Plaster of Paris and dental plaster are both commonly used materials derived from gypsum, but they differ significantly in properties and applications. Plaster of Paris has a finer particle size and sets quickly, making it ideal for casting molds and sculptures, while dental plaster features a coarser texture and is specifically formulated for creating dental impressions and models due to its strength and accuracy. Understanding these differences ensures the appropriate plaster type is chosen for precise and durable results in pet-related or dental projects.
Table of Comparison
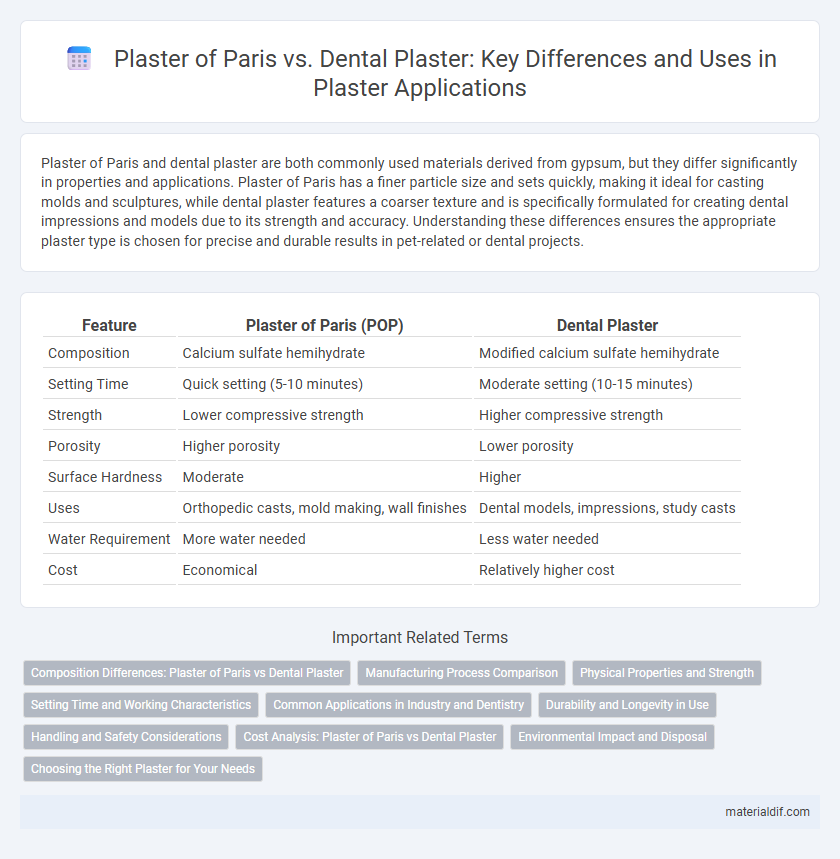
| Feature | Plaster of Paris (POP) | Dental Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium sulfate hemihydrate | Modified calcium sulfate hemihydrate |
| Setting Time | Quick setting (5-10 minutes) | Moderate setting (10-15 minutes) |
| Strength | Lower compressive strength | Higher compressive strength |
| Porosity | Higher porosity | Lower porosity |
| Surface Hardness | Moderate | Higher |
| Uses | Orthopedic casts, mold making, wall finishes | Dental models, impressions, study casts |
| Water Requirement | More water needed | Less water needed |
| Cost | Economical | Relatively higher cost |
Composition Differences: Plaster of Paris vs Dental Plaster
Plaster of Paris is primarily composed of calcium sulfate hemihydrate, which sets rapidly when mixed with water, making it ideal for molding and casting applications. Dental plaster, a specific type of Plaster of Paris, contains fewer air bubbles and has a finer particle size, resulting in higher strength and better detail reproduction for precise dental impressions. The compositional differences, such as purity and particle morphology, directly affect the setting time, hardness, and dimensional accuracy between the two materials.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Plaster of Paris is produced by heating natural gypsum to about 150degC, which drives off water molecules and results in a fine, white powder that sets quickly upon mixing with water. Dental plaster undergoes a similar calcination process but at controlled temperatures to achieve a finer particle size and optimized setting times suitable for detailed dental impressions. The manufacturing variations influence properties such as setting time, strength, and porosity, making each type tailored for its specific clinical applications.
Physical Properties and Strength
Plaster of Paris (POP) is a quick-setting material with high compressive strength, typically ranging from 0.7 to 1.2 MPa, making it ideal for molding and casting applications. Dental plaster, a type of gypsum product, has a finer particle size and lower compressive strength, usually between 3.5 to 5 MPa, providing better detail reproduction for dental impressions but less durability under load. The physical properties of Dental plaster include increased porosity and reduced density compared to standard Plaster of Paris, influencing its mechanical strength and setting time.
Setting Time and Working Characteristics
Plaster of Paris typically has a rapid setting time of 5 to 15 minutes, allowing quick mold creation but requiring fast handling, while dental plaster sets more slowly, approximately 10 to 20 minutes, providing extended working time for precise dental impressions. The working characteristics of Plaster of Paris involve a smooth, fine texture suitable for detailed casts but are more brittle once set, whereas dental plaster offers enhanced strength and slightly coarser consistency optimized for oral applications. These differences in setting time and workability directly impact their suitability for specific clinical and modeling uses.
Common Applications in Industry and Dentistry
Plaster of Paris is extensively used in construction for mold making, casting, and sculpting due to its rapid setting and strong bonding properties. Dental plaster, a specialized gypsum product, is primarily employed in dentistry for fabricating dental molds, orthodontic models, and treatment casts because of its precise detail reproduction and adequate hardness. Both materials utilize gypsum but differ in setting time, strength, and porosity, which tailor their respective applications in industry and dental practice.
Durability and Longevity in Use
Plaster of Paris offers moderate durability with quick setting time, making it suitable for temporary molds and casts but less ideal for long-term applications due to its brittleness and susceptibility to moisture. Dental plaster, specifically formulated with higher density and strength, provides superior durability and longevity, resisting wear and maintaining structural integrity in oral applications over extended periods. Optimal use depends on the balance between required structural endurance and application environment, with dental plaster favored for sustained performance.
Handling and Safety Considerations
Plaster of Paris offers quick setting times but generates heat during curing, requiring careful handling to avoid burns, whereas dental plaster sets more slowly and is designed to be non-toxic for safe intraoral use. Proper ventilation and protective gloves are essential when working with Plaster of Paris to minimize exposure to dust and skin irritation. Dental plaster formulations emphasize biocompatibility and reduced dust hazards, making them safer for dental professionals and patients during mold impressions.
Cost Analysis: Plaster of Paris vs Dental Plaster
Plaster of Paris generally costs less than dental plaster due to its widespread availability and industrial-scale production, making it ideal for construction and casting purposes. Dental plaster, formulated with higher purity standards and fine particle sizes, involves more complex manufacturing, resulting in higher costs tailored to medical and dental applications. Evaluating expenses requires considering not only material price but also the specific use-cases where precision and safety in dental treatments justify the premium price of dental plaster.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
Plaster of Paris, primarily composed of calcium sulfate hemihydrate, releases sulfur dioxide during disposal, contributing to air pollution and posing environmental concerns. Dental plaster, often formulated with similar components, may contain additives that complicate biodegradability and increase landfill burden. Both materials require careful waste management practices to minimize ecological impact, emphasizing recycling and containment to prevent soil and water contamination.
Choosing the Right Plaster for Your Needs
Plaster of Paris offers rapid setting and smooth finish ideal for decorative molding and orthopedic casts, whereas Dental Plaster provides greater strength and abrasion resistance tailored for dental molds and prosthetics. Choosing the right plaster depends on specific application requirements, with Plaster of Paris suiting short-term casts and aesthetic projects, while Dental Plaster excels in durability and precision for dental applications. Consider factors such as setting time, strength, and surface detail when selecting between Plaster of Paris and Dental Plaster to ensure optimal performance.
Plaster of Paris vs Dental Plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com