Viscose rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose that offers a silky texture and breathability, making it ideal for lightweight garments. Modal rayon, a type of viscose, undergoes a more refined production process resulting in stronger fibers with enhanced moisture absorption and durability. Choosing between viscose and modal rayon depends on the desired fabric strength, softness, and moisture-wicking properties for pet clothing or accessories.
Table of Comparison
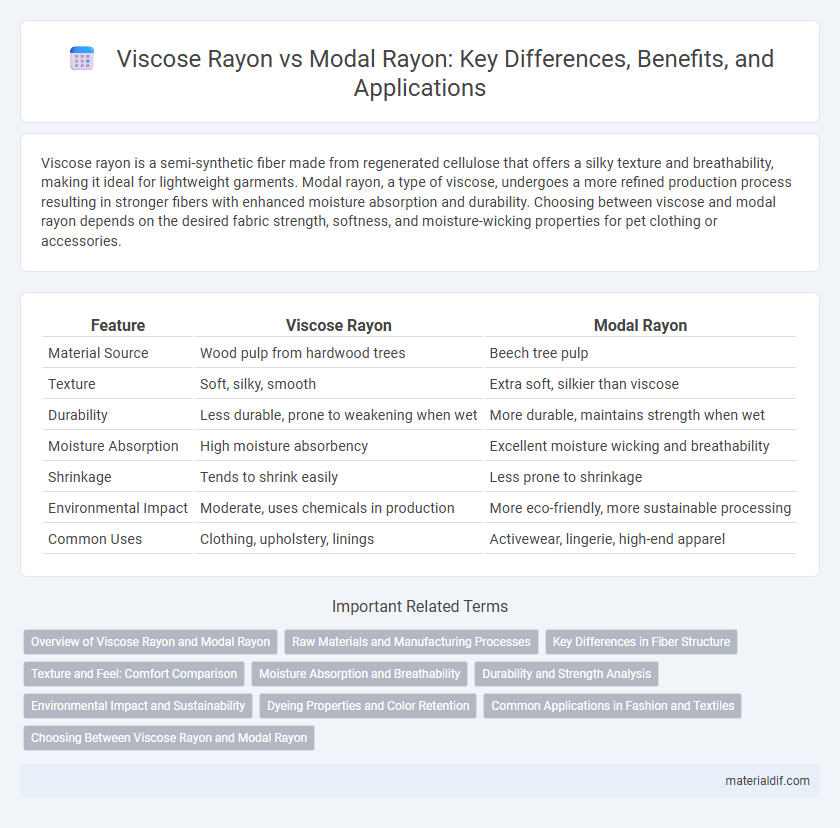
| Feature | Viscose Rayon | Modal Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Wood pulp from hardwood trees | Beech tree pulp |
| Texture | Soft, silky, smooth | Extra soft, silkier than viscose |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to weakening when wet | More durable, maintains strength when wet |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorbency | Excellent moisture wicking and breathability |
| Shrinkage | Tends to shrink easily | Less prone to shrinkage |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, uses chemicals in production | More eco-friendly, more sustainable processing |
| Common Uses | Clothing, upholstery, linings | Activewear, lingerie, high-end apparel |
Overview of Viscose Rayon and Modal Rayon
Viscose rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, known for its silk-like feel, breathability, and affordability, making it widely used in textiles and apparel. Modal rayon, a type of viscose, is produced from beech tree pulp and is characterized by higher durability, superior softness, and enhanced moisture-wicking properties compared to standard viscose. Both fibers contribute to sustainable fashion through biodegradability, but modal rayon often offers improved performance for activewear and luxury clothing.
Raw Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Viscose rayon is produced from wood pulp primarily derived from hardwood trees such as beech, pine, or eucalyptus, whereas modal rayon uses high-quality beechwood pulp known for its finer fiber structure. The manufacturing process for viscose involves steeping wood pulp in sodium hydroxide, followed by treatment with carbon disulfide to create cellulose xanthate, while modal rayon undergoes an advanced spinning process with additional washing and stretching steps to enhance fiber strength and softness. Modal rayon's production emphasizes sustainability and eco-friendly practices by recycling chemicals and using less water compared to the traditional viscose process.
Key Differences in Fiber Structure
Viscose rayon, produced through chemical processing of wood pulp, features longer and less uniform fibers creating a smooth and shiny fabric surface, while modal rayon, a type of high-wet-modulus rayon, has finer, more uniform fibers offering enhanced strength and elasticity. Fiber structure differences result in modal's superior moisture wicking and durability compared to viscose, contributing to improved fabric resilience under repeated washing. These key distinctions in fiber morphology influence fabric texture, performance, and application suitability in textiles and apparel industries.
Texture and Feel: Comfort Comparison
Viscose rayon features a smooth and silky texture that drapes well, offering a soft and breathable feel ideal for warm climates. Modal rayon is known for its exceptionally soft, smooth touch and higher moisture-wicking properties, providing greater comfort and durability in activewear and loungewear. Both fibers enhance comfort, but modal rayon generally offers a plusher feel and improved resistance to shrinkage and pilling.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Viscose rayon absorbs moisture effectively, making it suitable for warm and humid conditions by keeping the skin dry and comfortable. Modal rayon offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing airflow and reducing sweat retention. Both fibers excel in moisture management, but modal rayon provides a more breathable fabric ideal for activewear and intimate apparel.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Viscose rayon offers moderate durability and tensile strength, making it suitable for everyday apparel but prone to weakening when wet. Modal rayon, derived from beech tree pulp, provides superior durability and enhanced wet strength, retaining its integrity better through multiple washes. The improved fiber structure of modal rayon contributes to higher abrasion resistance and longer-lasting fabric performance compared to viscose rayon.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Viscose rayon production involves extensive use of chemicals and water, leading to deforestation and pollution, which significantly impacts environmental sustainability. Modal rayon, made from beech tree pulp, is generally considered more eco-friendly due to its closed-loop production process that recycles water and solvents, reducing waste and emissions. Both fibers derive from cellulose, but modal's sustainable harvesting practices and lower environmental footprint make it a preferable choice for green textiles.
Dyeing Properties and Color Retention
Viscose rayon exhibits excellent dyeing properties due to its high absorbency, allowing vibrant and uniform color uptake, but it may experience moderate fading over time. Modal rayon, made from beechwood pulp, offers superior color retention and enhanced resistance to fading, maintaining brightness even after multiple washes. Both fibers accept a wide range of dyes, but Modal's molecular structure provides increased durability and longevity in dyed fabrics.
Common Applications in Fashion and Textiles
Viscose rayon is widely used in fashion for its silky texture and breathability, making it ideal for shirts, dresses, and linings. Modal rayon, known for its superior softness and durability, is commonly found in high-end underwear, activewear, and loungewear. Both fibers offer excellent moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort in a variety of textile applications.
Choosing Between Viscose Rayon and Modal Rayon
Viscose rayon, derived from wood pulp, offers a smooth, silky texture with excellent breathability, making it ideal for lightweight garments and summer apparel. Modal rayon, a type of high-wet-modulus viscose, provides enhanced durability, superior moisture-wicking properties, and a softer feel, often preferred for activewear and intimate clothing. When choosing between viscose and modal rayon, consider the fabric's end-use requirements such as durability, moisture management, and comfort to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Viscose Rayon vs Modal Rayon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com