Casting slip is a liquid suspension of clay particles used primarily for creating detailed molds and intricate shapes through slip casting, offering fine detail and smooth surfaces. Plastic clay has a higher moisture content and a malleable consistency, making it ideal for hand-building techniques like coiling, pinching, and sculpting. Choosing between casting slip and plastic clay depends on the desired method and final texture, with casting slip being best for precision and plastic clay for flexible, tactile work.
Table of Comparison
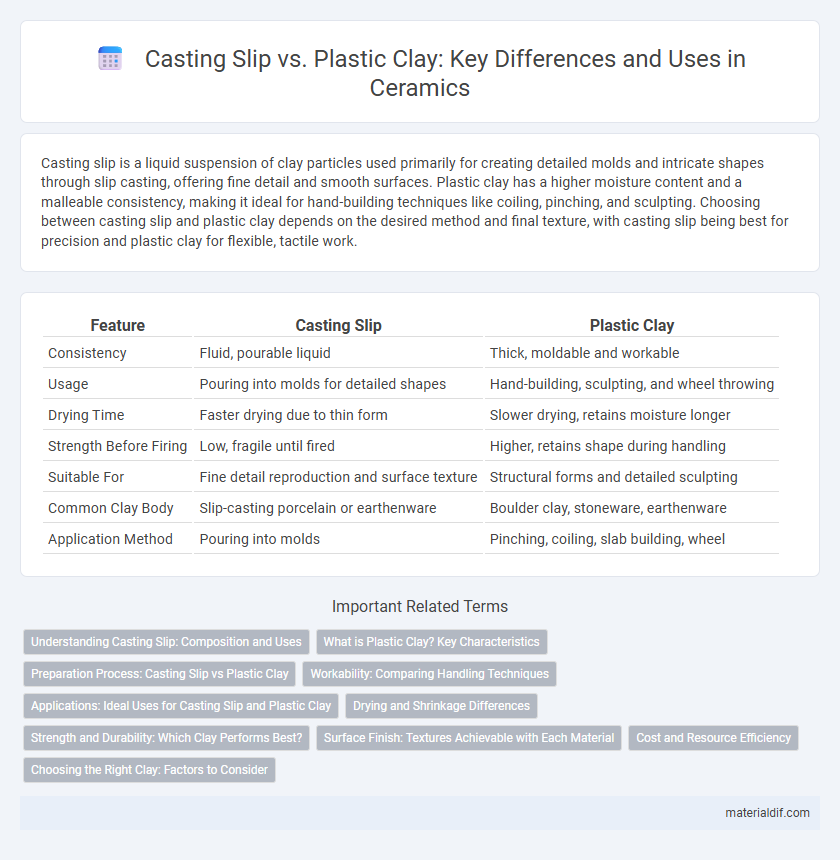
| Feature | Casting Slip | Plastic Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Fluid, pourable liquid | Thick, moldable and workable |
| Usage | Pouring into molds for detailed shapes | Hand-building, sculpting, and wheel throwing |
| Drying Time | Faster drying due to thin form | Slower drying, retains moisture longer |
| Strength Before Firing | Low, fragile until fired | Higher, retains shape during handling |
| Suitable For | Fine detail reproduction and surface texture | Structural forms and detailed sculpting |
| Common Clay Body | Slip-casting porcelain or earthenware | Boulder clay, stoneware, earthenware |
| Application Method | Pouring into molds | Pinching, coiling, slab building, wheel |
Understanding Casting Slip: Composition and Uses
Casting slip is a liquid mixture primarily composed of finely ground clay particles suspended in water, optimized for smooth flow into molds to create detailed ceramic forms. Its high water content and particle size distribution enhance mold filling while reducing air bubbles compared to plastic clay, which is more malleable and suitable for handbuilding or shaping. Commonly used in slip casting, casting slip allows for precise reproduction of intricate shapes and is essential in producing hollow or uniform-thickness ceramic objects.
What is Plastic Clay? Key Characteristics
Plastic clay is a malleable, water-based material commonly used in pottery and sculpture for its flexibility and ease of shaping. Its key characteristics include high plasticity, allowing it to hold intricate details and maintain form during drying and firing. Unlike casting slip, plastic clay can be easily worked by hand or with tools to create varied textures and shapes before kiln firing.
Preparation Process: Casting Slip vs Plastic Clay
Casting slip requires thorough mixing of clay particles with water to achieve a smooth, pourable consistency, often filtered to remove lumps and air bubbles. Plastic clay involves kneading or wedging to create an even, pliable texture by removing air pockets and ensuring uniform moisture content. Both preparation methods optimize the clay's workability but differ significantly in their approach to handling moisture and consistency.
Workability: Comparing Handling Techniques
Casting slip offers superior fluidity, allowing for easy pouring into molds and intricate detail replication, ideal for delicate forms. Plastic clay provides a firmer texture, enabling hand-building and sculpting with greater control, suitable for tactile manipulation and shaping. Understanding these handling techniques enhances material selection for specific ceramic projects and desired artistic outcomes.
Applications: Ideal Uses for Casting Slip and Plastic Clay
Casting slip is ideal for detailed molds and mass production of ceramics due to its liquid consistency, allowing precise replication of fine textures and complex shapes. Plastic clay suits hand-building and sculpting applications where workability and flexibility are required, enabling techniques like coiling, pinching, and slab construction. Both materials serve unique artistic and functional needs, with casting slip excelling in uniformity and plastic clay in creative manipulation.
Drying and Shrinkage Differences
Casting slip, a liquid mixture of clay and water, dries more slowly than plastic clay, allowing for more uniform moisture evaporation and reducing the risk of cracks during drying. Plastic clay, with its malleable consistency, shrinks more predictably as it contains less water content compared to casting slip, which experiences significant shrinkage due to water loss. Understanding these differences in drying rates and shrinkage is crucial for selecting the right material in ceramics to ensure structural integrity and minimize warping.
Strength and Durability: Which Clay Performs Best?
Casting slip, composed of fine clay particles suspended in water, offers excellent detail capture but generally lacks strength and durability once dried and fired, making it more prone to cracking and chipping under stress. Plastic clay, with its higher plasticity and cohesiveness, delivers superior structural integrity and resilience, ideal for sculpting and functional pottery that requires durability. When comparing performance, plastic clay surpasses casting slip in strength and long-term durability, especially for objects subjected to handling or mechanical pressure.
Surface Finish: Textures Achievable with Each Material
Casting slip offers a smooth, fine surface finish ideal for detailed textures and intricate designs due to its liquid consistency that flows into molds effortlessly. Plastic clay provides a more tactile, hands-on texture, allowing for varied surface effects such as carving, imprinting, and layering to create unique, textured finishes. The choice between casting slip and plastic clay significantly influences the final surface quality and the range of achievable textures in ceramic artwork.
Cost and Resource Efficiency
Casting slip offers cost advantages due to its ability to be reused and its minimal material waste during the molding process. Plastic clay, while more malleable for hand-building and sculpting, often results in higher material consumption and increased expenses due to less efficient usage. Resource efficiency favors casting slip in large-scale productions where material conservation and cost control are critical.
Choosing the Right Clay: Factors to Consider
When choosing between casting slip and plastic clay, consider factors such as workability, drying time, and final texture. Casting slip is ideal for detailed molds and creating hollow forms due to its liquid consistency, while plastic clay offers more flexibility for hand-building and sculpting. Evaluate project requirements, including surface finish and firing techniques, to select the best clay type for optimal results.
Casting Slip vs Plastic Clay Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com