Bamboo pulp is primarily used in the production of eco-friendly paper and textiles due to its soft texture and high fiber content. Bamboo charcoal, created by carbonizing bamboo at high temperatures, excels in air purification, moisture absorption, and odor control, making it ideal for environmental and health applications. Understanding the distinct properties and uses of bamboo pulp and bamboo charcoal helps maximize the sustainability benefits of bamboo.
Table of Comparison
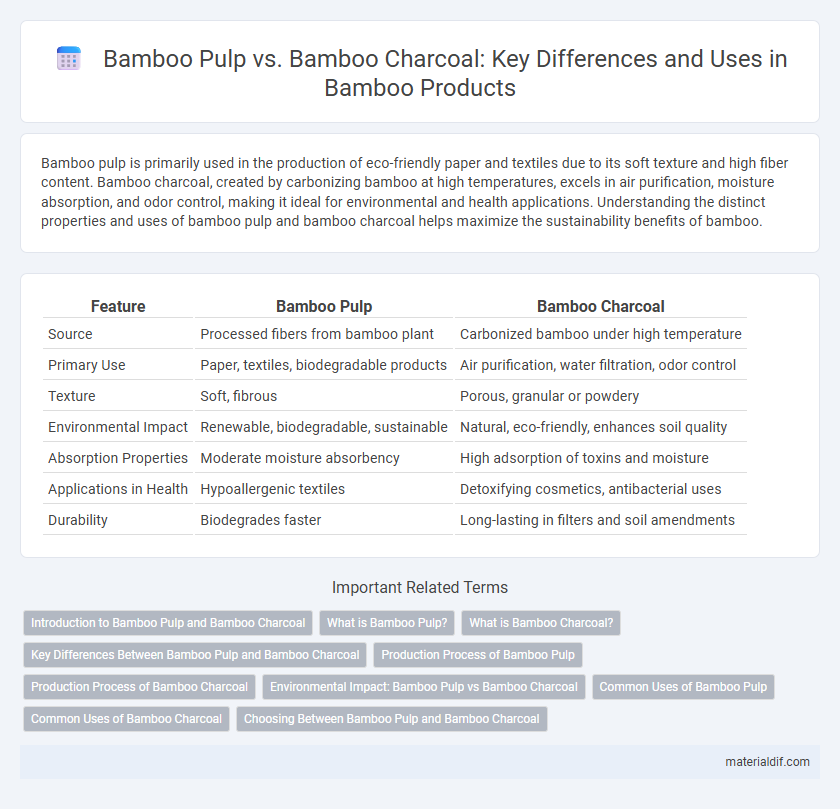
| Feature | Bamboo Pulp | Bamboo Charcoal |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Processed fibers from bamboo plant | Carbonized bamboo under high temperature |
| Primary Use | Paper, textiles, biodegradable products | Air purification, water filtration, odor control |
| Texture | Soft, fibrous | Porous, granular or powdery |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, sustainable | Natural, eco-friendly, enhances soil quality |
| Absorption Properties | Moderate moisture absorbency | High adsorption of toxins and moisture |
| Applications in Health | Hypoallergenic textiles | Detoxifying cosmetics, antibacterial uses |
| Durability | Biodegrades faster | Long-lasting in filters and soil amendments |
Introduction to Bamboo Pulp and Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo pulp is derived from the processing of bamboo fibers into a soft, biodegradable material widely used in paper, textiles, and hygiene products. Bamboo charcoal is produced by carbonizing bamboo at high temperatures, resulting in a porous substance known for its excellent odor-absorbing, moisture-wicking, and air-purifying properties. Both bamboo pulp and bamboo charcoal leverage the natural sustainability and fast-growing characteristics of bamboo, but serve distinctly different industrial and environmental functions.
What is Bamboo Pulp?
Bamboo pulp is a fibrous material derived from the cellulose of bamboo plants, primarily used in the production of paper, textiles, and biodegradable products due to its strength and eco-friendly attributes. Unlike bamboo charcoal, which is created through the pyrolysis of bamboo for filtration and detoxification purposes, bamboo pulp undergoes a chemical or mechanical process to break down bamboo fibers into a usable pulp form. The high cellulose content of bamboo pulp makes it a sustainable alternative to traditional wood pulp, promoting faster growth cycles and reduced environmental impact.
What is Bamboo Charcoal?
Bamboo charcoal is produced by heating bamboo stalks in a high-temperature pyrolysis process without oxygen, resulting in a porous, carbon-rich material. It is widely used for air purification, moisture absorption, and soil conditioning due to its excellent adsorption properties. Unlike bamboo pulp, which is processed into fibers for textiles and paper, bamboo charcoal serves primarily as a natural deodorizer and purifier.
Key Differences Between Bamboo Pulp and Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo pulp is a cellulose fiber derived from the bamboo plant used primarily in textile and paper production, offering soft texture and biodegradability. Bamboo charcoal is created by pyrolyzing bamboo at high temperatures, resulting in a porous carbon-rich material utilized for air purification, moisture absorption, and deodorization. The key differences lie in their composition, processing methods, and end-use applications, with bamboo pulp emphasizing fiber extraction and bamboo charcoal focused on carbonization for environmental benefits.
Production Process of Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo pulp is produced through a mechanical or chemical process that breaks down bamboo fibers into a fibrous slurry used in papermaking, involving steps like cutting, steaming, and washing bamboo stalks. Bamboo charcoal, contrastingly, is made by carbonizing bamboo through pyrolysis at high temperatures in a low-oxygen environment, resulting in a porous carbon material. The production of bamboo pulp emphasizes fiber extraction and purification to ensure quality for textile or paper applications.
Production Process of Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo charcoal is produced by pyrolyzing bamboo at high temperatures between 600degC and 900degC in an oxygen-limited environment, which removes moisture and volatile compounds, leaving behind a carbon-rich material. This process differs from bamboo pulp production, which involves chemical or mechanical treatment of bamboo fibers to create a slurry for paper manufacturing. The controlled carbonization in bamboo charcoal production enhances its porosity and adsorption properties, making it useful in filtration, deodorization, and soil amendment applications.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo Pulp vs Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo pulp production involves chemical processing that can generate wastewater containing pollutants, whereas bamboo charcoal is produced through pyrolysis, a carbonization process with lower water consumption and minimal chemical discharge. Bamboo charcoal offers benefits such as soil enhancement and air purification due to its porous structure, contributing to carbon sequestration and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable bamboo harvesting combined with responsible production methods of charcoal and pulp significantly affects their environmental footprint, with bamboo charcoal generally favored for eco-friendly applications.
Common Uses of Bamboo Pulp
Bamboo pulp is widely used in the production of eco-friendly paper, textiles, and packaging materials due to its sustainable fiber content and biodegradability. Its softness and absorbency make it ideal for hygiene products such as tissues, diapers, and sanitary napkins. Bamboo pulp also serves as a raw material in the manufacturing of biodegradable composites and bio-based plastics, promoting greener industrial applications.
Common Uses of Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo charcoal is widely used in air and water purification due to its porous structure that effectively absorbs odors, toxins, and moisture. It is also popular in skincare products for its natural antibacterial properties and ability to balance oily skin. Common applications include air fresheners, water filters, deodorizers, and beauty masks, highlighting its multifunctional benefits compared to bamboo pulp primarily used in paper and textile production.
Choosing Between Bamboo Pulp and Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo pulp and bamboo charcoal serve different purposes in sustainable product manufacturing; bamboo pulp is primarily used for creating soft, biodegradable textiles and paper products, while bamboo charcoal excels in air purification, moisture absorption, and odor control. Choosing between bamboo pulp and bamboo charcoal depends on the application: bamboo pulp is ideal for eco-friendly fabrics and disposable paper goods, whereas bamboo charcoal is preferred for natural deodorizing agents, water filters, and soil enhancers. Evaluating factors like product functionality, environmental impact, and end-user benefits can guide the selection process between these versatile bamboo derivatives.
Bamboo pulp vs Bamboo charcoal Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com