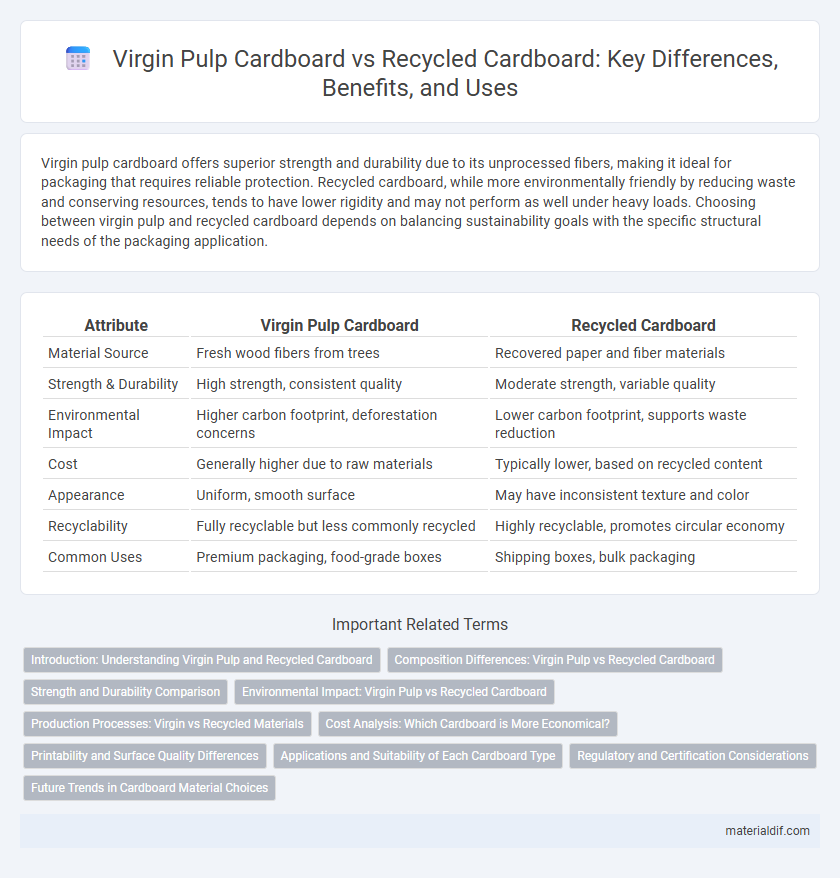
Virgin pulp cardboard offers superior strength and durability due to its unprocessed fibers, making it ideal for packaging that requires reliable protection. Recycled cardboard, while more environmentally friendly by reducing waste and conserving resources, tends to have lower rigidity and may not perform as well under heavy loads. Choosing between virgin pulp and recycled cardboard depends on balancing sustainability goals with the specific structural needs of the packaging application.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Virgin Pulp Cardboard | Recycled Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Fresh wood fibers from trees | Recovered paper and fiber materials |
| Strength & Durability | High strength, consistent quality | Moderate strength, variable quality |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint, deforestation concerns | Lower carbon footprint, supports waste reduction |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw materials | Typically lower, based on recycled content |
| Appearance | Uniform, smooth surface | May have inconsistent texture and color |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable but less commonly recycled | Highly recyclable, promotes circular economy |
| Common Uses | Premium packaging, food-grade boxes | Shipping boxes, bulk packaging |
Introduction: Understanding Virgin Pulp and Recycled Cardboard
Virgin pulp cardboard is produced directly from freshly harvested trees, providing superior strength, brightness, and uniformity essential for high-quality packaging solutions. Recycled cardboard, made from recovered paper fibers, offers eco-friendly benefits by reducing waste and conserving natural resources, though it may compromise on durability and color consistency. Understanding the differences in fiber origin and processing helps manufacturers select the right material for specific performance and sustainability requirements.
Composition Differences: Virgin Pulp vs Recycled Cardboard
Virgin pulp cardboard is made from freshly harvested wood fibers, resulting in a smoother, stronger, and more uniform material ideal for high-quality packaging. Recycled cardboard consists of fibers recovered from used paper products, which are often shorter and weaker due to previous processing, leading to a less durable but more environmentally friendly option. The composition differences impact not only the physical properties but also the sustainability profile, with virgin pulp requiring more natural resources and recycled cardboard reducing waste and energy consumption.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Virgin pulp cardboard exhibits superior strength and durability compared to recycled cardboard due to its higher fiber quality and longer fiber length, which contribute to enhanced structural integrity. Recycled cardboard, while more environmentally friendly, often contains shorter, weaker fibers from multiple recycling cycles, leading to reduced strength and increased susceptibility to wear and tear. For applications requiring maximum load-bearing capacity and resistance to crushing, virgin pulp cardboard remains the preferred choice.
Environmental Impact: Virgin Pulp vs Recycled Cardboard
Virgin pulp cardboard relies on freshly harvested trees, resulting in higher carbon emissions, deforestation, and greater energy consumption during production. Recycled cardboard reduces landfill waste, conserves natural resources, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions by reprocessing existing paper fibers. The environmental impact of recycled cardboard is significantly less than virgin pulp cardboard, making it a more sustainable choice in packaging and manufacturing.
Production Processes: Virgin vs Recycled Materials
Virgin pulp cardboard is produced directly from freshly harvested wood fibers, involving processes such as pulping, bleaching, and refining to ensure high strength and uniformity. Recycled cardboard is made from post-consumer and post-industrial waste paper, which undergoes deinking, cleaning, and re-pulping before being formed into new sheets. The production of recycled cardboard consumes less energy and water compared to virgin pulp but may require additives to restore strength lost during fiber recycling.
Cost Analysis: Which Cardboard is More Economical?
Virgin pulp cardboard typically incurs higher production costs due to the need for raw wood fibers and energy-intensive processing, resulting in a higher market price compared to recycled cardboard. Recycled cardboard significantly reduces material expenses by reusing fibers from post-consumer waste, lowering both production costs and environmental impact. For businesses prioritizing cost-efficiency, recycled cardboard offers a more economical solution without substantially compromising quality.
Printability and Surface Quality Differences
Virgin pulp cardboard offers superior printability and surface quality compared to recycled cardboard, due to its smoother and more uniform fibers resulting in higher ink absorption and sharper image reproduction. Recycled cardboard often contains mixed fibers and contaminants, leading to a rougher surface texture that can cause ink bleed and reduced print clarity. Brands seeking premium packaging aesthetics prioritize virgin pulp cardboard for its consistent surface finish and vibrant color fidelity.
Applications and Suitability of Each Cardboard Type
Virgin pulp cardboard offers superior strength, making it ideal for packaging fragile or high-value items requiring durability and protection. Recycled cardboard suits applications like shipping boxes and general packaging where eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. Each type's fiber quality influences its suitability, with virgin pulp retaining structural integrity for demanding uses, while recycled materials serve well in everyday, less critical packaging needs.
Regulatory and Certification Considerations
Virgin pulp cardboard adheres to stringent regulatory standards such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), ensuring sustainable forest management and compliance with international forestry laws. Recycled cardboard often meets certifications like SFI (Sustainable Forestry Initiative) and carries Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) compliance for incorporating post-consumer waste, but it may have stricter limits on chemical residues and dye usage to meet safety regulations. Both types must conform to FDA and EU food contact safety standards when used in packaging, influencing material selection based on regulatory and certification requirements.
Future Trends in Cardboard Material Choices
Virgin pulp cardboard offers superior strength and purity, making it ideal for premium packaging despite higher environmental impact. Recycled cardboard continues to improve in quality and sustainability, driven by advancements in sorting technology and chemical treatments. Future trends indicate a growing preference for hybrid materials combining virgin and recycled fibers to balance performance with eco-consciousness.
Virgin pulp cardboard vs Recycled cardboard Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com