Cement plaster offers excellent durability and water resistance, making it ideal for exterior walls and rough surfaces due to its strong bonding properties. Acrylic plaster provides superior flexibility and is more resistant to cracking, with a smoother finish suitable for both interior and exterior applications where aesthetic appeal is important. Choosing between cement plaster and acrylic plaster depends on the specific requirements for durability, flexibility, and surface texture.
Table of Comparison
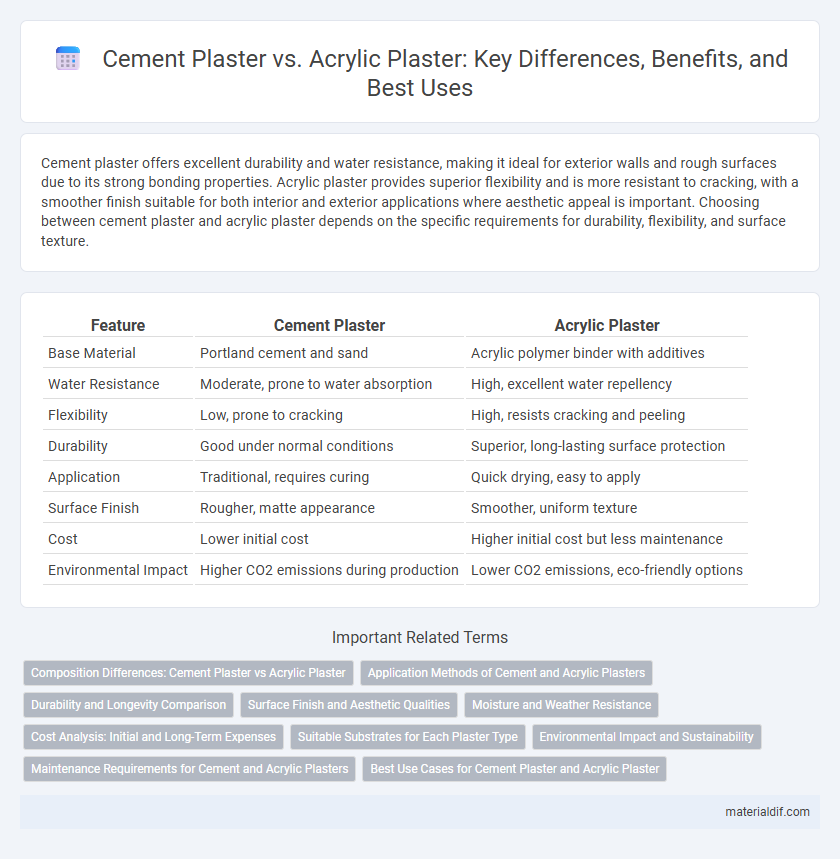
| Feature | Cement Plaster | Acrylic Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Portland cement and sand | Acrylic polymer binder with additives |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, prone to water absorption | High, excellent water repellency |
| Flexibility | Low, prone to cracking | High, resists cracking and peeling |
| Durability | Good under normal conditions | Superior, long-lasting surface protection |
| Application | Traditional, requires curing | Quick drying, easy to apply |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, matte appearance | Smoother, uniform texture |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but less maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Higher CO2 emissions during production | Lower CO2 emissions, eco-friendly options |
Composition Differences: Cement Plaster vs Acrylic Plaster
Cement plaster primarily consists of a mixture of cement, sand, and water, providing a strong and durable finish ideal for exterior walls. Acrylic plaster incorporates synthetic polymers along with sand and water, enhancing flexibility, water resistance, and adhesion compared to traditional cement plaster. The presence of acrylic polymers in acrylic plaster significantly reduces cracking and allows for better breathability in building surfaces.
Application Methods of Cement and Acrylic Plasters
Cement plaster is applied by mixing cement, sand, and water into a thick paste, then manually troweling it onto surfaces, ensuring firm adhesion and rough texture suitable for base coats. Acrylic plaster, composed of synthetic polymers, is applied using spray machines or trowels, allowing for smoother finishes and faster drying times due to its flexible and water-resistant properties. The application of acrylic plaster requires less water and offers better workability, making it ideal for intricate designs and exterior surfaces exposed to weather variations.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Cement plaster offers strong durability and is highly resistant to weathering, making it suitable for exterior surfaces exposed to harsh conditions. Acrylic plaster provides superior flexibility and crack resistance, enhancing its longevity by preventing surface damage in environments with temperature fluctuations. Both materials deliver long-lasting performance, but cement plaster excels in hardness, while acrylic plaster outperforms in maintaining appearance over time.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Cement plaster offers a rougher and more porous surface finish, suitable for traditional and rustic appearances, while acrylic plaster provides a smoother, more uniform finish with enhanced color retention and resistance to cracking. Acrylic plaster's elasticity allows for greater design flexibility and vibrant aesthetic qualities, making it ideal for modern facades and intricate textures. Cement plaster is more economical but less durable against weathering compared to acrylic plaster's superior longevity and maintenance of visual appeal.
Moisture and Weather Resistance
Cement plaster offers excellent durability and strong resistance to moisture, making it ideal for exterior walls exposed to harsh weather conditions. Acrylic plaster provides superior elasticity and water repellency, effectively preventing cracks and resisting weathering in fluctuating climates. Both plasters are moisture-resistant, but acrylic plaster's flexibility ensures enhanced protection against prolonged exposure to rain and temperature variations.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Cement plaster typically has a lower initial cost compared to acrylic plaster, making it budget-friendly for large-scale applications. However, acrylic plaster involves higher upfront expenses due to specialized materials and application processes but offers superior durability and resistance to weathering, reducing long-term maintenance costs. Over time, the increased longevity and lower repair frequency of acrylic plaster often result in more cost-effective investment despite the initial premium.
Suitable Substrates for Each Plaster Type
Cement plaster is best suited for substrates like brick, concrete, and masonry where high durability and water resistance are required. Acrylic plaster performs well on a variety of surfaces including wood, metal, and previously painted walls owing to its flexibility and strong adhesion properties. Choosing the right plaster depends on the substrate's porosity, movement, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cement plaster, made primarily from cement, sand, and water, has a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive cement production and limited recyclability, contributing significantly to CO2 emissions. Acrylic plaster, composed of synthetic polymers, offers better durability and flexibility, reducing maintenance frequency and material waste, which supports environmental sustainability. The choice between cement and acrylic plaster should consider long-term ecological effects, with acrylic plaster generally providing a more sustainable option due to lower energy consumption and enhanced lifespan.
Maintenance Requirements for Cement and Acrylic Plasters
Cement plaster demands regular maintenance such as sealing cracks promptly and periodic repainting to prevent water infiltration and surface degradation. Acrylic plaster offers superior durability with low maintenance needs, resisting cracking and fading while requiring minimal cleaning and occasional repainting. Choosing acrylic plaster reduces long-term upkeep costs and extends the lifespan of exterior and interior wall finishes.
Best Use Cases for Cement Plaster and Acrylic Plaster
Cement plaster offers superior durability and water resistance, making it ideal for exterior walls, foundations, and high-moisture areas such as bathrooms and kitchens. Acrylic plaster provides better flexibility and adhesion to various substrates, making it suitable for decorative finishes, interior walls, and surfaces prone to minor cracks due to thermal expansion. Choosing cement plaster ensures long-lasting structural protection, while acrylic plaster excels in enhancing aesthetic appeal and accommodating building movements.
Cement plaster vs Acrylic plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com