Gypsum panels offer excellent fire resistance and ease of installation due to their lightweight and smooth surface, making them ideal for interior wall applications. Calcium silicate panels provide superior moisture resistance and higher durability, which suits humid or industrial environments better than gypsum. Choosing between these panels depends on the specific requirements of fire protection, moisture exposure, and structural strength.
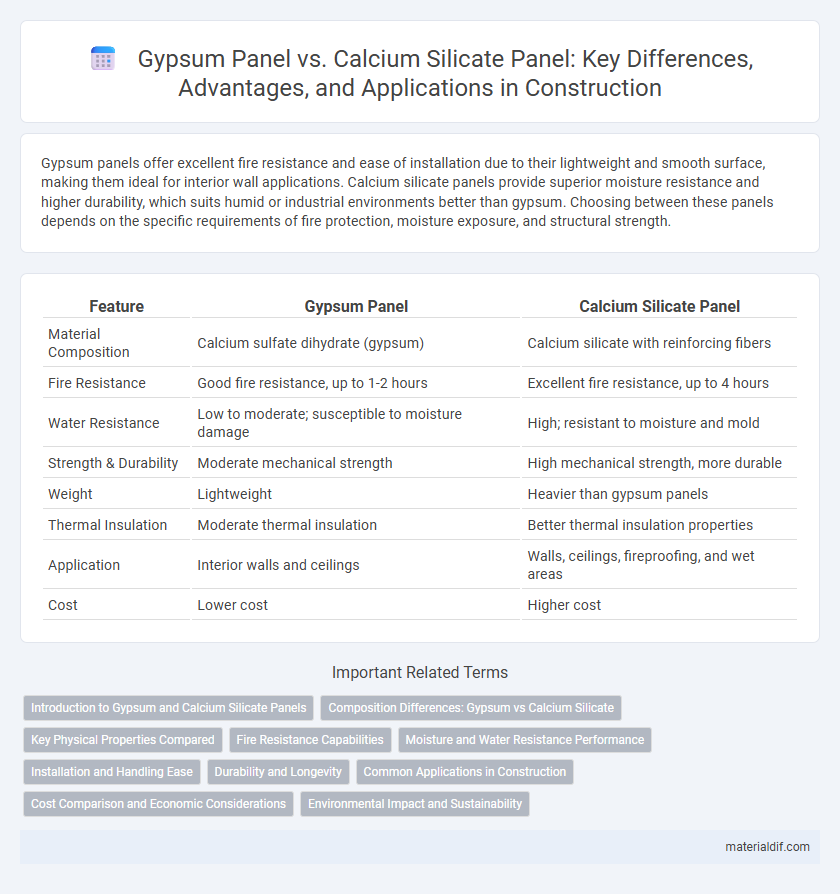
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gypsum Panel | Calcium Silicate Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) | Calcium silicate with reinforcing fibers |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire resistance, up to 1-2 hours | Excellent fire resistance, up to 4 hours |
| Water Resistance | Low to moderate; susceptible to moisture damage | High; resistant to moisture and mold |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate mechanical strength | High mechanical strength, more durable |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than gypsum panels |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate thermal insulation | Better thermal insulation properties |
| Application | Interior walls and ceilings | Walls, ceilings, fireproofing, and wet areas |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Gypsum and Calcium Silicate Panels
Gypsum panels consist primarily of calcium sulfate dihydrate, offering excellent fire resistance, sound insulation, and smooth finishing for interior walls and ceilings. Calcium silicate panels are engineered from a mixture of silica sand and lime, providing superior moisture resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal insulation for both interior and exterior applications. Both materials serve critical roles in construction but vary significantly in durability and suitability depending on environmental conditions.
Composition Differences: Gypsum vs Calcium Silicate
Gypsum panels primarily consist of calcium sulfate dihydrate, which provides excellent fire resistance and moisture regulation but has lower resistance to high moisture environments. Calcium silicate panels are composed mainly of calcium silicate hydrate, giving them superior durability, higher water resistance, and enhanced mechanical strength compared to gypsum panels. The distinct chemical structures of gypsum and calcium silicate directly influence their performance in construction, making calcium silicate panels preferable for damp or exterior applications.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Gypsum panels exhibit lower density, typically around 800-900 kg/m3, compared to calcium silicate panels which range between 1200-1400 kg/m3, resulting in lighter weight for gypsum. Calcium silicate panels demonstrate superior compressive strength, generally exceeding 8 MPa, whereas gypsum panels usually have compressive strengths around 5 MPa. Water absorption rates are significantly lower in calcium silicate panels, often less than 10%, compared to gypsum panels that can absorb up to 20%, enhancing moisture resistance in calcium silicate products.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Gypsum panels exhibit excellent fire resistance due to their chemically bound water content, which releases steam and slows heat transfer during exposure to fire. Calcium silicate panels also provide robust fire protection, with higher thermal stability and resistance to structural deformation under extreme temperatures compared to gypsum. Choosing between gypsum and calcium silicate panels depends on the required fire rating and environmental conditions of the installation site.
Moisture and Water Resistance Performance
Gypsum panels typically offer moderate moisture resistance but are prone to degradation when exposed to prolonged water or high humidity, making them less ideal for wet environments. Calcium silicate panels exhibit superior water resistance and dimensional stability, maintaining structural integrity and resisting mold growth even under continuous moisture exposure. Selecting calcium silicate panels enhances durability and longevity in high-moisture applications compared to conventional gypsum panels.
Installation and Handling Ease
Gypsum panels offer superior installation and handling ease due to their lightweight nature and standardized dimensions, allowing quicker cutting and fitting compared to calcium silicate panels. Calcium silicate panels, being denser and more brittle, require specialized tools and cautious handling to prevent cracks and dust generation during installation. The easier manipulation of gypsum panels typically reduces labor time and effort on construction sites.
Durability and Longevity
Gypsum panels offer moderate durability with resistance to fire and sound insulation but are prone to moisture damage and swelling over time. Calcium silicate panels provide superior longevity due to their enhanced moisture resistance, high compressive strength, and excellent dimensional stability under varying environmental conditions. The robust composition of calcium silicate panels makes them ideal for long-term use in high-humidity or structural applications where durability is critical.
Common Applications in Construction
Gypsum panels are widely used for interior walls and ceilings in residential and commercial buildings due to their fire resistance and ease of installation. Calcium silicate panels are preferred in industrial environments because of their superior moisture resistance and high-temperature durability. Both materials serve as essential components for partition walls, ceiling linings, and fireproofing systems in construction projects.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Gypsum panels generally have a lower initial cost compared to calcium silicate panels, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious construction projects. Calcium silicate panels, despite higher upfront expenses, offer superior durability and fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses highlights calcium silicate panels as economically advantageous in demanding environments despite higher installation costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gypsum panels exhibit lower embodied energy and higher recyclability compared to calcium silicate panels, which require higher kiln temperatures resulting in greater CO2 emissions. The natural mineral composition of gypsum allows for efficient recycling and less environmental degradation, whereas calcium silicate panels often rely on energy-intensive production processes involving lime and silica. Sustainable construction projects favor gypsum panels due to their minimal environmental footprint and better end-of-life recyclability, aligning with green building certifications and eco-friendly standards.
Gypsum panel vs Calcium silicate panel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com