Tinted glass pet containers reduce glare and protect contents from UV rays, helping to maintain freshness and extend shelf life. Untinted glass offers clearer visibility, allowing for an unobstructed view of the pet inside, which is ideal for display purposes. Choosing between tinted and untinted glass depends on the balance between protection needs and aesthetic preferences.
Table of Comparison
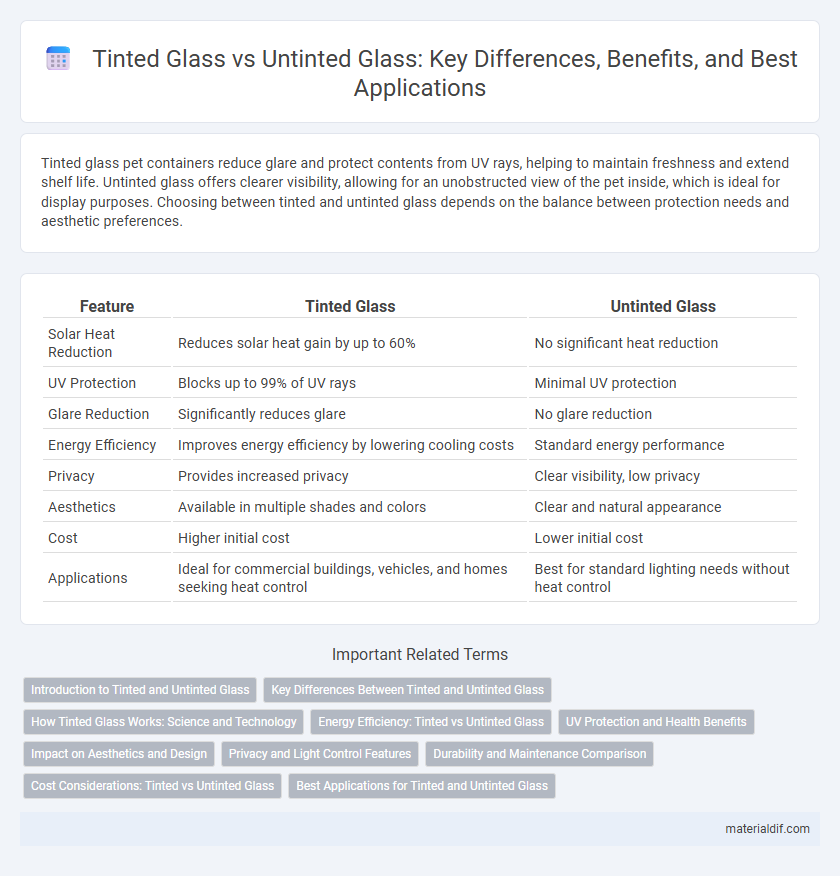
| Feature | Tinted Glass | Untinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Heat Reduction | Reduces solar heat gain by up to 60% | No significant heat reduction |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of UV rays | Minimal UV protection |
| Glare Reduction | Significantly reduces glare | No glare reduction |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves energy efficiency by lowering cooling costs | Standard energy performance |
| Privacy | Provides increased privacy | Clear visibility, low privacy |
| Aesthetics | Available in multiple shades and colors | Clear and natural appearance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Applications | Ideal for commercial buildings, vehicles, and homes seeking heat control | Best for standard lighting needs without heat control |
Introduction to Tinted and Untinted Glass
Tinted glass contains additives or coatings that absorb solar heat and reduce glare, improving energy efficiency and comfort in buildings and vehicles. Untinted glass is clear and transparent, offering maximum natural light transmission but minimal heat reduction or glare control. Choosing between tinted and untinted glass depends on factors like climate, energy savings goals, and aesthetic preferences.
Key Differences Between Tinted and Untinted Glass
Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and glare by filtering sunlight, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort, while untinted glass allows maximum natural light but increases heat transmission. Tinted glass offers improved UV protection, reducing furniture and interior fading, whereas untinted glass provides clearer visibility and true color representation. The choice impacts building aesthetics, energy costs, and indoor environment quality, with tinted glass better suited for hot climates and untinted preferred where natural light and unobstructed views are prioritized.
How Tinted Glass Works: Science and Technology
Tinted glass works by incorporating metal oxides or dyes into the glass during manufacturing, which selectively absorb and reflect specific wavelengths of sunlight, reducing heat and glare. This technology improves energy efficiency by minimizing solar heat gain while maintaining natural light transmission, achieved through complex molecular structures that target infrared and ultraviolet rays. Advanced coatings in tinted glass enhance its performance by increasing durability and optimizing light filtration without compromising visibility.
Energy Efficiency: Tinted vs Untinted Glass
Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain significantly, improving energy efficiency by minimizing cooling costs in warm climates. Untinted glass allows more natural light but increases heat transfer, leading to higher energy consumption for air conditioning. Choosing tinted glass enhances thermal insulation, contributing to lower energy bills and a more sustainable building design.
UV Protection and Health Benefits
Tinted glass significantly reduces UV radiation penetration, blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays which helps prevent skin damage and reduces the risk of skin cancer. Untinted glass allows more UV exposure, increasing potential health risks such as premature skin aging and eye problems including cataracts. By choosing tinted glass for windows or vehicles, users benefit from enhanced UV protection, contributing to overall better skin and eye health.
Impact on Aesthetics and Design
Tinted glass enhances architectural aesthetics by adding color depth and reducing glare, creating a sleek, modern appearance that complements contemporary design styles. Untinted glass maintains maximum transparency, preserving natural light and providing unobstructed views, which is ideal for minimalist and open-concept interiors. The choice between tinted and untinted glass significantly influences the building's visual impact, energy efficiency, and overall ambiance.
Privacy and Light Control Features
Tinted glass offers superior privacy by limiting visibility from the outside while reducing glare and controlling solar heat gain, making it ideal for residential and commercial spaces requiring discretion and energy efficiency. Untinted glass allows maximum natural light penetration, enhancing indoor brightness but provides minimal privacy and less effective light control, often necessitating additional window treatments. Choosing between tinted and untinted glass depends on the balance between desired privacy levels and natural light requirements in the specific application.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Tinted glass offers enhanced durability by reducing heat buildup and minimizing UV damage, which helps prevent warping and extends the lifespan of the glass. Untinted glass requires more frequent cleaning due to visible smudges and dirt, whereas tinted glass's coatings can repel dust and reduce maintenance needs. Both types benefit from standard cleaning methods but tinted glass provides a more resilient surface against environmental stressors.
Cost Considerations: Tinted vs Untinted Glass
Tinted glass generally incurs higher initial costs compared to untinted glass due to the added materials and manufacturing processes involved. While untinted glass is more affordable upfront, tinted glass can provide energy savings by reducing heat gain, potentially lowering cooling expenses over time. Balancing the upfront investment with long-term energy efficiency is critical when choosing between tinted and untinted glass for construction or automotive applications.
Best Applications for Tinted and Untinted Glass
Tinted glass is ideal for automotive windows, commercial buildings, and sunrooms where solar heat reduction and glare control are essential, improving energy efficiency and comfort. Untinted glass is preferred for storefronts, picture windows, and display cases that require maximum natural light and true color visibility without distortion. Each glass type enhances specific applications based on light transmission and heat control properties.
Tinted Glass vs Untinted Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com