Enamel sheets offer superior corrosion resistance and vibrant, durable finishes compared to traditional metal sheets, making them ideal for decorative and protective applications. Metal sheets provide greater structural strength and flexibility but often require additional coatings to prevent rust and wear. Choosing between enamel and metal sheets depends on the desired balance of aesthetics, durability, and functional performance.
Table of Comparison
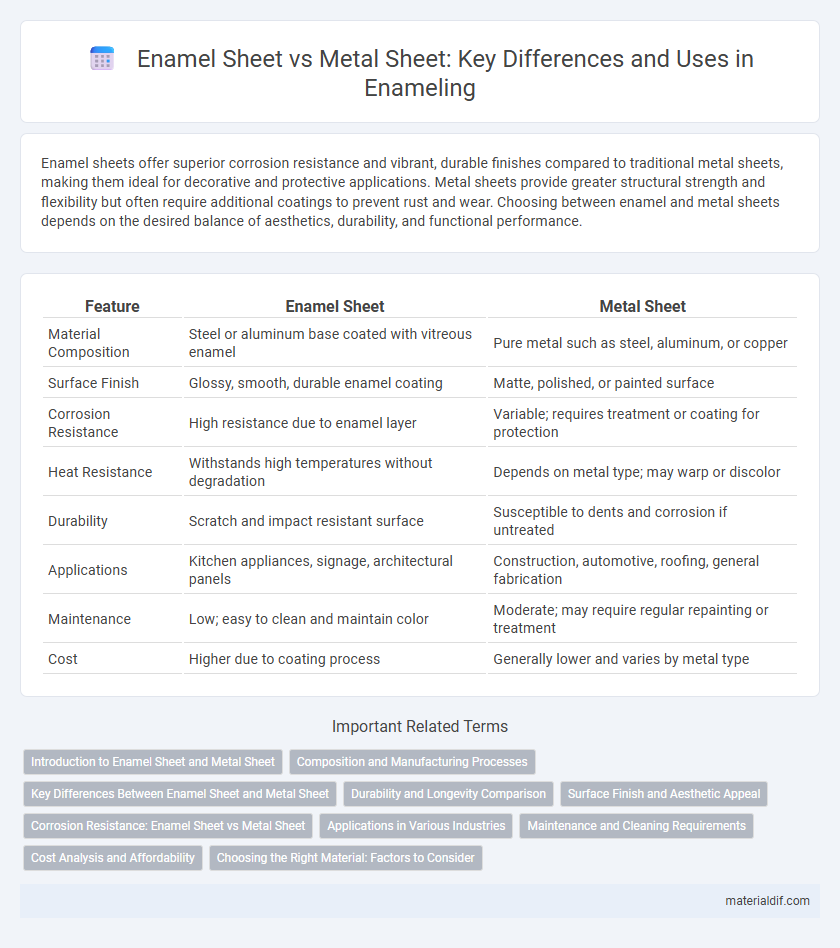
| Feature | Enamel Sheet | Metal Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Steel or aluminum base coated with vitreous enamel | Pure metal such as steel, aluminum, or copper |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, smooth, durable enamel coating | Matte, polished, or painted surface |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance due to enamel layer | Variable; requires treatment or coating for protection |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures without degradation | Depends on metal type; may warp or discolor |
| Durability | Scratch and impact resistant surface | Susceptible to dents and corrosion if untreated |
| Applications | Kitchen appliances, signage, architectural panels | Construction, automotive, roofing, general fabrication |
| Maintenance | Low; easy to clean and maintain color | Moderate; may require regular repainting or treatment |
| Cost | Higher due to coating process | Generally lower and varies by metal type |
Introduction to Enamel Sheet and Metal Sheet
Enamel sheets consist of metal substrates coated with a durable layer of vitreous enamel, providing corrosion resistance, heat tolerance, and aesthetic appeal. Metal sheets, typically made from steel, aluminum, or copper, serve as the base material offering strength and flexibility used in numerous industrial applications. The enamel coating on enamel sheets enhances surface durability and chemical resistance compared to untreated metal sheets, making them ideal for environments requiring long-lasting protection and decorative finishes.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Enamel sheets consist of a glassy coating fused onto a metal substrate, typically steel or aluminum, through high-temperature firing processes that create a durable, corrosion-resistant surface. Metal sheets are primarily pure or alloyed metals formed by rolling, pressing, or extrusion, lacking the protective vitreous enamel layer. The enamel manufacturing process involves applying powdered glass slurry onto the metal sheet followed by kiln firing at temperatures around 750-850degC to achieve a smooth, glossy finish that enhances chemical resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Key Differences Between Enamel Sheet and Metal Sheet
Enamel sheets differ from metal sheets primarily due to their protective and decorative coating of fused glass, which provides enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Metal sheets consist solely of the base metal, offering greater structural strength but lower resistance to environmental damage compared to enamel sheets. The application of enamel coating also allows for customizable colors and finishes, making enamel sheets ideal for architectural and artistic purposes.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Enamel sheets provide superior resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemical exposure compared to traditional metal sheets, enhancing overall durability in harsh environments. The vitrified glass coating on enamel sheets prevents rust and surface degradation, extending the lifespan of the material beyond that of uncoated metal sheets. Metal sheets, while strong, are prone to oxidation and wear, which can shorten their longevity without specialized treatments or coatings.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Appeal
Enamel sheets offer a glossy, smooth surface finish that resists scratches, stains, and corrosion, making them ideal for applications requiring high aesthetic appeal and durability. Metal sheets typically have a raw or coated finish that can vary in texture but often lacks the vibrant, long-lasting sheen of enameled surfaces. The vibrant colors and customized designs achievable with enamel sheets provide superior decorative options compared to standard metal sheet finishes.
Corrosion Resistance: Enamel Sheet vs Metal Sheet
Enamel sheets provide superior corrosion resistance compared to standard metal sheets due to their glass-like coating that protects underlying metals from moisture and chemical exposure. Metal sheets, lacking this protective layer, are more susceptible to rust and deterioration when exposed to harsh environments. The enamel coating significantly extends the lifespan of metal substrates, making enamel sheets ideal for applications requiring durable, corrosion-resistant surfaces.
Applications in Various Industries
Enamel sheets provide superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal compared to metal sheets, making them ideal for use in kitchen appliances, signage, and architectural panels. Industries such as chemical processing and food manufacturing prefer enamel sheets due to their resistance to harsh chemicals and ease of cleaning. Metal sheets remain popular in automotive and construction sectors for their strength and formability, but enamel coating enhances durability and surface protection in demanding environments.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Enamel sheets require minimal maintenance due to their smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and corrosion, making them easier to clean compared to metal sheets. Metal sheets often need regular protective treatments, such as painting or coating, to prevent rust and deterioration from exposure to moisture and environmental elements. Enamel's durability and resistance to scratches reduce the need for frequent cleaning, whereas metal sheets may accumulate grime and require more intensive upkeep to maintain appearance and structural integrity.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Enamel sheets generally present higher upfront costs compared to metal sheets due to the specialized coating process that enhances durability and resistance to corrosion. Metal sheets offer lower initial expenses but may incur additional maintenance costs over time due to susceptibility to rust and wear. Evaluating long-term affordability, enamel sheets provide better cost efficiency in applications requiring longevity and minimal upkeep, offsetting their initial investment.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
Enamel sheets offer superior corrosion resistance and vibrant color options, making them ideal for decorative and protective applications where durability against chemicals and heat is essential. Metal sheets provide higher structural strength and flexibility, suited for load-bearing or industrial uses requiring robustness and ease of fabrication. Consider factors such as exposure to environmental elements, mechanical stress, aesthetic requirements, and budget constraints when choosing between enamel and metal sheets.
Enamel Sheet vs Metal Sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com