Opaque ceramic offers superior masking properties, making it ideal for concealing underlying dental structures or discolorations. Translucent ceramic mimics the natural tooth appearance by allowing light to pass through, creating a more lifelike and aesthetic restoration. Choosing between opaque and translucent ceramics depends on the desired balance between strength, masking ability, and natural aesthetics in dental applications.
Table of Comparison
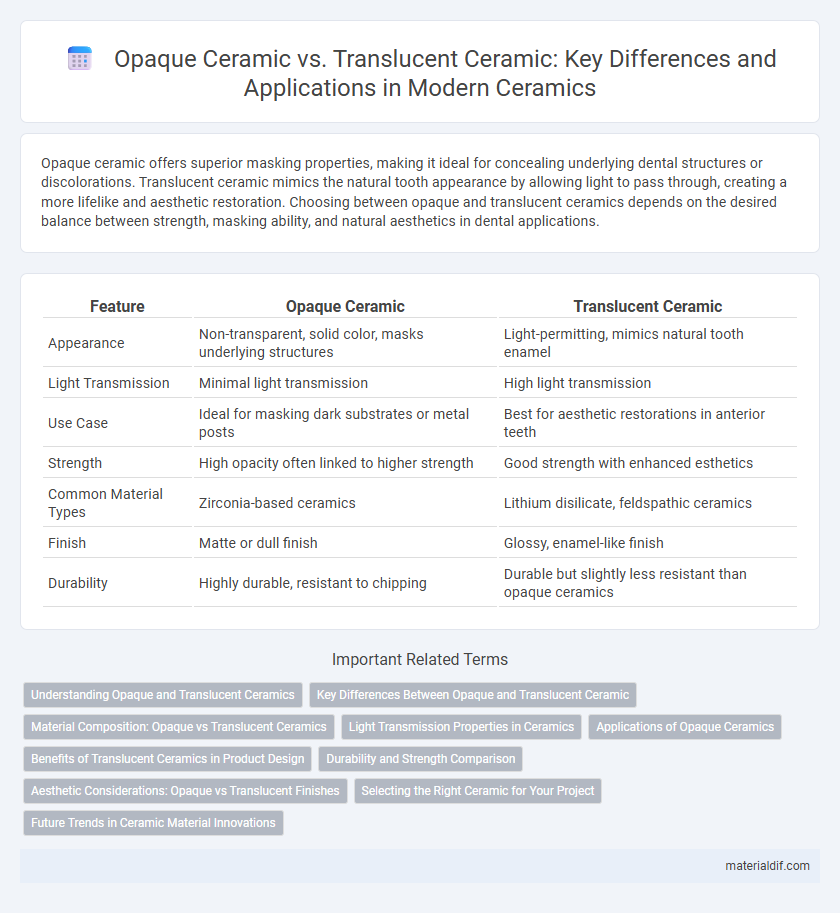
| Feature | Opaque Ceramic | Translucent Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Non-transparent, solid color, masks underlying structures | Light-permitting, mimics natural tooth enamel |
| Light Transmission | Minimal light transmission | High light transmission |
| Use Case | Ideal for masking dark substrates or metal posts | Best for aesthetic restorations in anterior teeth |
| Strength | High opacity often linked to higher strength | Good strength with enhanced esthetics |
| Common Material Types | Zirconia-based ceramics | Lithium disilicate, feldspathic ceramics |
| Finish | Matte or dull finish | Glossy, enamel-like finish |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to chipping | Durable but slightly less resistant than opaque ceramics |
Understanding Opaque and Translucent Ceramics
Opaque ceramics block the passage of light completely, making them ideal for applications requiring full coverage and high strength, such as industrial components and electrical insulators. Translucent ceramics allow some light to pass through while diffusing it, providing a balance between visibility and durability, commonly used in dental restorations and decorative tiles. The key difference lies in their microstructure and light-scattering properties, affecting their optical behavior and suitability for specific functional or aesthetic purposes.
Key Differences Between Opaque and Translucent Ceramic
Opaque ceramic blocks light completely, providing superior masking ability and hiding flaws beneath restorations, making them ideal for discolored teeth or metal posts. Translucent ceramic allows light to pass through, mimicking the natural tooth's appearance by enhancing depth and vitality, commonly used in aesthetic dental restorations like veneers and crowns. Key differences include optical properties, strength levels--opaque ceramics tend to be stronger but less aesthetic--while translucent ceramics prioritize lifelike appearance over maximum durability.
Material Composition: Opaque vs Translucent Ceramics
Opaque ceramics are primarily composed of crystalline structures with a higher content of alumina or zirconia, which enhances their opacity by scattering light within the material. Translucent ceramics often incorporate glassy phases or reduced crystalline content, such as lithium disilicate, allowing partial light transmission and a natural aesthetic appearance. The difference in material composition directly influences optical properties, mechanical strength, and clinical applications in dental restorations.
Light Transmission Properties in Ceramics
Opaque ceramics exhibit minimal light transmission, effectively blocking visible light due to their dense microstructure and high absorption coefficients, making them ideal for applications requiring light insulation and durability. Translucent ceramics, such as certain advanced alumina and zirconia formulations, allow partial light transmission by scattering and diffusing light within their microstructure, enabling applications in lighting, medical implants, and aesthetic dental restorations. The controlled balance of grain size, porosity, and phase composition in translucent ceramics optimizes their optical clarity while maintaining mechanical strength.
Applications of Opaque Ceramics
Opaque ceramics are widely used in applications requiring high strength and thermal insulation, such as in electronic substrates, cutting tools, and armor plating. Their ability to block light and withstand harsh environments makes them ideal for structural components in aerospace and automotive industries. The materials' excellent resistance to wear and corrosion further extends their use in industrial machinery and biomedical implants.
Benefits of Translucent Ceramics in Product Design
Translucent ceramics enhance product design by offering superior aesthetic appeal through natural light diffusion, creating a visually pleasing and lifelike appearance. These ceramics provide improved translucency and color depth compared to opaque ceramics, enabling designers to achieve intricate detailing and sophisticated textures. Their combination of strength and light transmission makes them ideal for innovations in lighting fixtures, decorative elements, and advanced display technologies.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Opaque ceramics typically exhibit higher durability due to their dense microstructure, making them more resistant to fractures and wear over time. Translucent ceramics, while aesthetically superior due to light transmission properties, often have slightly lower strength and can be more prone to chipping or cracking under heavy stress. The balance between translucency and mechanical robustness depends on the specific ceramic formulation and intended application.
Aesthetic Considerations: Opaque vs Translucent Finishes
Opaque ceramics offer a uniform, solid appearance that effectively conceals underlying substrates, making them ideal for restorations requiring color masking. Translucent ceramics replicate the natural light transmission and depth of enamel, enhancing the lifelike aesthetic of dental restorations. Choosing between opaque and translucent finishes depends on the specific aesthetic goals and the shade of the abutment or tooth structure beneath the ceramic.
Selecting the Right Ceramic for Your Project
Selecting the right ceramic for your project depends heavily on the desired visual effect and functional requirements. Opaque ceramics offer superior coverage and are ideal for applications needing solid colors or intricate patterns where background interference must be minimized. Translucent ceramics provide natural light transmission and depth, making them perfect for aesthetic designs in lighting fixtures or artistic installations demanding subtle diffusion and visual appeal.
Future Trends in Ceramic Material Innovations
Opaque ceramic materials provide superior strength and durability for structural applications, while translucent ceramics offer enhanced aesthetic appeal and light transmission for dental and decorative uses. Future trends in ceramic material innovations emphasize the development of hybrid composites combining translucency and opacity to optimize both mechanical performance and visual effects. Advancements in nanotechnology and additive manufacturing are driving the creation of ceramics with tailored optical properties and increased functional versatility.
Opaque Ceramic vs Translucent Ceramic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com