Gum Rosin Wax, derived from natural pine tree resin, offers superior tackiness and biodegradability compared to Petroleum Wax, which is synthesized from non-renewable fossil fuels. This natural wax enhances the grip and adhesion in pet care products, promoting safer and eco-friendlier applications. Petroleum Wax, while cost-effective and consistent in quality, lacks the environmental benefits and natural chemical properties of Gum Rosin Wax.
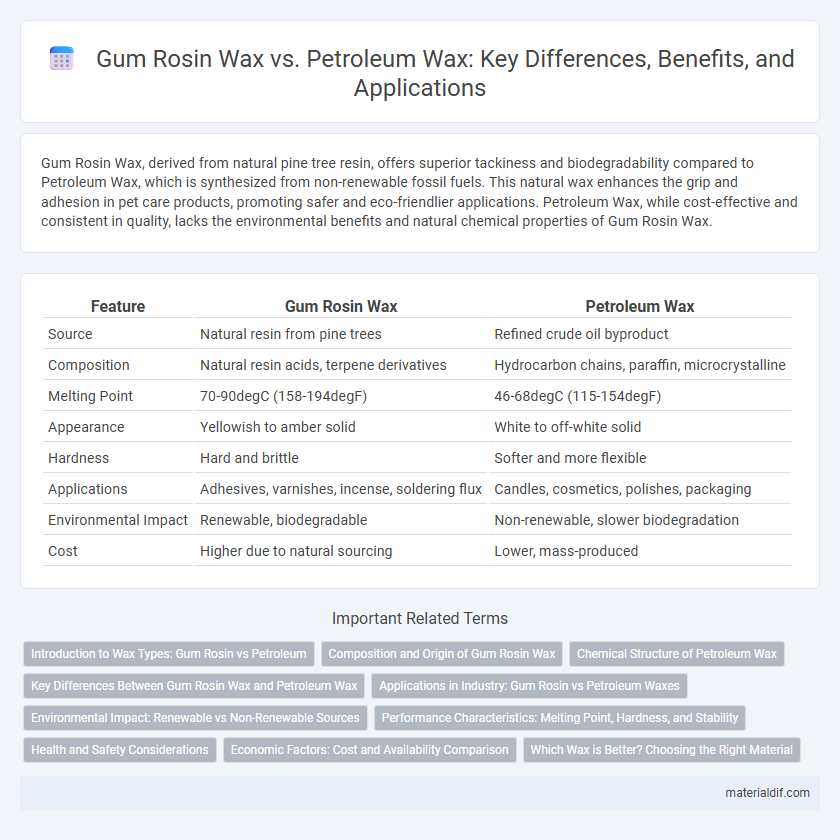
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gum Rosin Wax | Petroleum Wax |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural resin from pine trees | Refined crude oil byproduct |
| Composition | Natural resin acids, terpene derivatives | Hydrocarbon chains, paraffin, microcrystalline |
| Melting Point | 70-90degC (158-194degF) | 46-68degC (115-154degF) |
| Appearance | Yellowish to amber solid | White to off-white solid |
| Hardness | Hard and brittle | Softer and more flexible |
| Applications | Adhesives, varnishes, incense, soldering flux | Candles, cosmetics, polishes, packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable | Non-renewable, slower biodegradation |
| Cost | Higher due to natural sourcing | Lower, mass-produced |
Introduction to Wax Types: Gum Rosin vs Petroleum
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine resin, offers superior tackiness and water resistance compared to petroleum-based waxes, which are synthesized from crude oil and feature a more consistent texture and melting point. Petroleum waxes like paraffin and microcrystalline are widely used across industries due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility, while gum rosin wax finds specialized applications in adhesives, inks, and varnishes for enhanced performance. Understanding the chemical origins and physical properties of these wax types is essential for selecting the appropriate material in manufacturing and product formulation.
Composition and Origin of Gum Rosin Wax
Gum rosin wax is a natural product derived from the distillation of gum rosin, which is sourced from the oleoresin of pine trees primarily found in temperate regions. Its composition includes a complex mixture of resin acids, primarily abietic acid, and small amounts of neutral components such as hydrocarbons and fatty acids. In contrast, petroleum wax, also known as paraffin wax, is a hydrocarbon-based product obtained from the refining of crude oil and consists mainly of straight-chain alkanes.
Chemical Structure of Petroleum Wax
Petroleum wax, primarily consisting of long-chain saturated hydrocarbons such as paraffins and microcrystalline components, differs significantly from gum rosin wax in its chemical structure. Unlike gum rosin wax, which is composed mainly of complex resin acids and esters, petroleum wax exhibits a stable, non-polar hydrocarbon matrix contributing to its distinct melting behavior and chemical inertness. This structural composition enhances petroleum wax's utility in applications requiring resistance to oxidation and moisture, setting it apart from naturally derived waxes.
Key Differences Between Gum Rosin Wax and Petroleum Wax
Gum rosin wax, derived from pine tree resin, features a natural composition with high tackiness and thermal stability, making it ideal for adhesives and varnishes. Petroleum wax originates from refining crude oil, exhibiting lower melting points and hydrophobic properties suited for candles and packaging. Key differences include source material, melting temperature, and application suitability, with gum rosin wax providing better grip and weather resistance compared to the more flexible and moisture-resistant petroleum wax.
Applications in Industry: Gum Rosin vs Petroleum Waxes
Gum Rosin wax is widely used in the adhesives, inks, and varnishes industries due to its excellent tackifying properties and natural origin, making it ideal for eco-friendly products. Petroleum wax, including paraffin and microcrystalline waxes, dominates the packaging, candle, and cosmetics sectors, offering superior moisture resistance, pliability, and melting point consistency. Industrial applications favor Gum Rosin wax for biodegradable solutions, while Petroleum wax is preferred for large-scale manufacturing requiring cost-efficiency and uniform performance.
Environmental Impact: Renewable vs Non-Renewable Sources
Gum rosin wax is derived from renewable natural sources such as pine tree sap, making it biodegradable and more environmentally sustainable. Petroleum wax, sourced from non-renewable fossil fuels, contributes to resource depletion and poses higher risks of environmental pollution. The renewable nature of gum rosin wax significantly reduces carbon footprint compared to the ecological concerns linked with petroleum-based waxes.
Performance Characteristics: Melting Point, Hardness, and Stability
Gum Rosin Wax offers a higher melting point ranging from 120degC to 160degC, providing superior thermal stability compared to Petroleum Wax, which typically melts between 45degC and 65degC. The hardness of Gum Rosin Wax is greater, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to deformation. Its chemical stability under various environmental conditions surpasses Petroleum Wax, which tends to oxidize and degrade more rapidly, affecting product longevity.
Health and Safety Considerations
Gum rosin wax, derived from natural pine resin, offers lower toxicity and reduced chemical exposure compared to petroleum wax, which is a byproduct of crude oil refining and may contain harmful hydrocarbons. Health risks linked to petroleum wax include skin irritation and respiratory issues due to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and possible carcinogens present in some formulations. Using gum rosin wax reduces environmental impact and promotes safer handling practices with fewer allergens and less potential for adverse health effects in candle making and cosmetic applications.
Economic Factors: Cost and Availability Comparison
Gum Rosin Wax, derived from natural pine resin, often carries higher production costs due to limited raw material availability and seasonal fluctuations, impacting overall market price. Petroleum Wax, sourced from abundant crude oil byproducts, offers lower and more stable costs with widespread global availability, making it economically favorable for large-scale industrial use. Price volatility in petroleum wax depends on crude oil market trends, while gum rosin wax prices are influenced by forestry supply chains and environmental factors.
Which Wax is Better? Choosing the Right Material
Gum Rosin Wax offers superior natural adhesion and biodegradability compared to Petroleum Wax, making it ideal for eco-friendly applications like adhesives and coatings. Petroleum Wax, derived from crude oil, provides excellent moisture resistance and longer shelf life, preferred in packaging and cosmetics. Selecting the right wax depends on whether sustainability or performance in moisture barrier properties is the primary requirement.
Gum Rosin Wax vs Petroleum Wax Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com