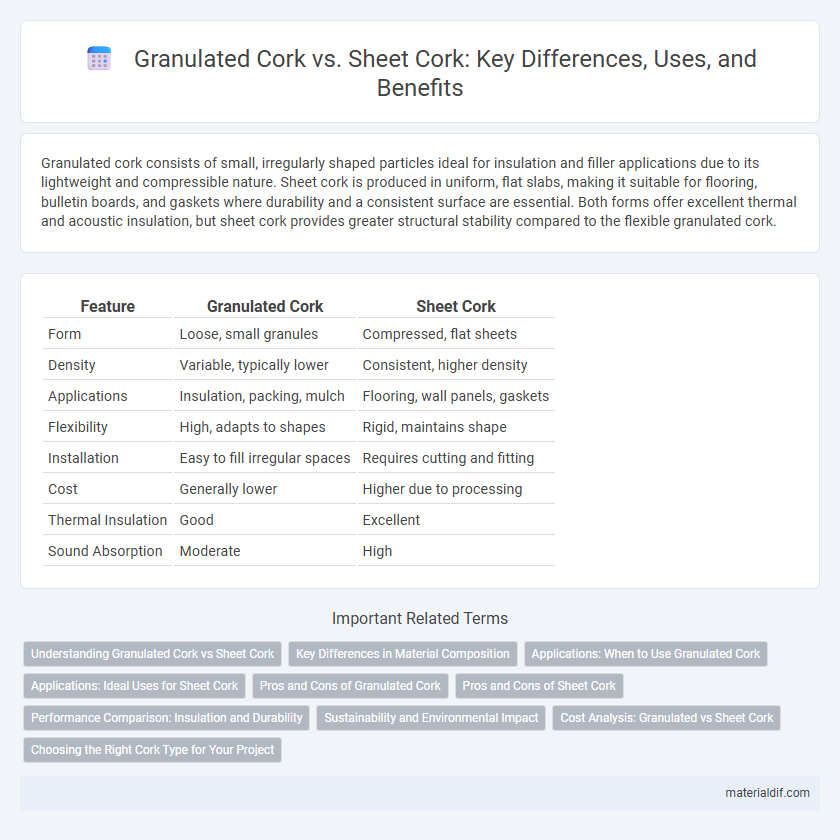
Granulated cork consists of small, irregularly shaped particles ideal for insulation and filler applications due to its lightweight and compressible nature. Sheet cork is produced in uniform, flat slabs, making it suitable for flooring, bulletin boards, and gaskets where durability and a consistent surface are essential. Both forms offer excellent thermal and acoustic insulation, but sheet cork provides greater structural stability compared to the flexible granulated cork.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Granulated Cork | Sheet Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Loose, small granules | Compressed, flat sheets |
| Density | Variable, typically lower | Consistent, higher density |
| Applications | Insulation, packing, mulch | Flooring, wall panels, gaskets |
| Flexibility | High, adapts to shapes | Rigid, maintains shape |
| Installation | Easy to fill irregular spaces | Requires cutting and fitting |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to processing |
| Thermal Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate | High |
Understanding Granulated Cork vs Sheet Cork
Granulated cork consists of small, loose particles derived from ground cork bark, providing flexibility and excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties commonly used in flooring underlays and composite materials. Sheet cork is produced by pressing and bonding cork granules into uniform, solid sheets ideal for wall coverings, bulletin boards, and crafts due to its durability and ease of installation. Both forms retain cork's natural characteristics of lightweight, moisture resistance, and eco-friendliness, but sheet cork offers structural stability while granulated cork excels in adaptability for mixed applications.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Granulated cork consists of small, irregular particles of cork harvested from the bark, providing a flexible and compressible material ideal for insulation and sealing applications. Sheet cork is made by compressing and binding larger cork granules into uniform, dense sheets, offering consistent thickness and durability for flooring and wall coverings. The primary distinction lies in granulated cork's loose particulate form versus sheet cork's solid, engineered structure, influencing their respective usage and performance characteristics.
Applications: When to Use Granulated Cork
Granulated cork is ideal for applications requiring flexibility and insulation, such as underlayment in flooring, soundproofing, and thermal insulation panels. Its loose, crumbly texture allows it to fill gaps and conform to irregular shapes, making it preferred for packing materials and sealing compounds. Sheet cork, by contrast, is better suited for structural uses like cork boards, gaskets, and wall coverings where uniform thickness and durability are essential.
Applications: Ideal Uses for Sheet Cork
Sheet cork is widely used for flooring, bulletin boards, wall tiles, and insulation due to its uniform thickness and durability. It offers excellent moisture resistance and sound absorption, making it ideal for interior design and construction projects. Granulated cork, in contrast, is typically used for composite materials, sealing, and gasketing applications where flexibility and moldability are needed.
Pros and Cons of Granulated Cork
Granulated cork offers excellent flexibility and adaptability, making it ideal for insulation, soundproofing, and cushioning applications. Its granular form allows for easy mixing with other materials, enhancing versatility but sacrificing the structural integrity found in sheet cork. However, granulated cork can be more prone to displacement and moisture absorption, which may reduce durability compared to the more rigid, dense sheet cork panels.
Pros and Cons of Sheet Cork
Sheet cork offers a uniform thickness and smooth surface, making it ideal for flooring, wall tiles, and decorative applications where consistency is crucial. Its durability and ease of installation provide a long-lasting and aesthetically pleasing finish, but it can be more expensive and less flexible in fitting irregular shapes compared to granulated cork. While sheet cork excels in structural applications, it lacks the eco-friendly recyclability and insulation versatility that granulated cork offers.
Performance Comparison: Insulation and Durability
Granulated cork offers superior insulation properties due to its ability to fill irregular spaces and provide excellent thermal resistance, making it ideal for energy-efficient applications. Sheet cork delivers enhanced durability with a dense, uniform structure that resists wear, compression, and moisture, ensuring long-lasting performance in flooring and wall coverings. Both types excel in eco-friendly construction, but the choice depends on application-specific insulation needs versus durability requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Granulated cork is produced by recycling leftover cork pieces, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact through circular resource use. Sheet cork, typically harvested directly from cork oak bark, supports sustainable forestry by promoting bark regeneration without tree felling, preserving biodiversity and carbon sequestration. Both forms contribute to eco-friendly practices, with granulated cork excelling in resource efficiency and sheet cork fostering long-term forest health.
Cost Analysis: Granulated vs Sheet Cork
Granulated cork typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to sheet cork due to its production from cork waste, resulting in lower material expenses and flexible application options. Sheet cork, while generally pricier, provides superior durability and aesthetic appeal for purposes like wall coverings or flooring, justifying higher initial investment. Selecting between granulated and sheet cork depends on project budget constraints, desired appearance, and long-term performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Cork Type for Your Project
Granulated cork offers flexibility and superior insulation qualities, making it ideal for irregular surfaces and soundproofing applications. Sheet cork provides uniform thickness and durability, perfect for flooring, wall panels, and decorative uses that require a smooth, consistent finish. Selecting the right cork type depends on your project's specific needs for texture, application method, and performance requirements.
Granulated Cork vs Sheet Cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com