Paraffin wax is a petroleum-based product known for its affordability and versatility in candle making and cosmetics, offering a smooth texture and easy availability. Beeswax, a natural substance produced by honeybees, is prized for its natural aroma, longer burning time, and eco-friendly properties, making it a popular choice for organic and high-quality products. Choosing between paraffin wax and beeswax depends on factors like environmental impact, scent preferences, and intended use, with beeswax favored for sustainability and paraffin for cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
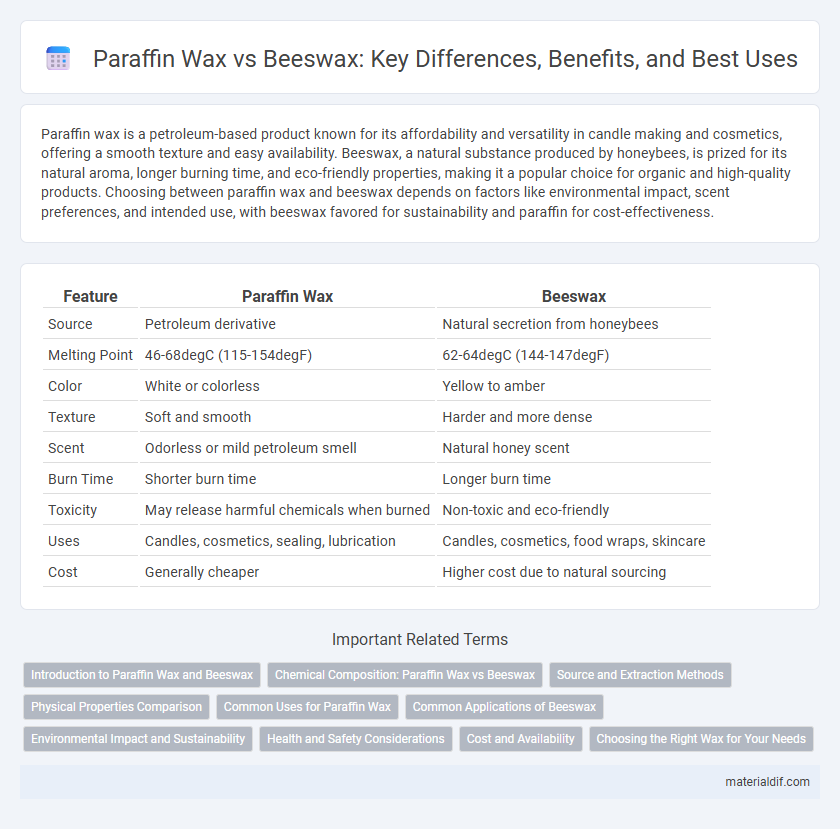
| Feature | Paraffin Wax | Beeswax |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Petroleum derivative | Natural secretion from honeybees |
| Melting Point | 46-68degC (115-154degF) | 62-64degC (144-147degF) |
| Color | White or colorless | Yellow to amber |
| Texture | Soft and smooth | Harder and more dense |
| Scent | Odorless or mild petroleum smell | Natural honey scent |
| Burn Time | Shorter burn time | Longer burn time |
| Toxicity | May release harmful chemicals when burned | Non-toxic and eco-friendly |
| Uses | Candles, cosmetics, sealing, lubrication | Candles, cosmetics, food wraps, skincare |
| Cost | Generally cheaper | Higher cost due to natural sourcing |
Introduction to Paraffin Wax and Beeswax
Paraffin wax is a petroleum-derived product commonly used in candles, cosmetics, and sealing applications due to its low cost and versatility. Beeswax, a natural substance produced by honeybees, is prized for its pleasant aroma, non-toxicity, and superior burning qualities in candle making. Both waxes serve distinct purposes, with paraffin favored for affordability and beeswax valued for eco-friendly and health-conscious uses.
Chemical Composition: Paraffin Wax vs Beeswax
Paraffin wax is a petroleum-derived hydrocarbon composed primarily of saturated alkanes with carbon chain lengths ranging from C20 to C40, making it chemically inert and stable. Beeswax consists mainly of esters of fatty acids and long-chain alcohols, including components such as myricyl palmitate, providing it with unique chemical properties like biodegradability and natural antimicrobial effects. The differing chemical compositions of paraffin wax and beeswax influence their melting points, flexibility, and applications across industries such as cosmetics, candle-making, and food packaging.
Source and Extraction Methods
Paraffin wax is derived from petroleum through a refining process that involves distillation and de-oiling of crude oil, making it a synthetic byproduct of fossil fuels. Beeswax is a natural secretion produced by honeybees, extracted by melting honeycomb structures harvested from beehives. The extraction of paraffin wax uses industrial chemical methods, whereas beeswax extraction relies on organic, manual processing techniques.
Physical Properties Comparison
Paraffin wax is a petroleum-derived substance characterized by a smooth, translucent texture and a melting point typically between 46 to 68degC, making it ideal for consistent moldability and cost-effective production. Beeswax, a natural secretion from honeybees, has a higher melting point ranging from 62 to 64degC, with a distinct golden color and a denser, more pliable texture that enhances durability in applications like candle making and cosmetics. Both waxes exhibit unique thermal conductivity and hardness properties, influencing their suitability across industrial and artistic uses.
Common Uses for Paraffin Wax
Paraffin wax is widely used in candle making, providing a smooth finish and excellent scent retention, making it a popular choice for decorative and aromatic candles. It is also commonly utilized in cosmetics and skincare products for its moisture-sealing properties and in industrial applications such as coating for food packaging and lubrication. The affordability and versatility of paraffin wax contribute to its extensive use across various consumer and commercial markets.
Common Applications of Beeswax
Beeswax is commonly used in cosmetics, candles, and skincare products due to its natural moisturizing properties and pleasant aroma. It also serves as a coating for food items, providing a protective barrier that preserves freshness without synthetic additives. Compared to paraffin wax, beeswax is favored for its biodegradability and antifungal qualities in various pharmaceutical and household applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Paraffin wax is derived from petroleum, making it non-renewable and contributing to environmental pollution through its extraction and production processes. Beeswax is a natural, renewable resource produced by honeybees, supporting biodiversity and sustainable beekeeping practices. The biodegradable nature of beeswax significantly reduces its environmental footprint compared to paraffin wax, which can release harmful toxins when burned.
Health and Safety Considerations
Paraffin wax, derived from petroleum, may release potentially harmful chemicals like toluene and benzene when burned, raising health concerns during prolonged use. Beeswax is natural, hypoallergenic, and emits negative ions that can purify indoor air, making it a safer option for individuals with allergies or respiratory issues. Both waxes should be handled with proper ventilation and kept away from open flames to prevent fire hazards.
Cost and Availability
Paraffin wax is significantly more affordable and widely available due to its petroleum-based production, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. Beeswax, derived from honeybee hives, is more expensive and less readily available, which limits its use primarily to specialty products and artisanal crafts. The price difference and accessibility heavily influence the selection between paraffin wax and beeswax in commercial and consumer markets.
Choosing the Right Wax for Your Needs
Paraffin wax, derived from petroleum, offers affordability and versatility, making it ideal for candles, cosmetics, and sealing applications. Beeswax, a natural product from honeybees, provides a longer burn time, natural aroma, and eco-friendly properties preferred in skincare and artisanal crafts. Selecting the right wax depends on factors like budget, desired scent, environmental impact, and intended use, ensuring optimal performance and satisfaction.
Paraffin wax vs Beeswax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com