Cement plaster offers superior strength, water resistance, and durability compared to mud plaster, making it ideal for exterior and high-moisture areas. Mud plaster, made from natural clay, sand, and water, is environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and provides excellent insulation but lacks the longevity and hardness of cement plaster. Choosing between cement plaster and mud plaster depends on factors such as budget, environmental conditions, and desired finish quality.
Table of Comparison
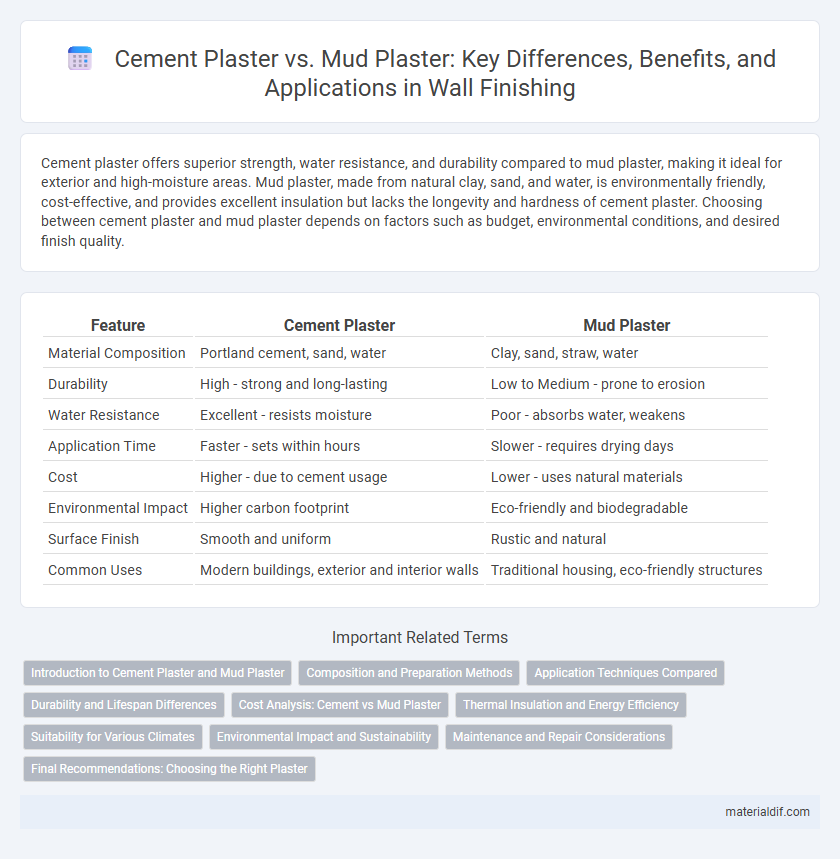
| Feature | Cement Plaster | Mud Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Portland cement, sand, water | Clay, sand, straw, water |
| Durability | High - strong and long-lasting | Low to Medium - prone to erosion |
| Water Resistance | Excellent - resists moisture | Poor - absorbs water, weakens |
| Application Time | Faster - sets within hours | Slower - requires drying days |
| Cost | Higher - due to cement usage | Lower - uses natural materials |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Eco-friendly and biodegradable |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and uniform | Rustic and natural |
| Common Uses | Modern buildings, exterior and interior walls | Traditional housing, eco-friendly structures |
Introduction to Cement Plaster and Mud Plaster
Cement plaster is a durable coating composed of cement, sand, and water, widely used for exterior and interior wall finishes due to its strong adhesion and weather resistance. Mud plaster, made from natural clay, sand, and water, offers excellent breathability and eco-friendliness, making it ideal for traditional and sustainable building practices. Both types of plaster serve different purposes, with cement plaster favored for long-lasting protection and mud plaster preferred for natural insulation and moisture regulation.
Composition and Preparation Methods
Cement plaster consists of a mixture of cement, sand, and water, creating a durable and water-resistant coating suitable for exterior and interior surfaces. Mud plaster is primarily composed of clay, sand, and water, often incorporating organic materials like straw to enhance binding and crack resistance, making it eco-friendly and breathable. Preparation of cement plaster involves precise measuring and mixing to achieve a consistent, workable mortar, while mud plaster preparation relies on hand-mixing and sometimes soaking the clay to improve texture and adhesion.
Application Techniques Compared
Cement plaster requires a base coat applied with a trowel, followed by a finishing coat that can be smoothed or textured, ideal for durable, weather-resistant surfaces. Mud plaster, commonly used in traditional construction, is applied in thicker layers using hand-pressing techniques, allowing for natural breathability and insulation. Both techniques demand careful surface preparation but differ significantly in drying time and structural compatibility with various wall materials.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Cement plaster offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to mud plaster due to its resistance to weathering, cracking, and erosion, making it ideal for exterior surfaces. Mud plaster, while eco-friendly and breathable, tends to have a shorter lifespan as it is more susceptible to moisture damage and requires frequent maintenance. The strong binding properties and water resistance of cement plaster contribute to its extended use in modern construction.
Cost Analysis: Cement vs Mud Plaster
Cement plaster generally incurs higher initial costs due to material prices and skilled labor requirements compared to mud plaster, which uses readily available natural materials and simple application techniques. Mud plaster offers significant savings in raw material expenses and environmental impact, making it a cost-effective choice for low-budget projects or eco-friendly constructions. Long-term maintenance costs for cement plaster may be higher, while mud plaster requires periodic repairs but remains economical overall.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Cement plaster offers moderate thermal insulation but tends to retain heat, making it less energy-efficient in hot climates compared to mud plaster, which provides superior natural insulation due to its high thermal mass and breathability. Mud plaster regulates indoor temperatures effectively by absorbing and releasing moisture, reducing the need for artificial cooling and heating, thus enhancing overall energy efficiency. Choosing mud plaster can significantly lower energy consumption, especially in regions with extreme temperature variations.
Suitability for Various Climates
Cement plaster offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for humid and rainy climates where moisture protection is crucial. Mud plaster, composed of natural materials like clay and sand, excels in hot and dry climates by providing excellent thermal insulation and breathability. Selecting the appropriate plaster depends on local climate conditions to optimize building longevity and indoor comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cement plaster generates higher carbon emissions due to the energy-intensive manufacturing of cement, contributing significantly to environmental degradation. Mud plaster, derived from natural materials like clay and sand, offers superior sustainability by being biodegradable and requiring minimal processing, thereby reducing its ecological footprint. Choosing mud plaster promotes eco-friendly construction practices and helps conserve natural resources, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Cement plaster offers higher durability and resistance to weathering, reducing the frequency of maintenance compared to mud plaster, which requires more frequent repairs due to its susceptibility to cracking and erosion. Repairing cement plaster involves filling cracks and reapplying a thin cement layer, whereas mud plaster repairs often require complete patch replacement to maintain structural integrity. The long-term cost-effectiveness of cement plaster is enhanced by its low maintenance needs, making it preferable for exterior applications subjected to harsh environmental conditions.
Final Recommendations: Choosing the Right Plaster
Cement plaster offers superior durability, water resistance, and smooth finish, making it ideal for exteriors and areas exposed to moisture. Mud plaster provides excellent breathability and eco-friendliness, well-suited for interior walls in dry climates and sustainable building projects. Select cement plaster for long-lasting protection and mud plaster for natural insulation and environmental benefits.
Cement Plaster vs Mud Plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com