Jute cordage is a natural fiber known for its softness, eco-friendliness, and resistance to rot, making it ideal for lightweight tying and decorative purposes. Manila cordage, derived from abaca plant fibers, offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to saltwater, commonly used in heavy-duty maritime and industrial applications. The choice between jute and manila cordage depends on specific requirements such as tensile strength, environmental exposure, and application type.
Table of Comparison
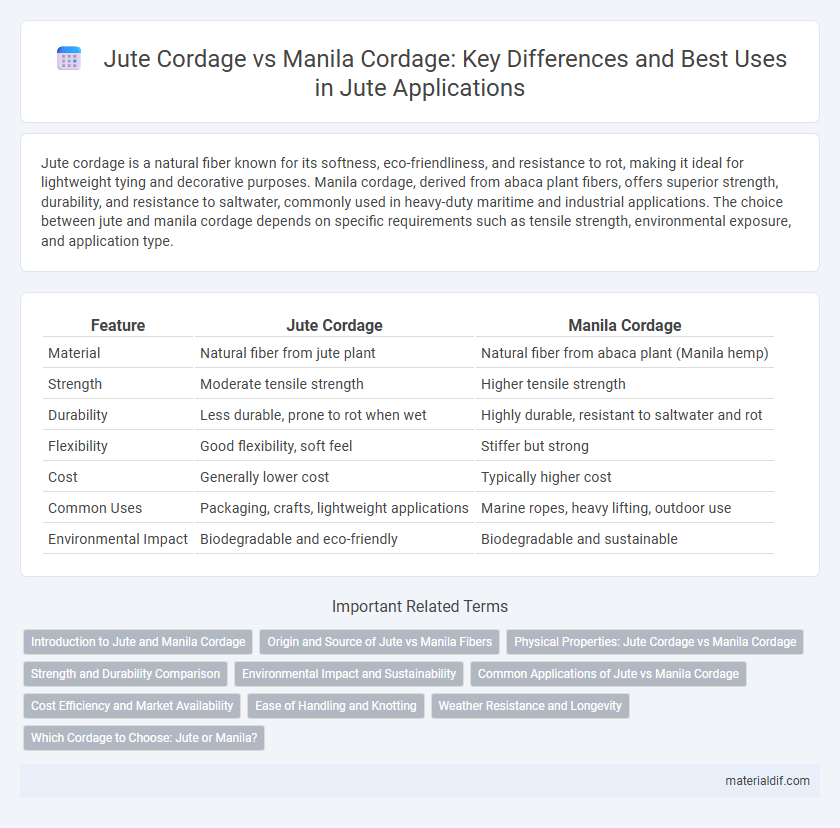
| Feature | Jute Cordage | Manila Cordage |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural fiber from jute plant | Natural fiber from abaca plant (Manila hemp) |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to rot when wet | Highly durable, resistant to saltwater and rot |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, soft feel | Stiffer but strong |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Common Uses | Packaging, crafts, lightweight applications | Marine ropes, heavy lifting, outdoor use |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Biodegradable and sustainable |
Introduction to Jute and Manila Cordage
Jute cordage is made from the natural fibers of the jute plant, known for its biodegradability, affordability, and moderate strength, making it ideal for agricultural and packaging uses. Manila cordage, derived from the abaca plant, offers superior durability, tensile strength, and resistance to saltwater, making it preferred in marine and heavy industrial applications. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives to synthetic ropes, with jute excelling in eco-friendly everyday tasks and manila suited for demanding environmental conditions.
Origin and Source of Jute vs Manila Fibers
Jute cordage is derived from the bast fibers of the Corchorus plant, primarily cultivated in Bangladesh and India, known for its renewable and sustainable properties. Manila cordage, on the other hand, is made from abaca fibers harvested from the Musa textilis plant native to the Philippines, recognized for its high strength and resistance to saltwater. The distinct botanical origins of jute and Manila fibers influence their durability, texture, and typical applications in rope-making.
Physical Properties: Jute Cordage vs Manila Cordage
Jute cordage is softer, more flexible, and has a lower tensile strength compared to manila cordage, which is known for its superior durability and higher tensile strength due to its abaca fiber composition. Manila cordage exhibits better resistance to abrasion, moisture, and UV exposure, making it ideal for heavy-duty marine and industrial applications, whereas jute cordage is more susceptible to rot and degradation when exposed to moisture for extended periods. Both cordages offer biodegradable options, but manila's robust physical properties make it preferable for tasks requiring enhanced strength and longevity.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Jute cordage offers moderate tensile strength but is less durable compared to manila cordage, which is known for its superior strength and resistance to wear and tear. Manila cordage, made from abaca fibers, excels in environments with exposure to moisture and heavy loads, making it more suitable for industrial applications. The natural softness of jute limits its longevity, whereas manila's robust fiber composition ensures extended usability in demanding conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Jute cordage offers superior environmental benefits compared to manila cordage due to its renewable, biodegradable nature and lower carbon footprint during cultivation and processing. Manila cordage, derived from abaca fibers, has a higher environmental impact related to chemical usage and energy-intensive production. Sustainable jute farming practices further enhance soil fertility and reduce deforestation risks, making jute cordage a more eco-friendly choice in rope manufacturing.
Common Applications of Jute vs Manila Cordage
Jute cordage is commonly used in agricultural applications such as bundling crops, making sacks, and garden twine due to its biodegradable and eco-friendly properties. Manila cordage, made from abaca fibers, excels in heavy-duty tasks like marine rigging, shipping, and industrial lifting because of its superior strength and resistance to saltwater. Both types serve unique purposes, with jute favored for light-duty, sustainable uses and manila chosen for durability and high-tension environments.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Jute cordage offers superior cost efficiency compared to manila cordage due to its lower raw material and production expenses, making it an economical choice for bulk applications. Market availability of jute cordage is widespread in regions with established jute cultivation, such as India and Bangladesh, ensuring steady supply and competitive pricing. In contrast, manila cordage, derived from abaca fibers, tends to have higher costs and more limited availability, impacting its overall market competitiveness.
Ease of Handling and Knotting
Jute cordage offers superior ease of handling due to its softer texture and flexibility compared to manila cordage, which tends to be stiffer and coarser. The natural pliability of jute fibers allows for smoother knotting and reduces fatigue during prolonged use, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent tying and untying. Conversely, manila cordage, while strong, demands more effort to manipulate and secure knots securely.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Jute cordage exhibits moderate weather resistance, making it suitable for indoor or temporary outdoor use but prone to faster degradation under prolonged moisture exposure. Manila cordage, derived from abaca fibers, offers superior resistance to UV rays, saltwater, and mildew, ensuring greater longevity in harsh marine and outdoor environments. The durability of manila cordage surpasses jute, making it the preferred choice for applications demanding sustained exposure to weather elements.
Which Cordage to Choose: Jute or Manila?
Jute cordage offers excellent biodegradability and is lightweight, making it ideal for eco-friendly packaging and gardening applications. Manila cordage, derived from abaca fibers, provides superior strength, durability, and resistance to saltwater, which suits marine and heavy-duty industrial uses. Choosing between jute and manila depends on the specific requirements for environmental impact, tensile strength, and exposure conditions.
Jute Cordage vs Manila Cordage Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com