Bamboo plywood consists of thin layers of bamboo laminated together, offering enhanced strength and stability compared to solid bamboo, which is a single, solid piece of the bamboo stalk. Plywood is less prone to warping and cracking, making it ideal for furniture and flooring applications where durability is essential. Solid bamboo provides a natural, uniform appearance but may require more maintenance to prevent splitting and moisture damage over time.
Table of Comparison
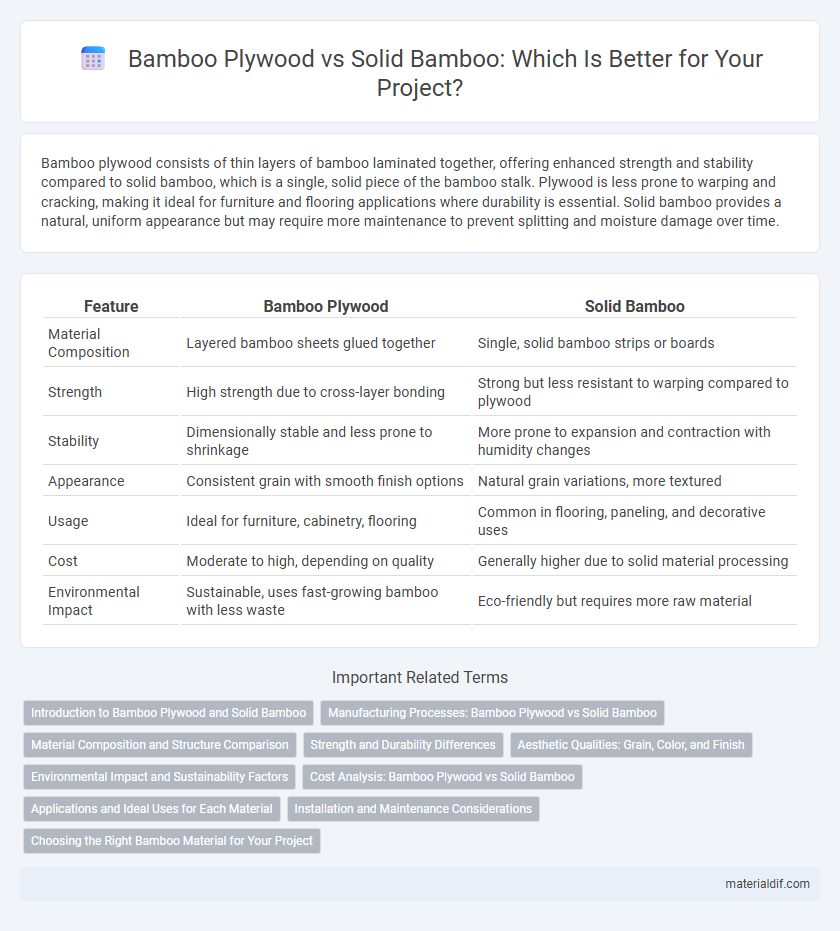
| Feature | Bamboo Plywood | Solid Bamboo |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Layered bamboo sheets glued together | Single, solid bamboo strips or boards |
| Strength | High strength due to cross-layer bonding | Strong but less resistant to warping compared to plywood |
| Stability | Dimensionally stable and less prone to shrinkage | More prone to expansion and contraction with humidity changes |
| Appearance | Consistent grain with smooth finish options | Natural grain variations, more textured |
| Usage | Ideal for furniture, cabinetry, flooring | Common in flooring, paneling, and decorative uses |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on quality | Generally higher due to solid material processing |
| Environmental Impact | Sustainable, uses fast-growing bamboo with less waste | Eco-friendly but requires more raw material |
Introduction to Bamboo Plywood and Solid Bamboo
Bamboo plywood consists of multiple layers of bamboo veneers laminated together, providing enhanced strength and stability compared to solid bamboo, which is made from a single, solid piece of bamboo. While solid bamboo showcases natural grain patterns and offers a uniform, dense structure, bamboo plywood is engineered for durability and resistance to warping. Both materials are sustainable, but bamboo plywood is often preferred in construction and furniture for its dimensional stability and versatility.
Manufacturing Processes: Bamboo Plywood vs Solid Bamboo
Bamboo plywood is manufactured by gluing together multiple thin layers of bamboo strips, enhancing its strength and stability while reducing susceptibility to warping and splitting. Solid bamboo is made by compressing whole bamboo fibers into dense, uniform boards, providing natural resistance to moisture but requiring careful treatment to prevent cracking. The manufacturing process of bamboo plywood allows for more consistent thickness and dimensional accuracy compared to the solid bamboo method.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Bamboo plywood consists of multiple layers of bamboo veneers laminated together, offering enhanced stability and resistance to warping compared to solid bamboo, which is made from a single dense piece of vertically or horizontally compressed bamboo fibers. The layered construction of bamboo plywood provides greater uniform strength and flexibility, making it more suitable for applications requiring durability and moisture resistance. In contrast, solid bamboo's natural grain and density variations can result in a harder surface but less dimensional stability under changing environmental conditions.
Strength and Durability Differences
Bamboo plywood consists of multiple layers of bamboo veneer laminated together, offering enhanced stability and resistance to warping compared to solid bamboo, which is made from a single, thick bamboo strand. Solid bamboo exhibits impressive natural strength but is more prone to cracking and splitting under stress due to its monolithic structure. The layered construction of bamboo plywood improves load distribution and durability, making it more suitable for heavy-use applications where consistent strength is critical.
Aesthetic Qualities: Grain, Color, and Finish
Bamboo plywood exhibits a uniform grain pattern and consistent light color due to its laminated construction, making it ideal for modern, sleek finishes and smooth surfaces. Solid bamboo features natural variations in grain and color, showcasing a richer, organic aesthetic with distinctive streaks and knots that enhance its visual depth. Both options offer versatile finishes, but solid bamboo provides a more textured, authentic look, while plywood enables greater control over uniformity and smoothness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Factors
Bamboo plywood utilizes laminated bamboo strips, reducing waste by repurposing smaller bamboo stalks and offering a higher yield per harvest compared to solid bamboo, which is milled from single stalks. The manufacturing of bamboo plywood typically consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases than processing solid bamboo, enhancing its environmental profile. Both materials are renewable and biodegradable, but bamboo plywood's efficient use of raw materials and durability make it a more sustainable choice in construction and furniture applications.
Cost Analysis: Bamboo Plywood vs Solid Bamboo
Bamboo plywood typically offers a more affordable option compared to solid bamboo due to its layered construction, which uses thinner bamboo strips bonded together, reducing material waste and manufacturing costs. Solid bamboo, made from thicker, single pieces of bamboo, tends to have higher production expenses and retail prices, reflecting its durability and uniform density. Choosing between bamboo plywood and solid bamboo depends on budget constraints and project requirements, with plywood favored for cost efficiency and solid bamboo for strength and longevity.
Applications and Ideal Uses for Each Material
Bamboo plywood offers superior dimensional stability and is ideal for cabinetry, furniture, and flooring due to its layered construction that resists warping. Solid bamboo, known for its natural strength and aesthetic appeal, is perfect for cutting boards, decorative elements, and structural applications where uniform grain is desired. Choosing between bamboo plywood and solid bamboo depends on the need for durability, flexibility, and specific project requirements.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Bamboo plywood offers easier installation due to its layered construction, which provides enhanced stability and resistance to warping compared to solid bamboo. Maintenance for bamboo plywood typically involves regular cleaning and occasional sealing to protect against moisture, whereas solid bamboo requires more frequent sealing and careful handling to prevent cracking and swelling. Both materials benefit from avoiding excessive water exposure and using non-abrasive cleaners to maintain their appearance and durability over time.
Choosing the Right Bamboo Material for Your Project
Solid bamboo offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for structural projects and heavy-use furniture, while bamboo plywood provides greater stability with its layered construction, reducing the risk of warping. For flooring and cabinetry, bamboo plywood's consistent thickness and resistance to moisture ensure long-lasting performance and easier installation. Selecting between solid bamboo and plywood depends on the specific demands of your project, balancing factors like load-bearing capacity, aesthetic preference, and environmental exposure.
Bamboo plywood vs Solid bamboo Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com