Emulsifying wax is a versatile, synthetic ingredient that effectively blends oil and water to create smooth, stable lotions and creams, enhancing texture and consistency. Stearic acid, a natural fatty acid derived from animal or plant fats, primarily functions as a thickener and stabilizer, adding firmness to cosmetic formulations. While emulsifying wax focuses on creating emulsions, stearic acid improves texture and durability, making both essential but distinct components in skincare product formulations.
Table of Comparison
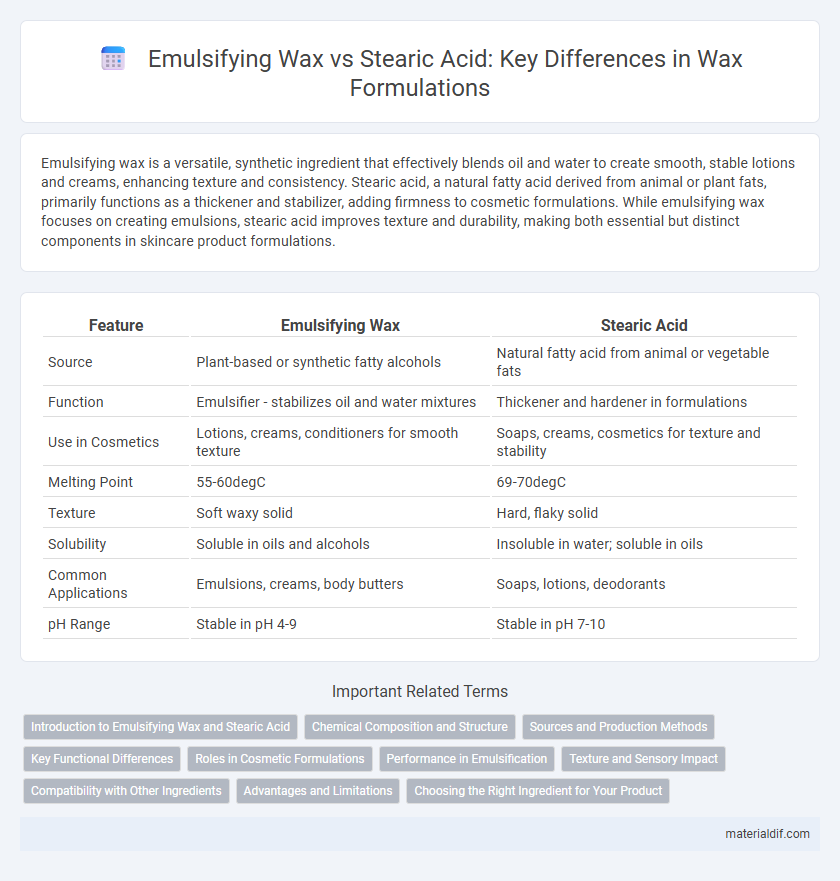
| Feature | Emulsifying Wax | Stearic Acid |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based or synthetic fatty alcohols | Natural fatty acid from animal or vegetable fats |
| Function | Emulsifier - stabilizes oil and water mixtures | Thickener and hardener in formulations |
| Use in Cosmetics | Lotions, creams, conditioners for smooth texture | Soaps, creams, cosmetics for texture and stability |
| Melting Point | 55-60degC | 69-70degC |
| Texture | Soft waxy solid | Hard, flaky solid |
| Solubility | Soluble in oils and alcohols | Insoluble in water; soluble in oils |
| Common Applications | Emulsions, creams, body butters | Soaps, lotions, deodorants |
| pH Range | Stable in pH 4-9 | Stable in pH 7-10 |
Introduction to Emulsifying Wax and Stearic Acid
Emulsifying wax and stearic acid are essential components in cosmetic formulations, serving distinct functions in product stability and texture. Emulsifying wax acts as a surfactant, enabling oil and water phases to blend seamlessly, while stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid, provides thickening and emollient properties. Understanding their chemical composition and roles helps formulators select the appropriate ingredient for creams, lotions, and other emulsions.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Emulsifying wax primarily consists of ethoxylated cetyl or stearyl alcohols, characterized by a blend of hydrophilic polyethylene glycol chains and hydrophobic fatty alcohols, enabling effective oil-water emulsification. Stearic acid, a saturated long-chain fatty acid (C18H36O2), features a carboxyl functional group that imparts amphiphilic properties, but its simpler molecular structure limits emulsifying capabilities compared to emulsifying wax. The ethoxylation in emulsifying wax enhances water solubility and surfactant action, whereas stearic acid relies on its fatty acid structure for thickening and stabilizing formulations.
Sources and Production Methods
Emulsifying wax is primarily derived from vegetable oils through ethoxylation, combining fatty acids and polyethylene glycol to create a stable, water-compatible ingredient essential for blending oil and water phases in cosmetic formulations. Stearic acid, naturally sourced from animal fats or vegetable oils like palm and coconut, undergoes hydrolysis and refining to yield a fatty acid used as a thickener and emulsifier in skincare products. Both ingredients differ significantly in production methods, with emulsifying wax involving chemical modification for enhanced emulsifying properties, while stearic acid remains a purified fatty acid extracted via saponification and distillation.
Key Functional Differences
Emulsifying wax creates stable oil-in-water emulsions by combining fatty alcohols and emulsifiers, making it ideal for lotions and creams, whereas stearic acid functions primarily as a thickening agent and emollient derived from fatty acids. Emulsifying wax enhances product stability and texture, while stearic acid contributes to viscosity and acts as a binding agent. Key functional differences include emulsification capacity for wax versus thickening and consistency adjustment for stearic acid in cosmetic formulations.
Roles in Cosmetic Formulations
Emulsifying wax acts as a surfactant, stabilizing oil and water mixtures in cosmetic formulations to create smooth creams and lotions. Stearic acid functions primarily as a thickening agent and emollient, enhancing texture and providing a protective barrier on the skin. Both ingredients contribute to product consistency and skin feel but serve distinct roles in formulation stability and sensory properties.
Performance in Emulsification
Emulsifying wax provides superior emulsification by effectively blending oil and water phases, creating stable, smooth, and homogenous emulsions ideal for cosmetic products. Stearic acid, while useful as a thickener and emollient, offers limited emulsifying properties and often requires combined use with other emulsifiers to achieve desired stability. The performance difference lies in emulsifying wax's ability to consistently maintain emulsion integrity under diverse conditions, enhancing texture and product lifespan.
Texture and Sensory Impact
Emulsifying wax delivers a smooth, creamy texture that enhances skin absorption and leaves a non-greasy finish, making it ideal for lotions and creams. Stearic acid contributes a firmer, more stable consistency with a slightly waxy feel, which improves product durability but can create a heavier sensory impression. Choosing between these ingredients depends on the desired texture and tactile experience in cosmetic and skincare formulations.
Compatibility with Other Ingredients
Emulsifying wax offers superior compatibility with a wide range of oils, butters, and active ingredients, creating stable and smooth formulations in skincare products. Stearic acid, while effective as a thickener and stabilizer, can sometimes cause separation when combined with certain oils or sensitive actives due to its fatty acid structure. Selecting emulsifying wax in emulsions enhances ingredient integration and stability, crucial for high-performance creams and lotions.
Advantages and Limitations
Emulsifying wax offers superior stability and ease of use in cosmetic formulations, providing smooth texture and enhanced mixing of oil and water phases compared to stearic acid. Stearic acid, a fatty acid, contributes to thickening and emollient properties but may cause brittleness in formulations and requires precise temperature control during processing. Emulsifying wax excels in creating consistent emulsions with better shelf life, while stearic acid remains valued for its natural origin and skin-conditioning benefits despite potential formulation challenges.
Choosing the Right Ingredient for Your Product
Emulsifying wax offers superior water and oil blending properties, making it ideal for stable lotions and creams, while stearic acid functions primarily as a thickener and opacifier. Selecting the right ingredient depends on the desired texture and stability of the product, with emulsifying wax providing better emulsion stability and stearic acid contributing to firmness and viscosity. For formulations requiring smooth, consistent emulsions, emulsifying wax is preferable, whereas stearic acid suits products needing enhanced thickness and opacity.
Emulsifying Wax vs Stearic Acid Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com