Acrylic pet sheets offer superior impact resistance and lighter weight compared to traditional glass, making them ideal for applications requiring safety and easy installation. Unlike glass, acrylic provides better clarity and UV resistance, ensuring long-lasting transparency without yellowing. Cost-effective and versatile, acrylic is a practical alternative for windows, displays, and protective barriers.
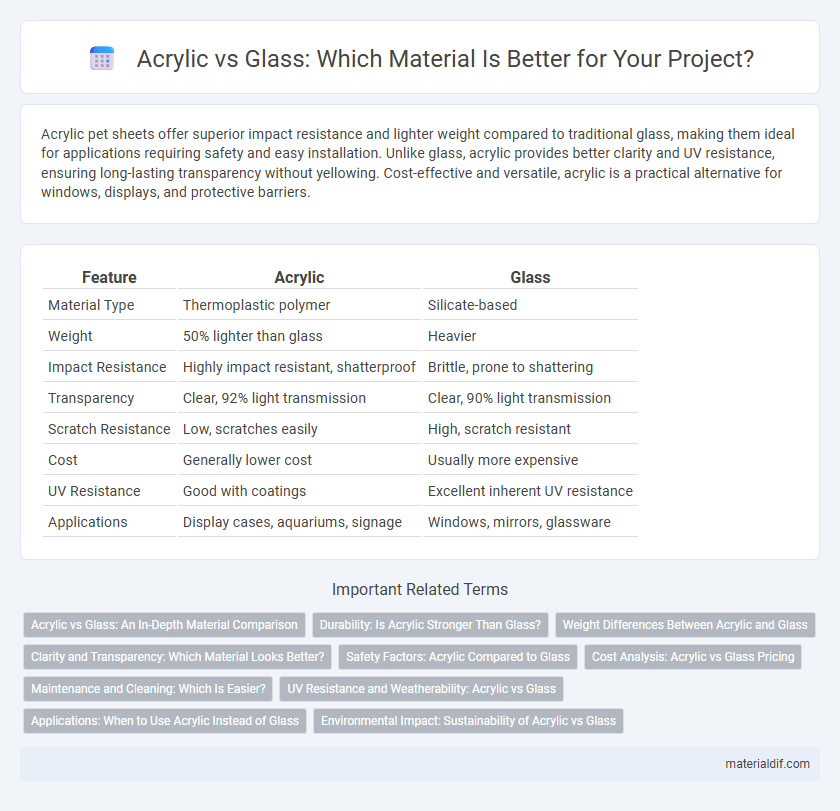
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acrylic | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Silicate-based |
| Weight | 50% lighter than glass | Heavier |
| Impact Resistance | Highly impact resistant, shatterproof | Brittle, prone to shattering |
| Transparency | Clear, 92% light transmission | Clear, 90% light transmission |
| Scratch Resistance | Low, scratches easily | High, scratch resistant |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually more expensive |
| UV Resistance | Good with coatings | Excellent inherent UV resistance |
| Applications | Display cases, aquariums, signage | Windows, mirrors, glassware |
Acrylic vs Glass: An In-Depth Material Comparison
Acrylic offers superior impact resistance compared to glass, making it nearly 17 times more shatter-resistant and ideal for safety applications. Its lightweight nature, being approximately half the weight of glass, contributes to easier handling and installation in architectural and display settings. Acrylic also provides greater optical clarity with less light distortion and is more versatile for shaping and coloring, whereas glass excels in scratch resistance and heat tolerance.
Durability: Is Acrylic Stronger Than Glass?
Acrylic is significantly more impact-resistant than glass, making it less likely to crack or shatter under pressure. With a tensile strength approximately 10 to 24 times greater than glass, acrylic is ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability. Its lightweight nature also contributes to a reduced risk of breakage, providing safer and longer-lasting alternatives to traditional glass panels.
Weight Differences Between Acrylic and Glass
Acrylic is significantly lighter than glass, weighing approximately half as much per square foot, which makes it ideal for applications requiring easy handling and reduced structural load. This weight difference, with acrylic typically around 1.18 g/cm3 compared to glass at about 2.5 g/cm3, contributes to decreased transportation costs and enhanced safety due to reduced breakage risk. The lighter weight of acrylic also enables greater design flexibility in large installations where glass's heaviness would pose challenges.
Clarity and Transparency: Which Material Looks Better?
Acrylic offers superior clarity and transparency compared to traditional glass, providing up to 92% light transmittance, while glass typically allows around 80-90%. Acrylic's crystal-clear appearance remains consistent over time due to its resistance to yellowing and fogging, which can degrade glass visibility. This enhanced optical quality makes acrylic the preferred choice for applications prioritizing visual clarity and brightness.
Safety Factors: Acrylic Compared to Glass
Acrylic offers significantly higher impact resistance, being approximately 17 times stronger than glass, which greatly reduces the risk of shattering and injury. Its lighter weight also makes acrylic safer to handle and install in various applications, from windows to protective barriers. Unlike glass, acrylic exhibits better resistance to breakage under stress, making it a preferred choice for environments prone to physical impact or requiring enhanced safety measures.
Cost Analysis: Acrylic vs Glass Pricing
Acrylic typically costs 50-70% less than glass, making it a budget-friendly option for windows, displays, and signage. While glass prices vary based on thickness and type, acrylic's lower manufacturing costs translate into significant savings for large projects. Its affordability paired with lightweight durability often offsets initial cost differences in long-term use and installation.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Which Is Easier?
Acrylic offers easier maintenance and cleaning compared to glass due to its lightweight and impact-resistant properties, reducing the risk of cracks and chips during handling. It requires only non-abrasive cleaners and soft cloths to prevent scratching, while glass often demands specialized glass cleaners to avoid streaks and buildup. Acrylic's resistance to shattering and simpler cleaning methods make it a practical choice for environments requiring low-maintenance surfaces.
UV Resistance and Weatherability: Acrylic vs Glass
Acrylic offers superior UV resistance compared to glass, preventing yellowing and degradation over time when exposed to sunlight. It demonstrates excellent weatherability, maintaining clarity and structural integrity in harsh outdoor conditions without the brittleness commonly experienced by glass. These properties make acrylic a preferred material for outdoor signage, skylights, and protective barriers where long-term exposure to UV rays and weather elements is critical.
Applications: When to Use Acrylic Instead of Glass
Acrylic is ideal for applications requiring lightweight and impact-resistant materials, such as protective barriers, signage, and display cases where glass's fragility is a limitation. Its excellent optical clarity and UV resistance make acrylic a preferred choice in outdoor lighting and aquarium windows, outperforming glass in durability. Acrylic's ease of fabrication and ability to be thermoformed suit custom architectural elements and vehicle windows better than traditional glass.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Acrylic vs Glass
Acrylic offers a lower carbon footprint during production compared to glass, as it requires less energy to manufacture and transport due to its lighter weight. However, acrylic is derived from petroleum-based materials and is not biodegradable, posing long-term environmental concerns unless properly recycled. Glass is more sustainable in terms of recyclability and longevity, as it can be reused indefinitely without quality loss, but its heavier weight increases transportation emissions.
Acrylic vs Glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com