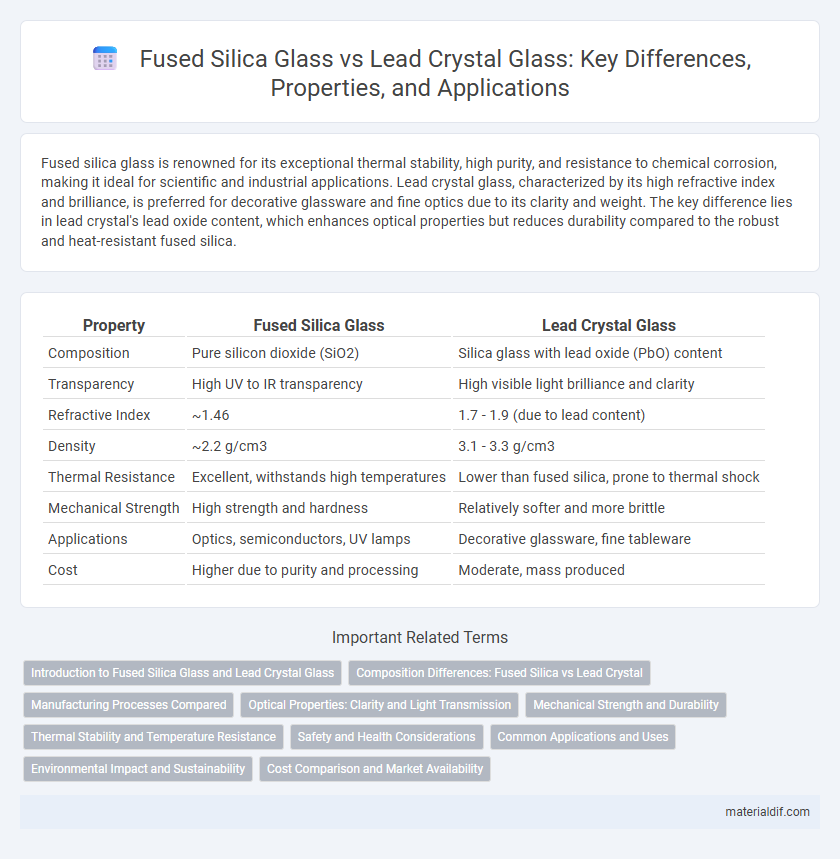
Fused silica glass is renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, high purity, and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for scientific and industrial applications. Lead crystal glass, characterized by its high refractive index and brilliance, is preferred for decorative glassware and fine optics due to its clarity and weight. The key difference lies in lead crystal's lead oxide content, which enhances optical properties but reduces durability compared to the robust and heat-resistant fused silica.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Silica Glass | Lead Crystal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) | Silica glass with lead oxide (PbO) content |
| Transparency | High UV to IR transparency | High visible light brilliance and clarity |
| Refractive Index | ~1.46 | 1.7 - 1.9 (due to lead content) |
| Density | ~2.2 g/cm3 | 3.1 - 3.3 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands high temperatures | Lower than fused silica, prone to thermal shock |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and hardness | Relatively softer and more brittle |
| Applications | Optics, semiconductors, UV lamps | Decorative glassware, fine tableware |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and processing | Moderate, mass produced |
Introduction to Fused Silica Glass and Lead Crystal Glass
Fused silica glass is a high-purity glass composed primarily of silicon dioxide, known for its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and optical clarity, making it ideal for scientific and industrial applications. Lead crystal glass contains lead oxide, enhancing its density, refractive index, and brilliance, which gives it the characteristic sparkle and weight favored in luxury glassware and decorative items. The distinct compositions and physical properties of fused silica and lead crystal glass determine their specific uses across optical technologies and fine craftsmanship.
Composition Differences: Fused Silica vs Lead Crystal
Fused silica glass is composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) in a highly pure and amorphous form, offering exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion. Lead crystal glass contains a significant amount of lead oxide (PbO), typically between 24% and 30%, which increases its density, refractive index, and brilliance. The inclusion of lead oxide in lead crystal glass alters its optical properties and weight compared to the chemically inert and durable fused silica glass.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Fused silica glass is manufactured through melting high-purity quartz sand at extremely high temperatures around 1720degC, resulting in a non-crystalline, homogenous structure with superior thermal and chemical resistance. Lead crystal glass production involves melting a mixture of silica, lead oxide (usually 24-30%), and other additives at lower temperatures near 1100-1300degC, producing a dense, refractive, and highly decorative material. The manufacturing differences affect properties like clarity, weight, and durability, making fused silica ideal for technical uses and lead crystal preferred for aesthetic glassware.
Optical Properties: Clarity and Light Transmission
Fused silica glass exhibits exceptional optical clarity with a high light transmission rate of approximately 92%, making it ideal for precision optics and ultraviolet applications. Lead crystal glass, while known for its brilliance and decorative appeal, has lower light transmission due to the presence of lead oxide, which increases refractive index but also causes slight light absorption. The superior clarity and ultraviolet transparency of fused silica make it preferable for scientific instruments, whereas lead crystal is favored for its aesthetic sparkle in glassware.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fused silica glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to lead crystal glass due to its high purity and low thermal expansion coefficient, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress. Lead crystal glass, containing lead oxide, has a softer composition that enhances brilliance but reduces its resistance to impact and scratches. The high silica content in fused silica results in enhanced hardness and longevity, making it ideal for industrial and laboratory applications requiring robust performance.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Fused silica glass offers exceptional thermal stability with a high melting point around 1,710degC (3,110degF) and minimal thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Lead crystal glass, containing lead oxide, has lower temperature resistance and is prone to thermal shock due to higher thermal expansion. The superior temperature tolerance of fused silica glass ensures durability in extreme heat environments compared to the more fragile lead crystal glass.
Safety and Health Considerations
Fused silica glass offers superior safety and health benefits due to its non-toxic composition, high chemical resistance, and absence of lead, making it ideal for medical and food-related applications. In contrast, lead crystal glass contains lead oxide, which poses significant health risks such as lead poisoning through prolonged exposure or ingestion. Handling lead crystal requires strict safety measures to prevent contamination, whereas fused silica glass is safer for everyday use and environmentally friendly.
Common Applications and Uses
Fused silica glass is widely used in high-performance applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, optics, and aerospace due to its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and high chemical resistance. Lead crystal glass is commonly found in decorative items, fine glassware, and chandeliers, prized for its clarity, brilliance, and ability to be easily cut and engraved. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with fused silica favored in industrial and scientific settings, while lead crystal remains popular in luxury and artistic products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fused silica glass exhibits lower environmental impact due to its high durability, recyclability, and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, which rely on abundant raw materials like pure quartz sand. Lead crystal glass, containing toxic lead oxide, poses significant environmental hazards during production and disposal, contributing to soil and water contamination. Sustainable glass choices favor fused silica for its minimal ecological footprint and safer long-term effects on ecosystems.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Fused silica glass typically costs significantly more than lead crystal glass due to its high purity and specialized manufacturing process, making it a premium material in scientific and industrial applications. Lead crystal glass, with its lower production costs and extensive decorative use, remains widely accessible and commonly found in consumer markets worldwide. The market availability of fused silica glass is limited to niche sectors, while lead crystal dominates retail and decorative glassware segments.
Fused silica glass vs Lead crystal glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com