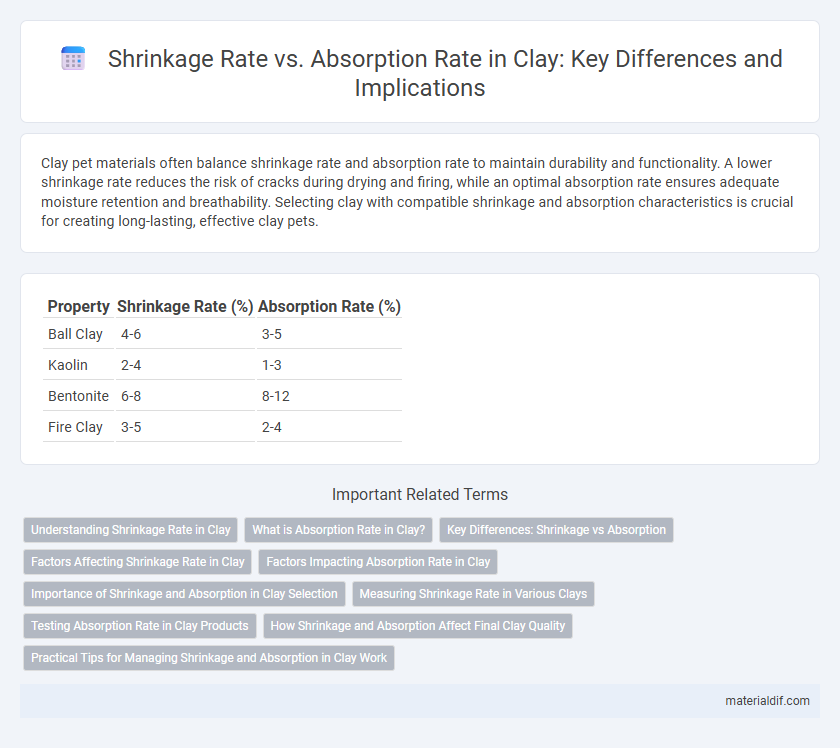
Clay pet materials often balance shrinkage rate and absorption rate to maintain durability and functionality. A lower shrinkage rate reduces the risk of cracks during drying and firing, while an optimal absorption rate ensures adequate moisture retention and breathability. Selecting clay with compatible shrinkage and absorption characteristics is crucial for creating long-lasting, effective clay pets.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Shrinkage Rate (%) | Absorption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Clay | 4-6 | 3-5 |
| Kaolin | 2-4 | 1-3 |
| Bentonite | 6-8 | 8-12 |
| Fire Clay | 3-5 | 2-4 |
Understanding Shrinkage Rate in Clay
Shrinkage rate in clay measures the percentage reduction in volume as the clay dries and undergoes dehydration, significantly impacting its structural integrity. This rate directly correlates with the clay's mineral composition and particle size, influencing how much the material contracts during the drying process. Understanding shrinkage rate helps predict potential warping or cracking, differentiating it from absorption rate, which quantifies the clay's ability to retain water.
What is Absorption Rate in Clay?
Absorption rate in clay refers to the percentage of water a clay material can absorb relative to its dry weight, directly influencing its durability and firing characteristics. A higher absorption rate typically indicates more porous clay, which may result in increased shrinkage during drying and firing. Understanding absorption rate helps in selecting appropriate clay types for specific ceramic or construction applications, ensuring optimal performance and structural integrity.
Key Differences: Shrinkage vs Absorption
Shrinkage rate in clay refers to the percentage reduction in volume during drying and firing, typically ranging from 5% to 15%, depending on the clay type and firing temperature. Absorption rate measures the clay's porosity by indicating the amount of water the fired clay can absorb, often expressed as a percentage of its dry weight and varying between low-fire and high-fire clays. Key differences include that shrinkage affects clay's dimensional stability and cracking potential, while absorption influences its durability, porosity, and suitability for functional ceramics.
Factors Affecting Shrinkage Rate in Clay
Shrinkage rate in clay is primarily influenced by moisture content, mineral composition, and particle size distribution. Higher moisture levels lead to greater shrinkage as water evaporates and clay particles pull closer together, while clays rich in montmorillonite exhibit more significant shrinkage than kaolinite due to their expansive crystal structure. Fine-grained clays with smaller particle sizes generally experience higher shrinkage rates compared to coarse-grained clays because of increased surface area and water retention capacity.
Factors Impacting Absorption Rate in Clay
Absorption rate in clay is primarily influenced by factors such as porosity, particle size, and mineral composition, which determine how much water the clay can retain. Higher porosity increases the surface area for water absorption, while finer particle size results in smaller pore spaces that hold water more effectively. Additionally, the presence of specific clay minerals like montmorillonite can significantly enhance absorption due to their molecular structure and swelling capacity.
Importance of Shrinkage and Absorption in Clay Selection
Shrinkage rate and absorption rate are critical factors in clay selection, directly impacting the durability and structural integrity of fired ceramics. High shrinkage can cause warping and cracking during drying and firing, while optimal absorption rates ensure proper water retention and porosity, influencing the clay's workability and final strength. Balancing these properties helps artisans and manufacturers achieve desired performance characteristics in pottery and construction materials.
Measuring Shrinkage Rate in Various Clays
Measuring shrinkage rate in various clays involves calculating the percentage reduction in volume as the clay dries from its plastic to kiln-dried state, a critical factor for predicting structural integrity and avoiding cracks. This process typically requires precise initial and final dimension measurements under standardized conditions, considering variations in clay mineral composition, particle size, and water content. Accurate shrinkage rate data, when correlated with absorption rates, helps determine the clay's stability and suitability for different ceramic or construction applications.
Testing Absorption Rate in Clay Products
Testing absorption rate in clay products involves measuring the percentage of water the material absorbs after being submerged for a specified time, typically 24 hours. The shrinkage rate is directly influenced by absorption rate, as higher water uptake often leads to greater dimensional changes during drying and firing processes. Accurate absorption rate testing ensures quality control by predicting the durability and structural integrity of clay items in practical applications.
How Shrinkage and Absorption Affect Final Clay Quality
Shrinkage rate directly influences the dimensional stability and structural integrity of clay products, with excessive shrinkage leading to cracks and deformation. Absorption rate determines the porosity and water resistance of the final clay body, impacting durability and suitability for various applications. Balancing shrinkage and absorption rates is essential to ensure optimal strength, durability, and aesthetic quality in fired ceramics.
Practical Tips for Managing Shrinkage and Absorption in Clay Work
Monitor clay's shrinkage rate, typically ranging from 5% to 15%, and absorption rate to prevent cracks and deformation during drying and firing. Use controlled drying environments and consistent water content to minimize uneven shrinkage and excessive water absorption. Selecting clay bodies with balanced shrinkage and absorption rates ensures durability and reduces warping in finished ceramic pieces.
Shrinkage Rate vs Absorption Rate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com