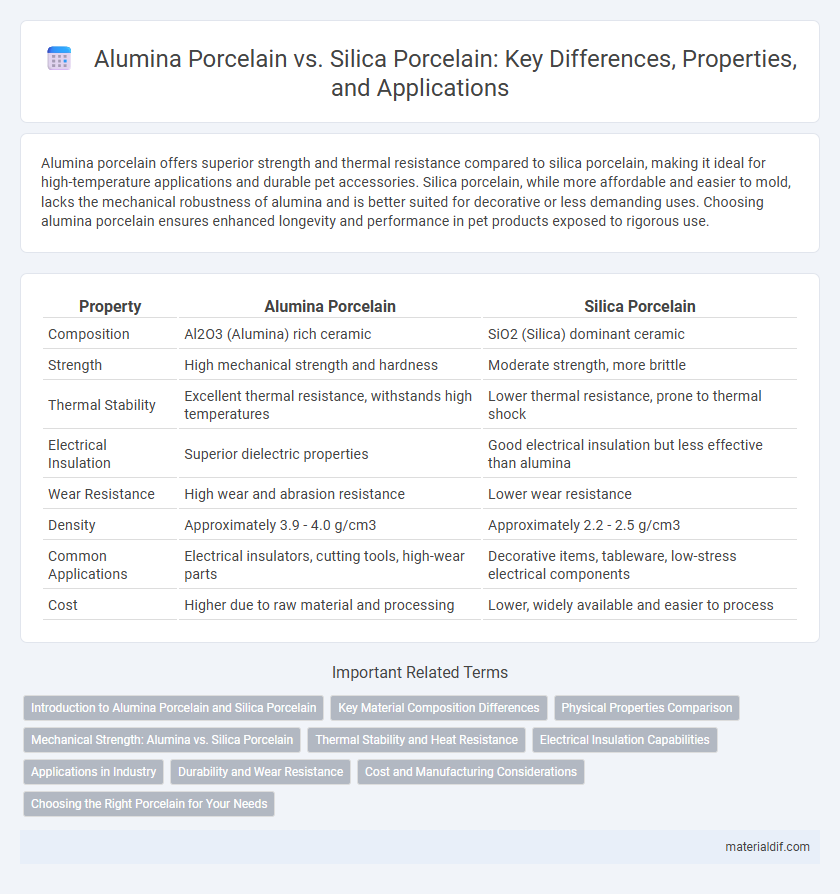
Alumina porcelain offers superior strength and thermal resistance compared to silica porcelain, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and durable pet accessories. Silica porcelain, while more affordable and easier to mold, lacks the mechanical robustness of alumina and is better suited for decorative or less demanding uses. Choosing alumina porcelain ensures enhanced longevity and performance in pet products exposed to rigorous use.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina Porcelain | Silica Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Al2O3 (Alumina) rich ceramic | SiO2 (Silica) dominant ceramic |
| Strength | High mechanical strength and hardness | Moderate strength, more brittle |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent thermal resistance, withstands high temperatures | Lower thermal resistance, prone to thermal shock |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric properties | Good electrical insulation but less effective than alumina |
| Wear Resistance | High wear and abrasion resistance | Lower wear resistance |
| Density | Approximately 3.9 - 4.0 g/cm3 | Approximately 2.2 - 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Common Applications | Electrical insulators, cutting tools, high-wear parts | Decorative items, tableware, low-stress electrical components |
| Cost | Higher due to raw material and processing | Lower, widely available and easier to process |
Introduction to Alumina Porcelain and Silica Porcelain
Alumina porcelain is a high-strength ceramic composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), known for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for industrial applications such as electrical insulators and cutting tools. Silica porcelain, on the other hand, contains a significant percentage of silicon dioxide (SiO2), which provides excellent thermal shock resistance and electrical insulation properties, widely used in cookware and laboratory equipment. Both types of porcelain are engineered for specific performance characteristics, with alumina porcelain excelling in mechanical strength and silica porcelain offering superior thermal and electrical insulation.
Key Material Composition Differences
Alumina porcelain contains a higher percentage of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which enhances its mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation properties compared to silica porcelain. Silica porcelain primarily consists of silicon dioxide (SiO2), providing excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation but with lower mechanical strength. The key material composition difference lies in alumina's contribution to toughness and durability, while silica porcelain emphasizes thermal shock resistance and dielectric characteristics.
Physical Properties Comparison
Alumina porcelain exhibits superior strength and higher hardness due to its increased alumina content, making it more resistant to mechanical wear and thermal shock compared to silica porcelain. Silica porcelain, characterized by a higher silica content, offers better thermal insulation and lower density but tends to be more brittle under stress. The enhanced fracture toughness and elevated melting point of alumina porcelain provide significant advantages in industrial applications requiring durability and high-temperature performance.
Mechanical Strength: Alumina vs. Silica Porcelain
Alumina porcelain exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to silica porcelain due to its increased alumina content, which enhances hardness and resistance to fracture. In contrast, silica porcelain offers better thermal shock resistance but has lower overall strength and durability in structural applications. The higher density and crystalline structure of alumina porcelain make it ideal for demanding environments requiring exceptional wear resistance and load-bearing capacity.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Alumina porcelain exhibits superior thermal stability and heat resistance due to its high alumina content, making it ideal for applications requiring exposure to extreme temperatures. Silica porcelain, while possessing good thermal shock resistance, generally has lower heat tolerance and can be more susceptible to thermal deformation at elevated temperatures. Alumina porcelain's enhanced mechanical strength and thermal insulation properties enable it to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking or warping.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Alumina porcelain offers superior electrical insulation properties compared to silica porcelain due to its higher dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity. The high purity alumina content enhances resistance to electrical breakdown, making it ideal for high-voltage applications in electrical insulators and electronic substrates. Silica porcelain, while providing good mechanical strength, generally exhibits lower insulation performance under extreme electrical stress.
Applications in Industry
Alumina porcelain, known for its high thermal resistance and mechanical strength, is widely used in electrical insulators, spark plugs, and industrial furnace components, where durability under high temperatures is critical. Silica porcelain, with excellent chemical stability and lower thermal conductivity, finds applications in laboratory ware, chemical reactors, and insulation materials in the electronics industry. Both materials serve specialized roles, with alumina porcelain favored for heavy-duty industrial demands and silica porcelain preferred for environments requiring chemical inertness and thermal insulation.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Alumina porcelain offers superior durability and wear resistance compared to silica porcelain due to its higher alumina content, which enhances hardness and mechanical strength. The dense microstructure of alumina porcelain significantly reduces porosity, leading to improved resistance against abrasion and surface damage. Silica porcelain, while more susceptible to wear and fracture under heavy use, remains cost-effective for applications requiring moderate durability.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Alumina porcelain, containing higher alumina content typically around 30-40%, offers superior mechanical strength and wear resistance at a higher production cost due to specialized raw materials and sintering processes. Silica porcelain, primarily composed of silica and kaolin, is more cost-effective and easier to manufacture with standard ceramic techniques but has lower durability and thermal resistance compared to alumina porcelain. Manufacturers choose alumina porcelain for high-performance industrial applications despite increased costs, while silica porcelain remains preferred for general-purpose, economical ceramic products.
Choosing the Right Porcelain for Your Needs
Alumina porcelain offers superior strength and thermal resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications and high-stress environments. Silica porcelain provides excellent translucency and aesthetic appeal, suited for decorative and household uses. Selecting the right porcelain depends on balancing durability requirements with visual qualities for optimal performance and appearance.
Alumina porcelain vs Silica porcelain Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com