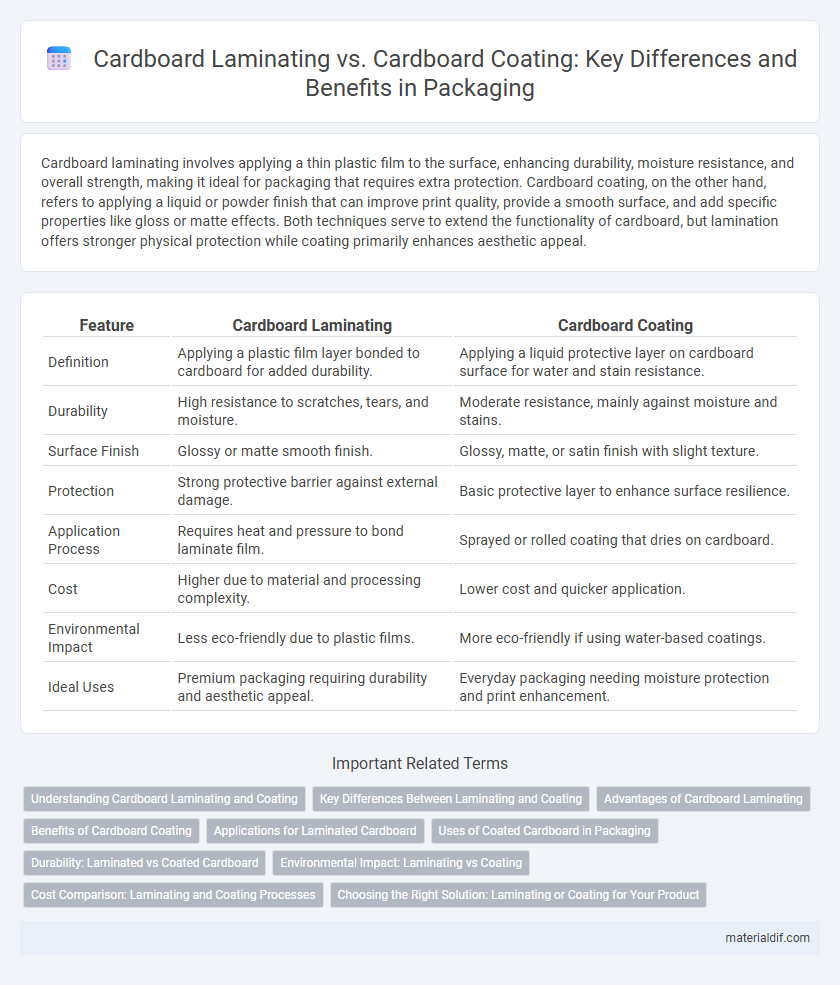
Cardboard laminating involves applying a thin plastic film to the surface, enhancing durability, moisture resistance, and overall strength, making it ideal for packaging that requires extra protection. Cardboard coating, on the other hand, refers to applying a liquid or powder finish that can improve print quality, provide a smooth surface, and add specific properties like gloss or matte effects. Both techniques serve to extend the functionality of cardboard, but lamination offers stronger physical protection while coating primarily enhances aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cardboard Laminating | Cardboard Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying a plastic film layer bonded to cardboard for added durability. | Applying a liquid protective layer on cardboard surface for water and stain resistance. |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches, tears, and moisture. | Moderate resistance, mainly against moisture and stains. |
| Surface Finish | Glossy or matte smooth finish. | Glossy, matte, or satin finish with slight texture. |
| Protection | Strong protective barrier against external damage. | Basic protective layer to enhance surface resilience. |
| Application Process | Requires heat and pressure to bond laminate film. | Sprayed or rolled coating that dries on cardboard. |
| Cost | Higher due to material and processing complexity. | Lower cost and quicker application. |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly due to plastic films. | More eco-friendly if using water-based coatings. |
| Ideal Uses | Premium packaging requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. | Everyday packaging needing moisture protection and print enhancement. |
Understanding Cardboard Laminating and Coating
Cardboard laminating involves applying a thin plastic film to the surface, enhancing durability, moisture resistance, and print vibrancy for packaging applications. Coating, on the other hand, uses a layer of wax, clay, or chemical compounds to improve cardboard's surface smoothness and barrier properties against grease or water. Understanding the functional differences between laminating and coating is essential for selecting the right finish based on protection needs and end-use requirements in cardboard manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Laminating and Coating
Cardboard laminating involves applying a thin plastic film layer to enhance durability, water resistance, and visual appeal, making it ideal for packaging requiring extra protection. Cardboard coating uses a sprayed or rolled application of coatings like varnish or aqueous solutions, focusing on improving surface smoothness, print quality, and moisture resistance without altering thickness significantly. The key difference lies in laminating adding a physical film, while coating modifies the surface finish, impacting cost, recyclability, and overall performance of the cardboard.
Advantages of Cardboard Laminating
Cardboard laminating enhances durability and moisture resistance, significantly extending the lifespan of cardboard products compared to coating. Laminating provides a thicker protective layer that guards against physical damage, making it ideal for packaging requiring extra strength. This process also improves print clarity and color vibrancy, boosting the visual appeal and brand presentation of cardboard materials.
Benefits of Cardboard Coating
Cardboard coating enhances durability by providing a protective layer that resists moisture, grease, and abrasion, extending the lifespan of packaging materials. Unlike laminating, coating maintains the cardboard's recyclability and breathability, making it more environmentally friendly. The coating process also improves print quality and visual appeal, ensuring vibrant graphics and brand presentation on the cardboard surface.
Applications for Laminated Cardboard
Laminated cardboard enhances durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging in food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer electronics industries. This lamination process strengthens the structural integrity of cardboard, allowing it to withstand handling, transportation, and environmental factors more effectively than coated cardboard. Applications for laminated cardboard frequently include protective packaging, retail display boxes, and high-quality printed materials requiring a glossy or matte finish.
Uses of Coated Cardboard in Packaging
Coated cardboard enhances packaging durability by providing moisture resistance and improved surface finish, making it ideal for food packaging and retail displays. The coating layer prevents ink bleed, ensuring vibrant and high-quality graphic prints that attract consumer attention. Its protective properties also increase shelf life of perishable products and provide a barrier against grease and contaminants in packaging applications.
Durability: Laminated vs Coated Cardboard
Laminated cardboard offers superior durability through a protective plastic film that resists moisture, scratches, and wear, extending the lifespan of packaging materials. Coated cardboard provides a thin layer of varnish or aqueous coating that enhances surface smoothness and print quality but offers less resistance to physical damage compared to lamination. For applications requiring long-term protection and enhanced durability, laminated cardboard is the preferred option over coated cardboard.
Environmental Impact: Laminating vs Coating
Cardboard laminating involves applying a plastic film, which creates durability but significantly reduces recyclability and increases environmental waste. Cardboard coating typically uses water-based or biodegradable substances that enhance moisture resistance while maintaining recyclability, resulting in a lower ecological footprint. Choosing coating over laminating supports sustainable packaging by minimizing plastic contamination and facilitating circular material use.
Cost Comparison: Laminating and Coating Processes
Cardboard laminating typically incurs higher upfront costs due to the use of plastic films and heat-press equipment, but it offers superior durability and moisture resistance. In contrast, cardboard coating involves applying a liquid layer such as varnish or clay, resulting in lower initial expenses and faster processing times. Overall, coating is more cost-effective for large-volume, low-durability needs, while laminating justifies investment for premium, long-lasting applications.
Choosing the Right Solution: Laminating or Coating for Your Product
Cardboard laminating provides a durable protective layer that enhances moisture resistance and structural strength, ideal for packaging requiring long-term durability. Cardboard coating offers a thinner, cost-effective solution primarily improving surface gloss, print quality, and limited water resistance. Selecting the right option depends on product requirements such as environmental exposure, budget constraints, and desired aesthetic finish.
Cardboard laminating vs Cardboard coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com