute matting, with its looser weave and thicker fibers, provides robust cushioning and protection but is less resistant to prolonged mechanical stress. Both materials benefit from natural jute fibers, though fabric excels in strength-related uses while matting prioritizes durability in surface coverage.
Common Applications of Jute Fabric
Jute fabric is widely used in the production of eco-friendly bags, upholstery, curtains, and home decor due to its durability and natural texture. Its breathable, biodegradable nature makes it ideal for textile applications such as clothing, sacks, and agricultural coverings. Compared to jute matting, which is primarily used for floor coverings and erosion control, jute fabric offers versatility in fashion and industrial products.
Widely Used Purposes of Jute Matting
Jute matting is widely used for erosion control, soil stabilization, and landscaping due to its natural biodegradability and durability, making it ideal for protecting slopes, riverbanks, and newly seeded areas. It also serves as a protective ground cover in horticulture and agriculture, retaining moisture and preventing weed growth. Unlike jute fabric, which is primarily utilized for packaging, bags, and textiles, jute matting is specialized for outdoor environmental applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Jute fabric, made from natural fibers, is biodegradable and compostable, significantly reducing environmental pollution compared to synthetic alternatives. Jute matting, often used for erosion control and landscaping, enhances soil health by breaking down naturally and preventing chemical runoff. Both products promote sustainability through renewable sourcing and minimal energy consumption during production, making jute an eco-friendly choice in textile and agricultural applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Jute fabric typically demands higher production costs due to its finer weaving process, making it more expensive than jute matting, which involves simpler, coarser weaving techniques suited for bulk applications. Market availability of jute fabric is concentrated in regions with established textile industries, such as India and Bangladesh, whereas jute matting enjoys broader distribution due to its utility in agriculture, landscaping, and construction sectors. Cost-efficiency and widespread availability position jute matting as a preferred choice for large-scale sustainable projects, while jute fabric serves niche markets focused on eco-friendly textiles and fashion.
Which to Choose: Jute Fabric or Jute Matting?
Jute fabric offers a soft, lightweight texture ideal for clothing, upholstery, and crafts, providing breathability and eco-friendliness. Jute matting, on the other hand, is thicker and more durable, commonly used for flooring, erosion control, and insulation due to its robustness and moisture resistance. Choosing between jute fabric and jute matting depends on the intended application, where fabric suits flexible, decorative uses and matting excels in structural, protective functions.
Jute Fabric vs Jute Matting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com