Alpaca wool is softer, warmer, and more hypoallergenic compared to sheep wool, making it ideal for sensitive skin and cold climates. It offers better moisture wicking and durability due to its hollow fiber structure, while sheep wool provides superior elasticity and water resistance. Choosing between alpaca and sheep wool depends on the desired balance of softness, warmth, and resilience for specific textile applications.
Table of Comparison
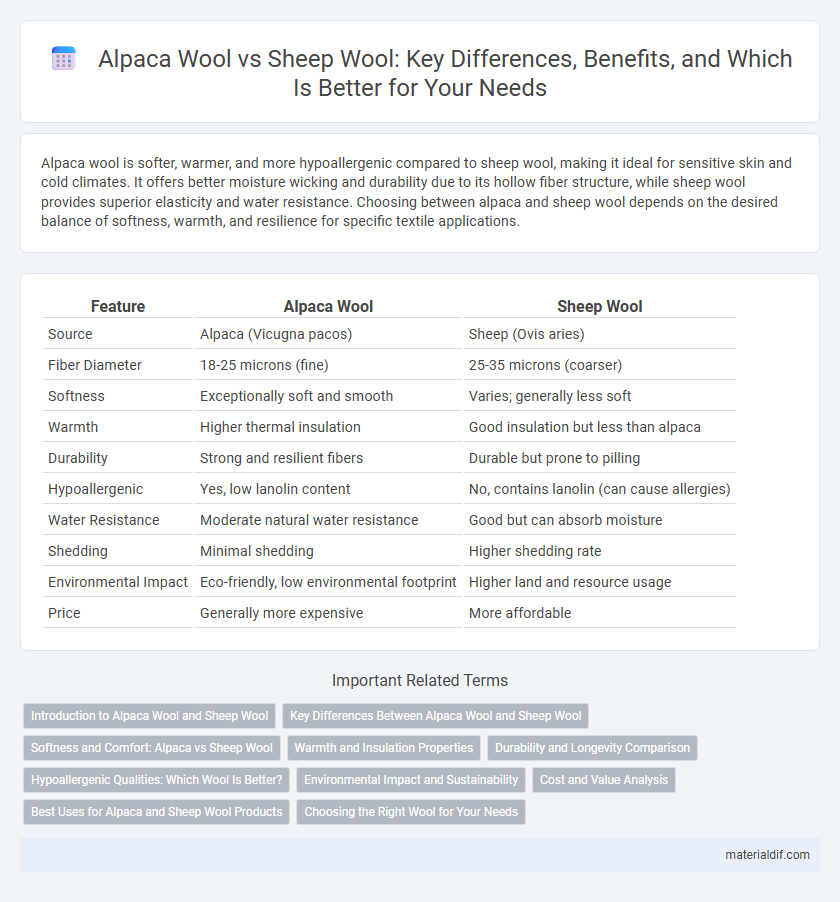
| Feature | Alpaca Wool | Sheep Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Alpaca (Vicugna pacos) | Sheep (Ovis aries) |
| Fiber Diameter | 18-25 microns (fine) | 25-35 microns (coarser) |
| Softness | Exceptionally soft and smooth | Varies; generally less soft |
| Warmth | Higher thermal insulation | Good insulation but less than alpaca |
| Durability | Strong and resilient fibers | Durable but prone to pilling |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, low lanolin content | No, contains lanolin (can cause allergies) |
| Water Resistance | Moderate natural water resistance | Good but can absorb moisture |
| Shedding | Minimal shedding | Higher shedding rate |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, low environmental footprint | Higher land and resource usage |
| Price | Generally more expensive | More affordable |
Introduction to Alpaca Wool and Sheep Wool
Alpaca wool, derived from the alpacas native to the Andes, is renowned for its exceptional softness, warmth, and hypoallergenic properties, making it a premium fiber in luxury textiles. Sheep wool, harvested from various breeds like Merino and Rambouillet, is widely utilized for its durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking capabilities across diverse clothing and insulation products. Both fibers offer unique benefits; alpaca wool excels in lightweight insulation and softness, while sheep wool provides robust resilience and versatility in textile manufacturing.
Key Differences Between Alpaca Wool and Sheep Wool
Alpaca wool is known for its superior softness, lightweight warmth, and hypoallergenic properties due to the lack of lanolin, unlike sheep wool which contains lanolin that can cause skin irritation. In terms of fiber structure, alpaca wool fibers have a smoother surface and higher tensile strength, resulting in more durable and less itchy garments compared to the coarser, more elastic sheep wool. Thermally, alpaca wool provides better insulation and moisture-wicking capabilities, making it ideal for both cold and damp environments.
Softness and Comfort: Alpaca vs Sheep Wool
Alpaca wool offers superior softness and comfort compared to sheep wool due to its finer fibers, which are naturally hypoallergenic and less likely to cause skin irritation. The smooth texture of alpaca fibers provides a luxuriously soft feel against the skin, making it ideal for sensitive complexions. In contrast, sheep wool typically has coarser fibers that may feel itchier and less comfortable for prolonged wear.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Alpaca wool offers superior warmth and insulation compared to sheep wool due to its hollow fiber structure, which traps more air and retains heat efficiently. The natural lanolin in sheep wool provides some water resistance but can also reduce breathability, whereas alpaca wool is hypoallergenic and moisture-wicking, enhancing comfort in cold environments. These properties make alpaca wool an excellent choice for thermal insulation in outdoor and winter clothing.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Alpaca wool is known for its exceptional durability and longevity, often lasting much longer than traditional sheep wool due to its fine, strong fibers that resist pilling and wear. Sheep wool, especially merino, provides good durability but tends to be more prone to abrasion and matting over time compared to alpaca. This makes alpaca wool a preferred choice for garments and textiles requiring extended lifespan and sustained quality.
Hypoallergenic Qualities: Which Wool Is Better?
Alpaca wool is naturally hypoallergenic because it lacks lanolin, a common irritant found in sheep wool, making it ideal for sensitive skin. Sheep wool contains lanolin that can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals despite its excellent insulation properties. For those seeking allergy-friendly fabrics, alpaca wool offers a softer, less allergenic alternative to traditional sheep wool.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alpaca wool demonstrates a significantly lower environmental impact compared to sheep wool due to alpacas' gentle grazing habits, which reduce soil degradation and promote biodiversity. With higher water and land efficiency, alpaca farming generates less methane emissions, contributing to lower greenhouse gas outputs than traditional sheep farming. Sustainable alpaca wool production supports eco-friendly textile industries, offering a renewable resource with minimal strain on natural ecosystems.
Cost and Value Analysis
Alpaca wool generally commands a higher price than sheep wool due to its rarity, softness, and hypoallergenic properties, positioning it as a premium fiber in the textile market. While sheep wool offers affordability and wider availability, alpaca wool's durability and thermal insulation qualities provide greater long-term value despite the initial cost. Buyers prioritizing luxury fiber and extended garment life often opt for alpaca wool, recognizing its investment potential compared to conventional sheep wool.
Best Uses for Alpaca and Sheep Wool Products
Alpaca wool is prized for its softness, warmth, and hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for luxury garments, scarves, and bedding that require gentle, insulating fibers. Sheep wool, particularly from breeds like Merino, excels in elasticity, durability, and moisture-wicking, making it best suited for activewear, outdoor clothing, and heavy-duty textiles. Both fibers serve distinct niches: alpaca wool for premium comfort and insulation, sheep wool for resilience and performance in varied climates.
Choosing the Right Wool for Your Needs
Alpaca wool offers superior softness, hypoallergenic properties, and exceptional insulation compared to traditional sheep wool, making it ideal for sensitive skin and cold climates. Sheep wool provides durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking capabilities, suitable for active wear and outdoor garments. Selecting between alpaca and sheep wool ultimately depends on your priorities for comfort, warmth, and fabric resilience.
Alpaca Wool vs Sheep Wool Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com