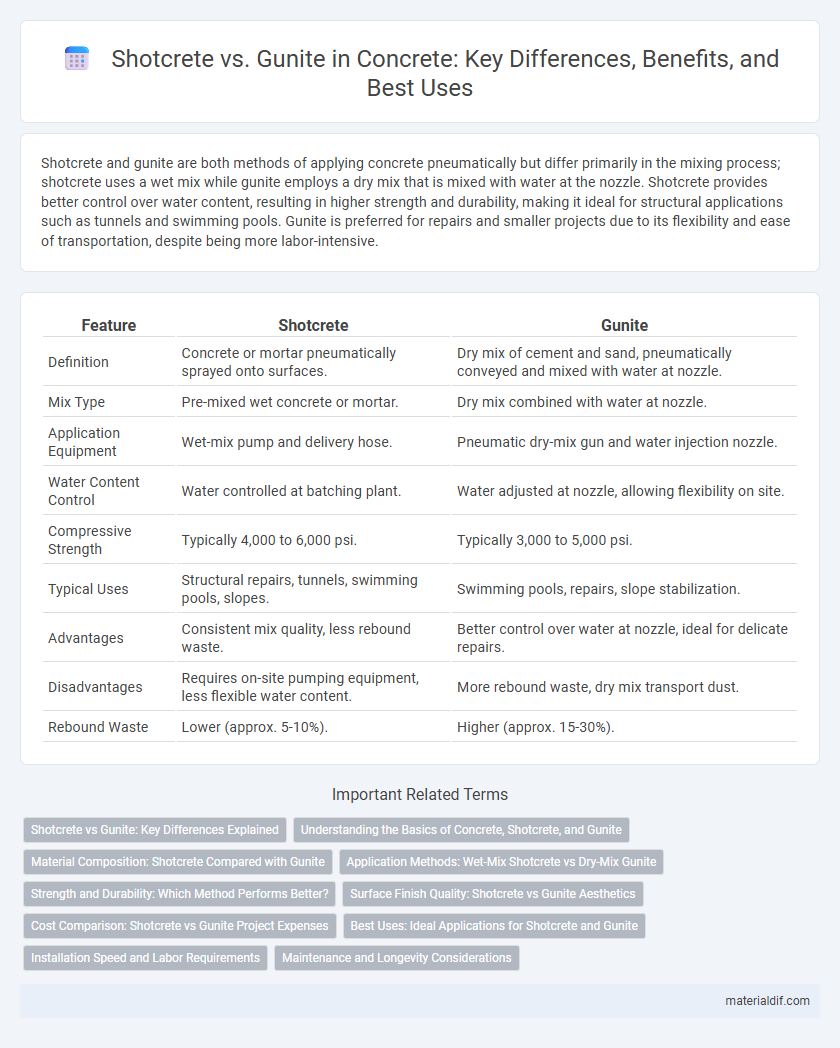
Shotcrete and gunite are both methods of applying concrete pneumatically but differ primarily in the mixing process; shotcrete uses a wet mix while gunite employs a dry mix that is mixed with water at the nozzle. Shotcrete provides better control over water content, resulting in higher strength and durability, making it ideal for structural applications such as tunnels and swimming pools. Gunite is preferred for repairs and smaller projects due to its flexibility and ease of transportation, despite being more labor-intensive.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shotcrete | Gunite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete or mortar pneumatically sprayed onto surfaces. | Dry mix of cement and sand, pneumatically conveyed and mixed with water at nozzle. |
| Mix Type | Pre-mixed wet concrete or mortar. | Dry mix combined with water at nozzle. |
| Application Equipment | Wet-mix pump and delivery hose. | Pneumatic dry-mix gun and water injection nozzle. |
| Water Content Control | Water controlled at batching plant. | Water adjusted at nozzle, allowing flexibility on site. |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 4,000 to 6,000 psi. | Typically 3,000 to 5,000 psi. |
| Typical Uses | Structural repairs, tunnels, swimming pools, slopes. | Swimming pools, repairs, slope stabilization. |
| Advantages | Consistent mix quality, less rebound waste. | Better control over water at nozzle, ideal for delicate repairs. |
| Disadvantages | Requires on-site pumping equipment, less flexible water content. | More rebound waste, dry mix transport dust. |
| Rebound Waste | Lower (approx. 5-10%). | Higher (approx. 15-30%). |
Shotcrete vs Gunite: Key Differences Explained
Shotcrete and gunite are both methods of applying concrete pneumatically, but shotcrete uses a wet mix while gunite employs a dry mix sprayed with water at the nozzle. Shotcrete offers better control over water content and consistency, resulting in higher strength and less rebound compared to gunite. Gunite is more suitable for smaller or more intricate applications due to its adaptability, while shotcrete is preferred for large-scale projects requiring uniformity and durability.
Understanding the Basics of Concrete, Shotcrete, and Gunite
Concrete is a composite material composed of cement, water, and aggregates that hardens into a stone-like structure, fundamental in construction. Shotcrete and gunite are specialized methods of placing concrete; shotcrete involves spraying a wet mixture of concrete at high velocity onto surfaces, whereas gunite uses a dry concrete mix sprayed and hydrated at the nozzle. Both techniques offer superior adhesion and density compared to conventional concrete pouring, making them ideal for complex shapes and repair work in structural and architectural applications.
Material Composition: Shotcrete Compared with Gunite
Shotcrete consists of a dry or wet mix of cement, aggregates, and water, applied pneumatically at high velocity to form dense, durable concrete layers. Gunite uses a dry mix of cement and fine aggregates pneumatically projected onto a surface, where water is added at the nozzle, allowing for greater control over moisture content during application. Material composition differences affect workability, strength, and adhesion properties, with shotcrete often preferred for structural applications requiring high compressive strength and gunite favored for intricate repairs and curved surfaces.
Application Methods: Wet-Mix Shotcrete vs Dry-Mix Gunite
Wet-mix shotcrete involves pre-mixing concrete with water before spraying it onto surfaces using a high-pressure hose, ensuring a consistent and controllable mixture ideal for large-scale projects like tunnels and swimming pools. Dry-mix gunite requires dry cement and sand to be conveyed through the hose, with water added at the nozzle, providing greater control over water content and better adhesion for smaller or intricately shaped applications such as repairs and patching. Both methods utilize pneumatic pressure to deliver concrete, but wet-mix shotcrete provides faster application and reduced rebound, while dry-mix gunite offers superior flexibility in water adjustment and is favored for precision work.
Strength and Durability: Which Method Performs Better?
Shotcrete and Gunite are both highly effective concrete applications, but Shotcrete typically offers superior strength and durability due to its higher cement content and wet-mix process, which ensures better compaction and bonding. Gunite, using a dry-mix method, can be more prone to inconsistencies in moisture content, potentially impacting long-term durability. For projects requiring maximum structural integrity and resistance to environmental stress, Shotcrete generally outperforms Gunite.
Surface Finish Quality: Shotcrete vs Gunite Aesthetics
Shotcrete offers a smoother surface finish with fewer voids and a more uniform texture, enhancing aesthetic appeal in concrete applications. Gunite tends to produce a rougher texture with visible aggregate, making it less suitable for projects requiring a polished or refined appearance. Surface finish quality favors shotcrete when visual consistency and smoothness are critical for architectural or decorative purposes.
Cost Comparison: Shotcrete vs Gunite Project Expenses
Shotcrete typically involves a higher upfront cost due to specialized spraying equipment and skilled labor, averaging $12 to $30 per square foot, while gunite generally costs between $10 and $25 per square foot, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale projects. Shotcrete projects may incur additional expenses related to material waste and curing time, whereas gunite's dry-mix method often reduces material waste and allows for more flexible application in complex structures. Long-term project expenses for both methods depend on factors like project size, labor rates, and local material costs, but gunite often provides a more economical solution for smaller, detailed applications.
Best Uses: Ideal Applications for Shotcrete and Gunite
Shotcrete is ideal for large-scale structural applications such as tunnel linings, swimming pools, and retaining walls due to its high compressive strength and excellent adhesion to complex surfaces. Gunite is better suited for smaller projects requiring detailed shaping and finishing, including patch repairs, curved architectural features, and slope stabilization. Both methods provide durable concrete placement, but shotcrete's pneumatic spraying process excels in heavy-duty construction, while gunite's dry-mix approach offers greater control for intricate work.
Installation Speed and Labor Requirements
Shotcrete installation is typically faster because it uses a continuous, high-pressure hose to spray concrete, reducing setup time and allowing for quicker application in large areas. Gunite requires dry-mix preparation onsite, increasing labor intensity and time for mixing before spraying, which slows down the overall process. The labor for shotcrete is generally less demanding since it minimizes handling and material wastage, streamlining the workforce needed for efficient project completion.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Shotcrete and gunite both provide durable concrete applications, but shotcrete often requires less frequent maintenance due to its higher density and superior compaction methods. Gunite, applied through dry-mix spraying, may exhibit more porosity, leading to increased susceptibility to water infiltration and potential long-term durability issues. Regular inspections and appropriate sealing treatments extend the lifespan of both materials, but shotcrete's reduced permeability typically enhances longevity in harsh environmental conditions.
Shotcrete vs Gunite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com