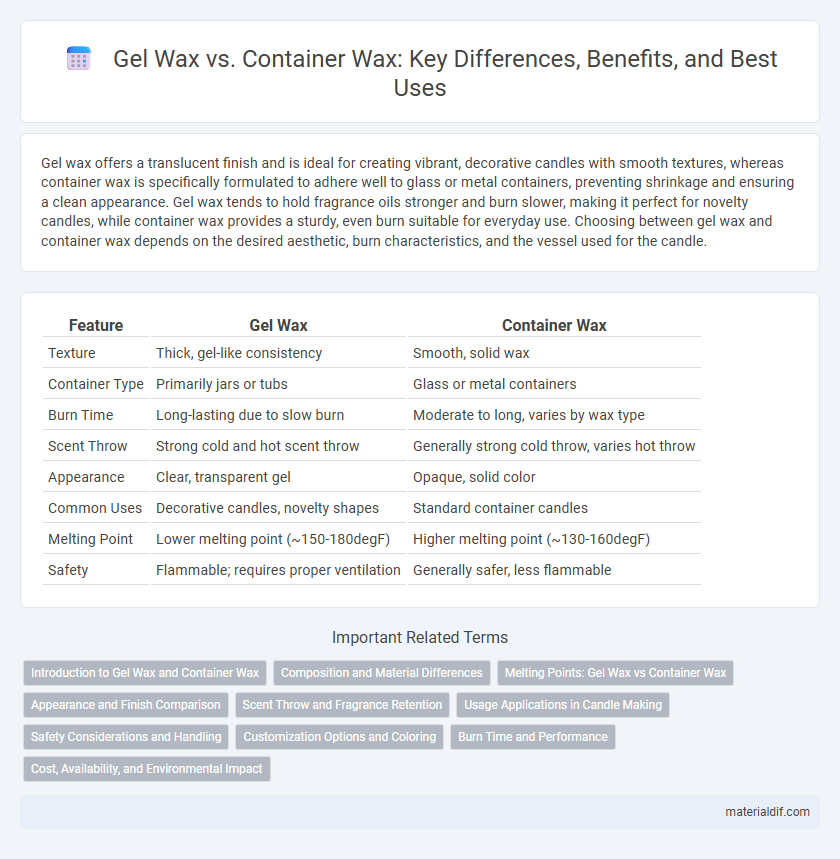
Gel wax offers a translucent finish and is ideal for creating vibrant, decorative candles with smooth textures, whereas container wax is specifically formulated to adhere well to glass or metal containers, preventing shrinkage and ensuring a clean appearance. Gel wax tends to hold fragrance oils stronger and burn slower, making it perfect for novelty candles, while container wax provides a sturdy, even burn suitable for everyday use. Choosing between gel wax and container wax depends on the desired aesthetic, burn characteristics, and the vessel used for the candle.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gel Wax | Container Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Thick, gel-like consistency | Smooth, solid wax |
| Container Type | Primarily jars or tubs | Glass or metal containers |
| Burn Time | Long-lasting due to slow burn | Moderate to long, varies by wax type |
| Scent Throw | Strong cold and hot scent throw | Generally strong cold throw, varies hot throw |
| Appearance | Clear, transparent gel | Opaque, solid color |
| Common Uses | Decorative candles, novelty shapes | Standard container candles |
| Melting Point | Lower melting point (~150-180degF) | Higher melting point (~130-160degF) |
| Safety | Flammable; requires proper ventilation | Generally safer, less flammable |
Introduction to Gel Wax and Container Wax
Gel wax is a translucent, jelly-like wax made from mineral oil and polymer resin, offering a unique aesthetic ideal for decorative candles and embeds. Container wax, typically a blend of paraffin, soy, or palm waxes, is formulated to adhere well to candle vessels, providing a smooth finish and excellent scent throw. Both wax types serve distinct purposes in candle making, with gel wax prized for its clarity and container wax valued for its stability and burn performance.
Composition and Material Differences
Gel wax is a blend of mineral oils, polymer resins, and petroleum-based gel, resulting in a translucent, jelly-like texture ideal for embedding decorative items in candles. Container wax typically consists of paraffin, soy, or beeswax blends formulated to have a solid but soft consistency that adheres well to glass or metal containers without shrinking. The key difference lies in gel wax's synthetic polymer base, which allows for greater flexibility and visual appeal, while container wax prioritizes melting point and adhesive properties suited for mold stability.
Melting Points: Gel Wax vs Container Wax
Gel wax typically has a lower melting point ranging from 180degF to 210degF, allowing for slower and more controlled melting compared to container wax, which usually melts between 120degF and 160degF. This difference in melting points affects burning time and scent throw, with gel wax often producing a longer-lasting burn and stronger fragrance release. Container wax is designed for solid, opaque candles, whereas gel wax maintains a translucent appearance even as it melts.
Appearance and Finish Comparison
Gel wax offers a translucent, glossy finish that enhances the visual appeal of candles with embedded decorations, creating vibrant and clear aesthetics. Container wax typically provides a smoother, more opaque surface that emphasizes a classic, polished look suitable for a wide range of candle styles. The choice between gel wax and container wax significantly influences the appearance by balancing clarity versus opacity and glossy shine versus smoothness.
Scent Throw and Fragrance Retention
Gel wax offers an impressive scent throw due to its transparent, gel-like composition that allows fragrances to disperse quickly and evenly when warmed. Container wax, typically made from soy or paraffin blends, provides superior fragrance retention, releasing scents gradually for a longer-lasting aroma. Choosing between gel and container wax depends on whether immediate scent impact or extended fragrance endurance is preferred.
Usage Applications in Candle Making
Gel wax is ideal for creating transparent candles that showcase embedded objects, making it popular for decorative and artistic candle designs. Container wax is formulated to adhere to glass or metal containers, providing a smooth surface and excellent scent throw, often used for traditional jar candles. Both wax types serve specific purposes, with gel wax enhancing visual appeal and container wax ensuring safety and durability in candle making.
Safety Considerations and Handling
Gel wax, composed of mineral oil and polymer resin, is non-toxic and burns cleaner but requires careful temperature control during melting to prevent overheating and potential fire hazards. Container wax, typically a blend of paraffin or soy wax, is safer to handle due to lower melting points and reduced risk of combustibility, making it suitable for beginners. Proper ventilation and use of heat-resistant containers are essential for both wax types to ensure safe candle-making practices.
Customization Options and Coloring
Gel wax offers extensive customization options with its translucent base, allowing vibrant and diverse coloring effects that enhance aesthetic appeal. Container wax, typically opaque, limits color blending but provides a uniform appearance ideal for classic candle designs. Both waxes support fragrance integration, yet gel wax's clarity accentuates scented oils with visually striking color combinations.
Burn Time and Performance
Gel wax typically offers longer burn times due to its dense composition, allowing candles to last significantly longer than those made with container wax. Container wax, often a blend of paraffin or soy, melts evenly and provides consistent fragrance throw but generally burns faster. Performance-wise, gel wax delivers a clearer, more vibrant appearance with a steady flame, while container wax excels in heat distribution and scent release efficiency.
Cost, Availability, and Environmental Impact
Gel wax typically costs more than container wax due to its unique polymer blend, which enhances scent throw and appearance. Container waxes are widely available and often derived from soy or paraffin, offering budget-friendly options for candle making. Environmentally, soy-based container waxes are biodegradable and renewable, while gel wax, being petroleum-based, poses greater ecological concerns due to slower decomposition and potential toxins.
Gel Wax vs Container Wax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com