Cement plaster offers superior strength and water resistance, making it ideal for exterior walls and high-moisture areas. Clay plaster provides natural insulation, breathability, and eco-friendliness, suitable for interior walls and sustainable building projects. Choosing between cement plaster and clay plaster depends on the specific requirements for durability, moisture control, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
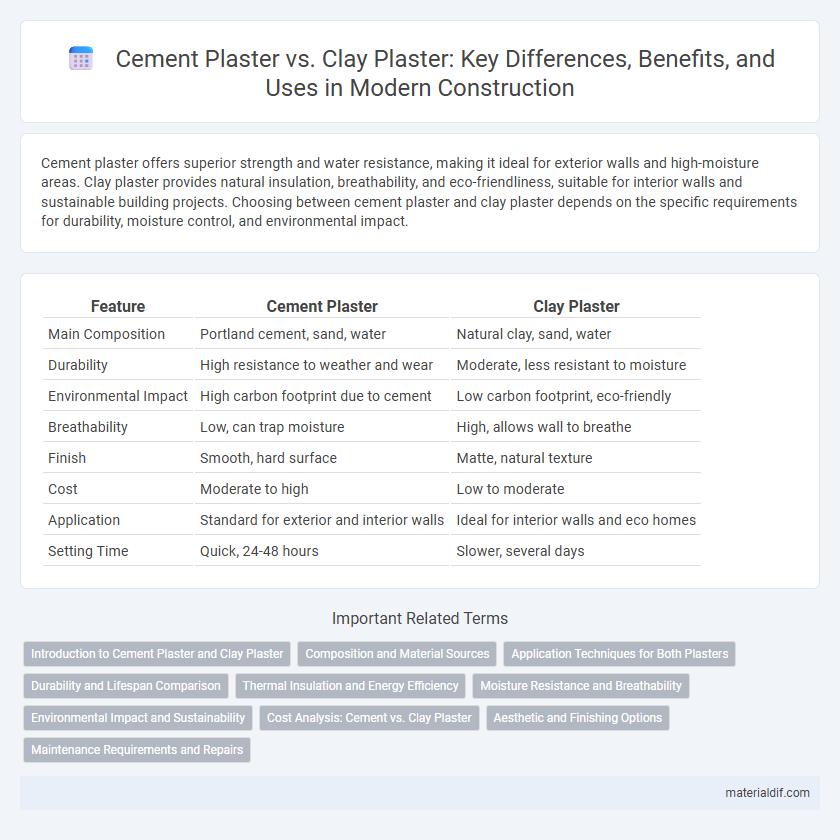
| Feature | Cement Plaster | Clay Plaster |
|---|---|---|
| Main Composition | Portland cement, sand, water | Natural clay, sand, water |
| Durability | High resistance to weather and wear | Moderate, less resistant to moisture |
| Environmental Impact | High carbon footprint due to cement | Low carbon footprint, eco-friendly |
| Breathability | Low, can trap moisture | High, allows wall to breathe |
| Finish | Smooth, hard surface | Matte, natural texture |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Application | Standard for exterior and interior walls | Ideal for interior walls and eco homes |
| Setting Time | Quick, 24-48 hours | Slower, several days |
Introduction to Cement Plaster and Clay Plaster
Cement plaster is a durable, water-resistant coating made from a mixture of cement, sand, and water, widely used for exterior and interior walls to provide a strong, protective layer. Clay plaster, composed primarily of natural clay, sand, and fiber, offers a breathable, eco-friendly alternative with excellent moisture regulation and thermal insulation properties. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with cement plaster favored for its robustness and clay plaster valued for its sustainability and indoor air quality benefits.
Composition and Material Sources
Cement plaster consists primarily of Portland cement, sand, and water, producing a durable and water-resistant surface suitable for exterior walls, often sourced from limestone and clay processed to create cement. Clay plaster comprises natural clay, sand, and organic fibers like straw, offering a breathable and eco-friendly finish, with raw materials typically extracted from local soil deposits. The key difference lies in cement plaster's synthetic composition versus clay plaster's natural, earth-derived ingredients impacting their environmental footprint and application properties.
Application Techniques for Both Plasters
Cement plaster requires mixing cement, sand, and water to create a durable, water-resistant layer applied with a trowel in multiple coats for smooth, long-lasting finishes. Clay plaster is prepared by blending clay, sand, and natural fiber, then applied by hand or trowel for a breathable, eco-friendly surface ideal for interior walls. Both techniques demand surface preparation, but cement plaster suits exterior use due to weather resistance, whereas clay plaster excels indoors for moisture regulation and aesthetic appeal.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Cement plaster offers superior durability compared to clay plaster due to its high resistance to moisture, weathering, and mechanical wear, making it ideal for exterior applications. Clay plaster, while eco-friendly and breathable, typically has a shorter lifespan as it is more susceptible to cracking and erosion under harsh environmental conditions. The lifespan of cement plaster can exceed 20 years with proper maintenance, whereas clay plaster generally lasts around 5 to 10 years before requiring repairs or replacement.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Cement plaster provides a durable, moisture-resistant surface but has lower thermal insulation properties compared to clay plaster, which naturally regulates indoor temperature through its porous structure. Clay plaster enhances energy efficiency by reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling, contributing to lower energy consumption. Its ability to absorb and release moisture also helps maintain indoor air quality, making it preferable for sustainable building designs focused on thermal comfort.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Cement plaster offers superior moisture resistance, making it ideal for exterior walls and wet areas prone to water exposure. Clay plaster excels in breathability, allowing moisture to evaporate naturally and reducing the risk of mold growth in interior spaces. Choosing between cement and clay plaster depends on the specific environmental conditions and moisture management requirements of the building.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cement plaster has a higher carbon footprint due to the energy-intensive production of Portland cement, contributing significantly to CO2 emissions, whereas clay plaster is more environmentally friendly with its natural, biodegradable components and minimal processing. Clay plaster enhances indoor air quality by regulating humidity and reducing toxins, unlike cement plaster, which can release harmful alkalis and dust during application and curing. The sustainability of clay plaster is reinforced by its low embodied energy and recyclability, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious construction and green building certifications.
Cost Analysis: Cement vs. Clay Plaster
Cement plaster generally costs more than clay plaster due to the higher price of raw materials like Portland cement and additives, whereas clay plaster is more economical, relying on naturally available materials like soil and sand. Labor costs for clay plaster can be lower since it requires simpler tools and less specialized skills compared to cement plaster, which demands careful mixing and skilled application. Long-term expenses also differ as cement plaster provides enhanced durability and weather resistance, potentially reducing maintenance costs compared to the more porous and less water-resistant clay plaster.
Aesthetic and Finishing Options
Cement plaster offers a smooth, durable finish suitable for modern and industrial aesthetics, allowing for a range of textures from fine to rough, while providing a neutral canvas for paints and coatings. Clay plaster presents an earthy, natural appearance with rich, warm tones and a matte finish, often enhanced by pigment blending and texturing techniques that highlight its organic qualities. The choice between cement and clay plaster significantly affects the visual depth and tactile experience of interior and exterior surfaces, influencing overall design style and ambiance.
Maintenance Requirements and Repairs
Cement plaster requires less frequent maintenance due to its durability and resistance to water, making it ideal for exterior surfaces exposed to harsh weather conditions. Clay plaster, while eco-friendly and breathable, demands regular upkeep to prevent cracking and deterioration, especially in areas with high humidity or moisture. Repairs for cement plaster typically involve patching with similar cementitious materials, whereas clay plaster repairs require careful matching of the original clay mix to maintain consistency and structural integrity.
Cement Plaster vs Clay Plaster Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com