Acrylic lamination provides lightweight and impact-resistant protection, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and clarity without the heavy weight of glass. Laminated glass offers superior strength and safety through its multiple glass layers bonded with interlayers, enhancing shatter resistance and security. Choosing between acrylic lamination and laminated glass depends on the balance of weight, clarity, impact resistance, and safety requirements for your specific project.
Table of Comparison
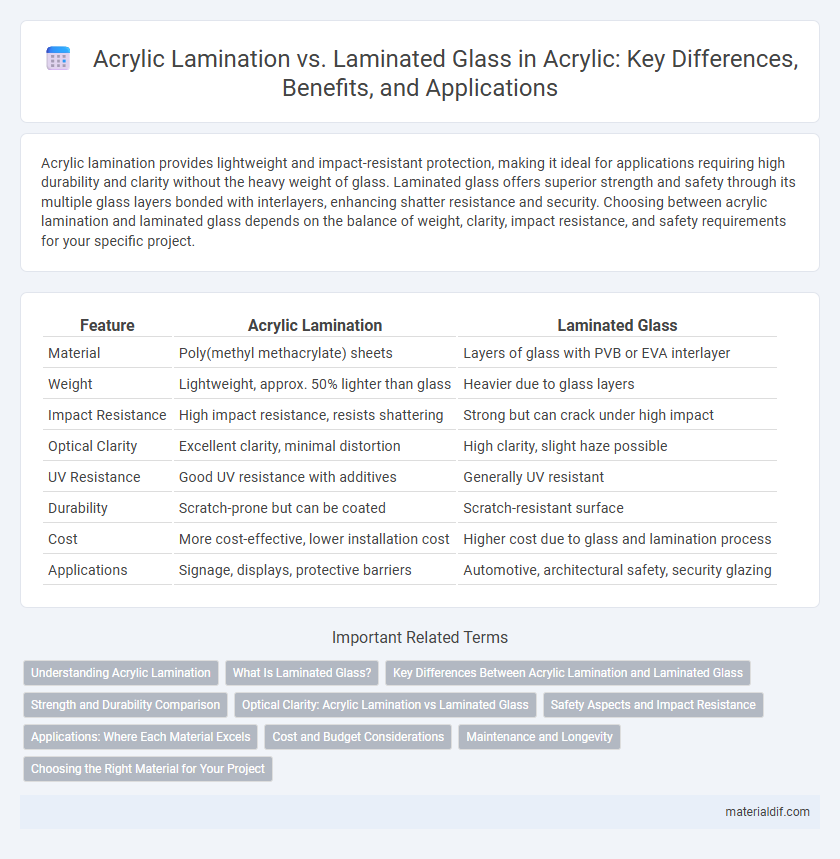
| Feature | Acrylic Lamination | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Poly(methyl methacrylate) sheets | Layers of glass with PVB or EVA interlayer |
| Weight | Lightweight, approx. 50% lighter than glass | Heavier due to glass layers |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance, resists shattering | Strong but can crack under high impact |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent clarity, minimal distortion | High clarity, slight haze possible |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance with additives | Generally UV resistant |
| Durability | Scratch-prone but can be coated | Scratch-resistant surface |
| Cost | More cost-effective, lower installation cost | Higher cost due to glass and lamination process |
| Applications | Signage, displays, protective barriers | Automotive, architectural safety, security glazing |
Understanding Acrylic Lamination
Acrylic lamination involves bonding multiple layers of acrylic sheets under heat and pressure, creating a lightweight, shatter-resistant material ideal for signage, displays, and protective barriers. Unlike laminated glass, which uses a plastic interlayer between glass sheets for safety and strength, acrylic lamination offers enhanced impact resistance and greater flexibility while maintaining clarity. Understanding acrylic lamination helps in selecting materials that provide durability, UV resistance, and ease of fabrication for various indoor and outdoor applications.
What Is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), providing enhanced safety and durability. Unlike acrylic lamination, laminated glass remains intact when shattered, preventing sharp shards and offering superior impact resistance and sound insulation. This construction makes laminated glass ideal for automotive windshields, architectural applications, and security glazing.
Key Differences Between Acrylic Lamination and Laminated Glass
Acrylic lamination involves bonding acrylic sheets to enhance impact resistance and clarity, offering superior shatter resistance and lighter weight compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing higher structural strength, UV protection, and improved sound insulation. The key differences lie in material composition, durability under impact, weight, optical clarity, and their respective applications in safety glazing and decorative uses.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Acrylic lamination offers superior impact resistance and shatterproof qualities compared to laminated glass, making it highly durable for applications requiring breakage prevention. Laminated glass, while structurally robust due to its interlayer bonding, remains more prone to cracking under extreme stress but provides better scratch resistance than acrylic. Both materials excel in strength, yet acrylic lamination often outperforms laminated glass in flexibility and weight-bearing capacity, enhancing long-term durability in dynamic environments.
Optical Clarity: Acrylic Lamination vs Laminated Glass
Acrylic lamination offers superior optical clarity compared to laminated glass due to its higher light transmission rate, typically around 92%, whereas laminated glass averages 85-90%. The polymeric nature of acrylic reduces haze and distortion, providing a clearer, more transparent finish. This enhanced clarity makes acrylic lamination ideal for applications requiring unobstructed visibility and superior aesthetic qualities.
Safety Aspects and Impact Resistance
Acrylic lamination offers superior impact resistance compared to laminated glass, significantly reducing the risk of shattering upon impact. Its flexible nature absorbs and disperses force more effectively, enhancing safety in environments prone to accidental collisions or vandalism. Laminated glass, while providing a safety interlayer to hold shards together, is more prone to cracking and less resilient under extreme impact, making acrylic lamination a preferred option for robust safety applications.
Applications: Where Each Material Excels
Acrylic lamination excels in applications requiring lightweight, impact-resistant, and shatterproof materials, commonly used in signage, displays, and protective barriers. Laminated glass is preferred in automotive windshields, architectural facades, and safety glazing due to its superior strength, UV resistance, and sound insulation properties. Both materials are chosen based on specific performance needs, balancing durability, clarity, and safety requirements across diverse industries.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Acrylic lamination offers a cost-effective alternative to laminated glass, with materials and installation expenses typically 30-50% lower, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects. Acrylic sheets weigh about half as much as glass, reducing transportation and handling costs, which further contributes to overall savings. However, laminated glass provides superior durability and impact resistance, potentially lowering long-term maintenance costs despite its higher upfront price.
Maintenance and Longevity
Acrylic lamination offers superior impact resistance and is less prone to shattering compared to laminated glass, resulting in lower maintenance costs over time. However, laminated glass provides better scratch resistance and UV protection, enhancing its longevity in outdoor applications. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for durability against ease of upkeep in specific environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Acrylic lamination offers superior impact resistance and lighter weight compared to laminated glass, making it ideal for projects requiring durability and ease of installation. Laminated glass provides enhanced security and UV protection by bonding multiple glass layers with an interlayer, suitable for architectural applications demanding safety and sound insulation. Evaluating factors such as budget, project environment, and specific performance requirements ensures the selection of the most appropriate material for optimal results.
Acrylic Lamination vs Laminated Glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com