Platinum Sendust offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications where durability is crucial. In contrast, Platinum Magnetic Alloys provide enhanced magnetic properties suited for advanced electronic devices and precision sensors. Choosing between them depends on whether mechanical strength or magnetic performance is the priority in your project.
Table of Comparison
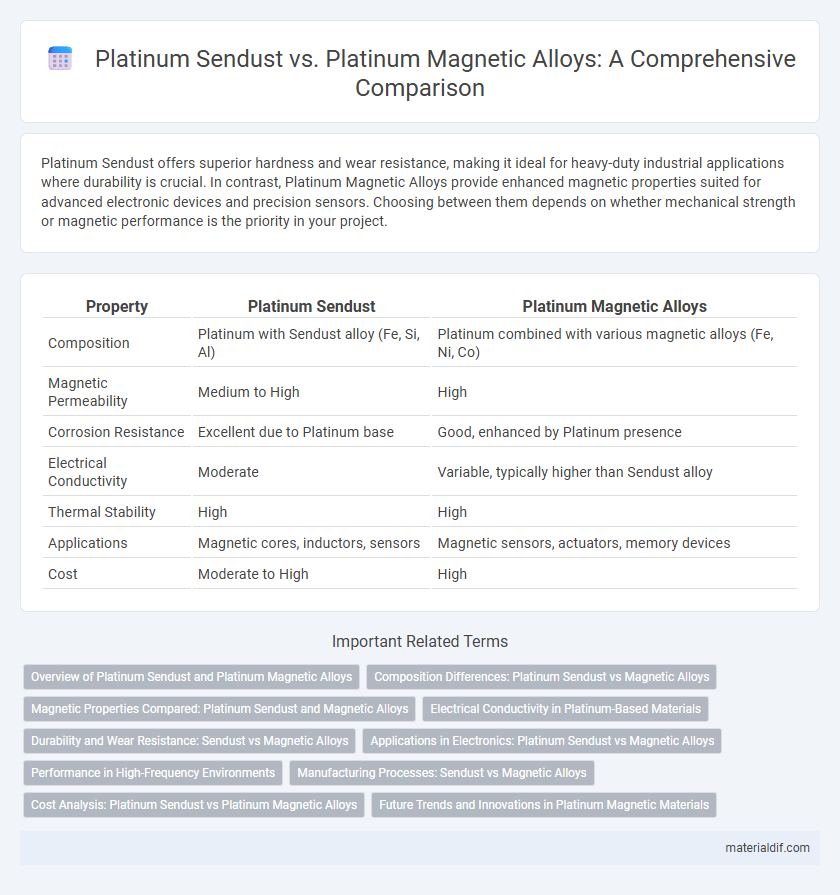
| Property | Platinum Sendust | Platinum Magnetic Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Platinum with Sendust alloy (Fe, Si, Al) | Platinum combined with various magnetic alloys (Fe, Ni, Co) |
| Magnetic Permeability | Medium to High | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent due to Platinum base | Good, enhanced by Platinum presence |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate | Variable, typically higher than Sendust alloy |
| Thermal Stability | High | High |
| Applications | Magnetic cores, inductors, sensors | Magnetic sensors, actuators, memory devices |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High |
Overview of Platinum Sendust and Platinum Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust is a specialized alloy known for its exceptional magnetic softness, combining platinum with iron, silicon, and aluminum to enhance core stability and reduce magnetic losses in high-frequency applications. Platinum Magnetic Alloys encompass a broader category of materials that integrate platinum with various ferromagnetic elements to optimize magnetic performance, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability across diverse industrial uses. These alloys are critical in electronics, sensors, and precision instruments where stable magnetic properties and durability are essential.
Composition Differences: Platinum Sendust vs Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust primarily consists of platinum combined with iron and silicon, forming a unique alloy optimized for magnetic properties and wear resistance. Platinum Magnetic Alloys, in contrast, incorporate platinum with elements such as nickel, cobalt, or chromium to tailor their magnetic strength and corrosion resistance. The composition differences significantly influence their respective applications in electronics and industrial components, where specific magnetic and durability requirements are critical.
Magnetic Properties Compared: Platinum Sendust and Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust exhibits exceptional magnetic permeability and low coercivity, making it ideal for high-frequency applications requiring minimal energy loss. In contrast, Platinum Magnetic Alloys offer a broader range of magnetic properties, including enhanced saturation magnetization and improved thermal stability, suited for demanding environments. The choice between Platinum Sendust and Platinum Magnetic Alloys depends on balancing factors like frequency response, magnetic saturation, and temperature tolerance for optimal performance.
Electrical Conductivity in Platinum-Based Materials
Platinum Sendust exhibits lower electrical conductivity compared to Platinum Magnetic Alloys due to its composition mainly of platinum, iron, and silicon, which enhances magnetic properties but reduces electron mobility. Platinum Magnetic Alloys, incorporating elements like cobalt and nickel, demonstrate higher electrical conductivity owing to their optimized electron density and crystalline structure. This conductivity difference is crucial for applications requiring efficient electrical current flow alongside magnetic performance.
Durability and Wear Resistance: Sendust vs Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust exhibits superior wear resistance due to its unique composition combining platinum with aluminum and silicon, resulting in enhanced hardness and reduced friction compared to conventional platinum magnetic alloys. Platinum Magnetic Alloys, while offering good magnetic properties, generally show lower durability under abrasive conditions because of their softer matrix and less optimized wear resistance. In applications demanding prolonged service life and minimal material degradation, platinum sendust is preferred for its robust durability and exceptional wear performance.
Applications in Electronics: Platinum Sendust vs Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust, an alloy of platinum, silicon, and aluminum, offers superior magnetic permeability and lower coercivity, making it ideal for high-frequency transformer cores and inductors in electronics. In contrast, platinum-based magnetic alloys, often combined with elements like cobalt or nickel, provide enhanced corrosion resistance and thermal stability, which are critical in harsh electronic environments such as sensors and magnetic recording heads. Electronic components benefit from Platinum Sendust's low core loss properties, while platinum magnetic alloys excel in durability and performance under extreme conditions.
Performance in High-Frequency Environments
Platinum Sendust alloys exhibit superior magnetic permeability and lower core losses compared to Platinum Magnetic Alloys, making them highly efficient in high-frequency environments such as RF transformers and inductors. The unique grain structure of Platinum Sendust enhances its performance by reducing eddy current losses and improving thermal stability under rapid magnetic field changes. In contrast, Platinum Magnetic Alloys, while offering good corrosion resistance, tend to have higher hysteresis losses that limit their efficiency at frequencies above 1 MHz.
Manufacturing Processes: Sendust vs Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust alloys are typically produced using powder metallurgy techniques that involve mixing fine powders of platinum with sendust components, followed by compaction and sintering to achieve a uniform microstructure and enhanced magnetic properties. In contrast, Platinum magnetic alloys are commonly manufactured through casting and subsequent heat treatment processes that refine their grain structure, improving magnetic performance and corrosion resistance. The powder metallurgy process of Platinum Sendust allows for precise control of particle size and composition, leading to superior wear resistance and stability compared to the more conventional melting and casting methods used for Platinum magnetic alloys.
Cost Analysis: Platinum Sendust vs Platinum Magnetic Alloys
Platinum Sendust offers a cost-effective alternative to Platinum Magnetic Alloys due to its lower raw material expenses and simplified manufacturing process. While Platinum Magnetic Alloys deliver superior magnetic properties, their higher production costs result from the use of expensive alloying elements and complex fabrication techniques. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals that Platinum Sendust provides a more economical solution for applications where moderate magnetic performance suffices.
Future Trends and Innovations in Platinum Magnetic Materials
Platinum Magnetic Alloys are poised to dominate future innovations due to their enhanced magnetic permeability and corrosion resistance, outperforming Platinum Sendust which is primarily valued for its stable electrical properties. Advances in nanostructuring and alloy composition in Platinum Magnetic Alloys are driving breakthroughs in energy-efficient electric motors and high-density data storage devices. Research in these alloys focuses on optimizing magnetic performance while reducing platinum content, aligning with sustainability goals and cost-effectiveness in emerging technologies.
Platinum Sendust vs Platinum Magnetic Alloys Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com