Hempseed oil finish offers a natural, eco-friendly option with excellent moisturizing properties that enhance wood grain without yellowing over time, making it ideal for sustainable woodworking projects. Linseed oil finish, derived from flax seeds, provides a durable and water-resistant coating but tends to darken or amber wood surfaces with age. Choosing between hempseed and linseed oil finishes depends on the desired aesthetic longevity and environmental impact for the finished wood product.
Table of Comparison
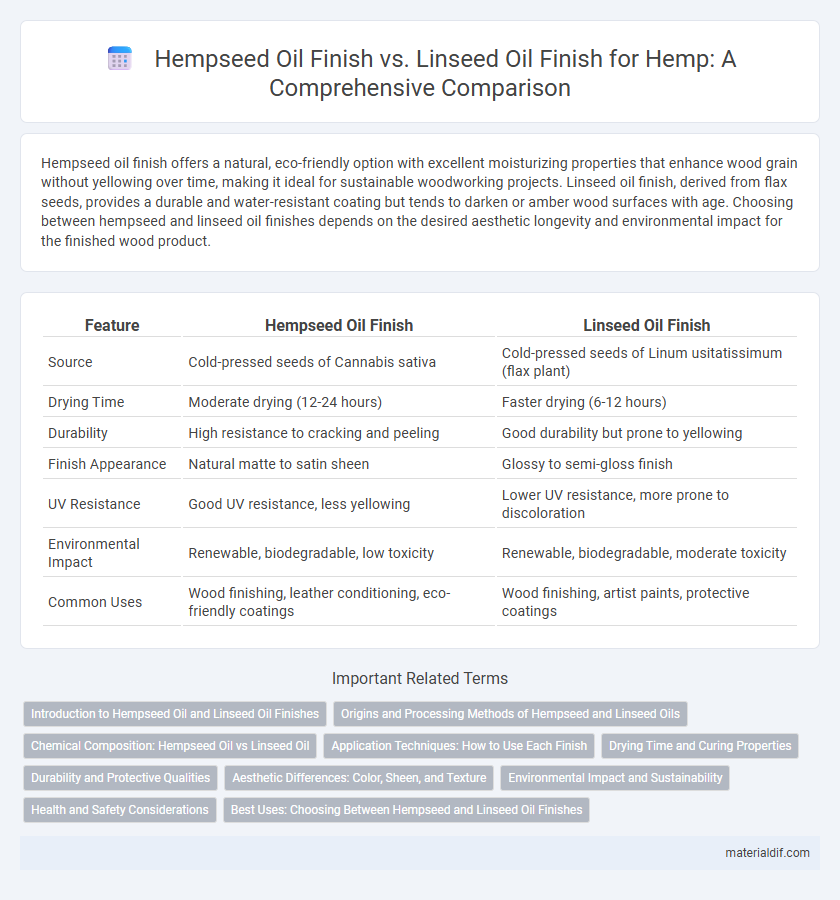
| Feature | Hempseed Oil Finish | Linseed Oil Finish |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Cold-pressed seeds of Cannabis sativa | Cold-pressed seeds of Linum usitatissimum (flax plant) |
| Drying Time | Moderate drying (12-24 hours) | Faster drying (6-12 hours) |
| Durability | High resistance to cracking and peeling | Good durability but prone to yellowing |
| Finish Appearance | Natural matte to satin sheen | Glossy to semi-gloss finish |
| UV Resistance | Good UV resistance, less yellowing | Lower UV resistance, more prone to discoloration |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, low toxicity | Renewable, biodegradable, moderate toxicity |
| Common Uses | Wood finishing, leather conditioning, eco-friendly coatings | Wood finishing, artist paints, protective coatings |
Introduction to Hempseed Oil and Linseed Oil Finishes
Hempseed oil finish is derived from the seeds of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its natural resistance to oxidation and ability to provide a durable, non-toxic coating that enhances wood grain while offering water-repellent properties. Linseed oil finish, extracted from flax seeds, is widely used for its deep penetration into wood fibers, creating a flexible, protective layer that ages to a rich amber tone. Both finishes serve as eco-friendly options with distinct drying times and durability, making them popular choices for sustainable woodworking and furniture restoration.
Origins and Processing Methods of Hempseed and Linseed Oils
Hempseed oil is extracted from the seeds of the Cannabis sativa plant, primarily through cold-pressing methods that preserve its rich omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, ensuring a natural, non-toxic finish. Linseed oil, derived from flax seeds of the Linum usitatissimum plant, undergoes either raw pressing or heat treatment, with boiled linseed oil incorporating drying agents for faster curing. The distinct botanical origins and extraction techniques influence the oils' drying times, durability, and environmental impact in wood finishing applications.
Chemical Composition: Hempseed Oil vs Linseed Oil
Hempseed oil contains a balanced composition of polyunsaturated fatty acids, predominantly linoleic acid (omega-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3), which contributes to its drying properties and resistance to oxidation in finishes. Linseed oil is rich in alpha-linolenic acid, typically around 50-60%, making it highly prone to polymerization and forming a durable, hard film when used in wood finishes. The higher omega-3 fatty acid content in linseed oil results in faster drying and harder finishes compared to hempseed oil, which has a more balanced fatty acid profile and imparts a slightly softer and more flexible finish.
Application Techniques: How to Use Each Finish
Hempseed oil finish requires gentle application with a soft cloth or brush, allowing it to penetrate the wood's pores for a natural, matte sheen, typically followed by multiple thin coats for enhanced durability. Linseed oil finish, often boiled for faster drying, should be applied in thin layers with a cloth or brush, sanding lightly between coats to achieve a smooth, glossy surface. Both finishes benefit from curing time in a well-ventilated area, but hempseed oil emphasizes subtle texture preservation while linseed oil enhances wood grain depth and gloss.
Drying Time and Curing Properties
Hempseed oil finish generally dries faster than linseed oil finish, typically requiring 24 to 48 hours to become tack-free, while linseed oil may take 48 to 72 hours or longer depending on conditions. Hempseed oil has superior curing properties due to its balanced profile of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, promoting a harder, more durable finish that resists yellowing. Linseed oil, derived from flax seeds, contains higher levels of linolenic acid, which can lead to a slower curing process and potential uneven drying under low-oxygen environments.
Durability and Protective Qualities
Hempseed oil finish offers superior durability due to its high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, which polymerize into a tough, water-resistant coating that protects wood surfaces longer than linseed oil. Unlike linseed oil finish, hempseed oil exhibits better resistance against cracking, peeling, and UV damage, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Its enhanced protective qualities reduce maintenance frequency, preserving the wood's appearance and structural integrity over time.
Aesthetic Differences: Color, Sheen, and Texture
Hempseed oil finish imparts a natural, light amber hue with a smooth, matte sheen that highlights wood grain subtly, while linseed oil finish produces a richer, warmer tone with a glossier surface enhancing depth and contrast. The texture of hempseed oil finish feels softer and less sticky, offering a more natural tactile experience compared to the slightly tacky and thicker feel of linseed oil finish. Both finishes enrich wood appearance, but hempseed oil is preferred for a muted, earthy look whereas linseed oil suits those seeking a polished, vibrant effect.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hempseed oil finish offers a significantly lower environmental impact than linseed oil finish due to its faster growth cycle and lower water usage, making it a more sustainable option in wood treatment and preservation. The cultivation of hemp absorbs more CO2 per hectare compared to flax, contributing to carbon sequestration and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike linseed oil, hempseed oil also requires fewer pesticides and synthetic fertilizers, enhancing its eco-friendly profile and minimizing soil degradation.
Health and Safety Considerations
Hempseed oil finish is prized for its nontoxic, food-safe properties, making it ideal for surfaces that come into contact with food or skin, while linseed oil finish, derived from flaxseed, may contain trace amounts of toxins unless fully purified. Hempseed oil naturally resists mold and UV damage without harmful additives, enhancing indoor air quality and reducing health risks associated with chemical off-gassing. Both oils improve wood durability, but hempseed oil's superior safety profile and faster drying time make it a preferred choice for health-conscious consumers.
Best Uses: Choosing Between Hempseed and Linseed Oil Finishes
Hempseed oil finish offers superior UV resistance and faster drying times, making it ideal for outdoor furniture and wooden surfaces exposed to sunlight. Linseed oil finish provides a deeper, rich patina and is preferred for indoor woodwork, such as antique restoration and fine furniture, where enhanced grain and color are desired. Selecting between hempseed and linseed oil finishes depends on the project's exposure conditions and desired aesthetic longevity.
Hempseed Oil Finish vs Linseed Oil Finish Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com