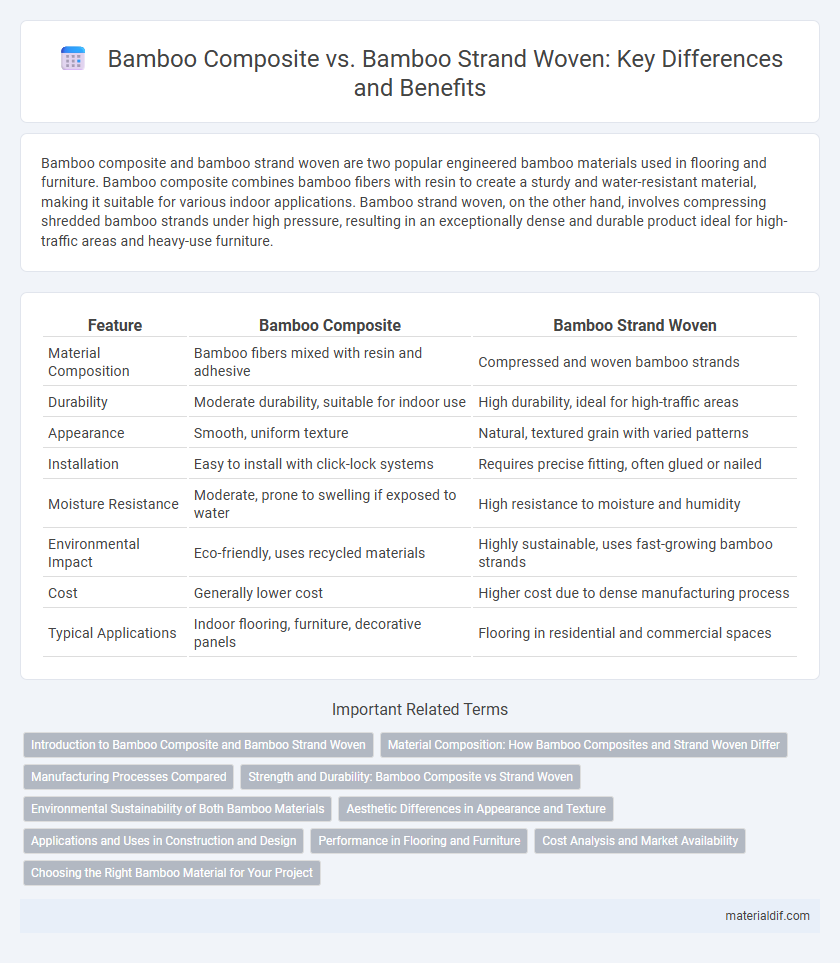
Bamboo composite and bamboo strand woven are two popular engineered bamboo materials used in flooring and furniture. Bamboo composite combines bamboo fibers with resin to create a sturdy and water-resistant material, making it suitable for various indoor applications. Bamboo strand woven, on the other hand, involves compressing shredded bamboo strands under high pressure, resulting in an exceptionally dense and durable product ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy-use furniture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Composite | Bamboo Strand Woven |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Bamboo fibers mixed with resin and adhesive | Compressed and woven bamboo strands |
| Durability | Moderate durability, suitable for indoor use | High durability, ideal for high-traffic areas |
| Appearance | Smooth, uniform texture | Natural, textured grain with varied patterns |
| Installation | Easy to install with click-lock systems | Requires precise fitting, often glued or nailed |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, prone to swelling if exposed to water | High resistance to moisture and humidity |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, uses recycled materials | Highly sustainable, uses fast-growing bamboo strands |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to dense manufacturing process |
| Typical Applications | Indoor flooring, furniture, decorative panels | Flooring in residential and commercial spaces |
Introduction to Bamboo Composite and Bamboo Strand Woven
Bamboo composite materials combine natural bamboo fibers with resins or adhesives to create durable, eco-friendly products suitable for flooring, furniture, and construction. Bamboo strand woven, a specific type of bamboo composite, involves compressing shredded bamboo strands under high pressure with adhesives, resulting in an exceptionally dense and resilient material. Both materials leverage bamboo's rapid renewability and strength, but bamboo strand woven offers superior hardness and stability compared to standard bamboo composites.
Material Composition: How Bamboo Composites and Strand Woven Differ
Bamboo composites are engineered materials combining bamboo fibers with adhesives and resins to create uniform, versatile products. Bamboo strand woven uses long bamboo strands that are compressed under high pressure and heat, resulting in a dense and durable flooring material. The key difference lies in composites mixing fibers for flexibility, while strand woven emphasizes strand alignment for enhanced strength.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Bamboo composite is manufactured by combining bamboo fibers with adhesives and heat-pressed into panels, allowing for diverse shapes and consistent density, while bamboo strand woven involves shredding bamboo into strands, aligning them, and compressing under high pressure to create dense, durable boards. The strand woven process yields higher density and greater structural strength compared to traditional bamboo composites. Manufacturing bamboo strand woven products typically requires more intensive processing and energy, resulting in enhanced hardness and moisture resistance.
Strength and Durability: Bamboo Composite vs Strand Woven
Bamboo composite materials exhibit superior dimensional stability and resistance to moisture compared to bamboo strand woven products, making them highly durable for various applications. Strand woven bamboo, created by compressing shredded bamboo fibers under high pressure, offers exceptional hardness and strength, often surpassing traditional hardwoods in durability. While both types are strong and sustainable, bamboo composite excels in resistance to environmental wear, whereas strand woven bamboo is preferred for applications demanding high structural load-bearing capacity.
Environmental Sustainability of Both Bamboo Materials
Bamboo composite and bamboo strand woven both offer significant environmental sustainability advantages due to their rapid renewability and carbon sequestration capabilities. Bamboo strand woven products typically have higher density and durability, resulting in longer lifespan and reduced material waste compared to some bamboo composites. Both materials contribute to sustainable forestry practices by utilizing fast-growing bamboo species, minimizing deforestation and promoting biodegradability.
Aesthetic Differences in Appearance and Texture
Bamboo composite features a smooth, uniform surface with subtle natural grain patterns, offering a sleek and polished aesthetic ideal for modern interiors. Bamboo strand woven displays a more pronounced texture with intricate, interwoven fibers that create a visually distinct, rustic appearance. The difference in manufacturing processes results in bamboo composite being softer to the touch, while bamboo strand woven provides a denser, more tactile surface texture.
Applications and Uses in Construction and Design
Bamboo composite materials are engineered by combining bamboo fibers with resins, creating versatile panels ideal for cabinetry, furniture, and interior wall cladding due to their uniformity and ease of customization. Bamboo strand woven (BSW) offers superior strength and durability through a high-pressure process that compresses bamboo strands into dense, hardwood-like flooring and structural beams suitable for load-bearing applications. Both materials are sustainable alternatives in construction and design, with bamboo composite favored for decorative surfaces and BSW preferred for flooring and heavy-duty structural elements.
Performance in Flooring and Furniture
Bamboo composite flooring exhibits superior dimensional stability and resistance to moisture compared to bamboo strand woven, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and humid environments. Bamboo strand woven outperforms traditional composites in hardness and durability, with a Janka hardness rating often exceeding 3,000 pounds, ensuring long-lasting furniture performance. Both materials offer sustainable options, but strand woven bamboo provides enhanced structural strength, suitable for heavy-use applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Bamboo composite materials generally have lower production costs due to simpler manufacturing processes compared to bamboo strand woven products, which involve intense heat and pressure treatments that increase expenses. In terms of market availability, bamboo composite panels are widely accessible in both residential and commercial construction sectors, while bamboo strand woven boards, prized for their strength and durability, are more niche but growing in demand among high-end flooring and furniture manufacturers. Price differences typically reflect the complexity of processing, with bamboo strand woven products commanding premium rates due to superior mechanical properties and longer life cycles.
Choosing the Right Bamboo Material for Your Project
Bamboo composite offers a balanced combination of natural fibers and resin, providing durability and moisture resistance ideal for outdoor projects and furniture. Bamboo strand woven, made by compressing bamboo fibers under high pressure, delivers exceptional hardness and density, making it suitable for high-traffic flooring and structural applications. Selecting the right bamboo material depends on project requirements such as strength, appearance, and environmental exposure.
Bamboo composite vs bamboo strand woven Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com