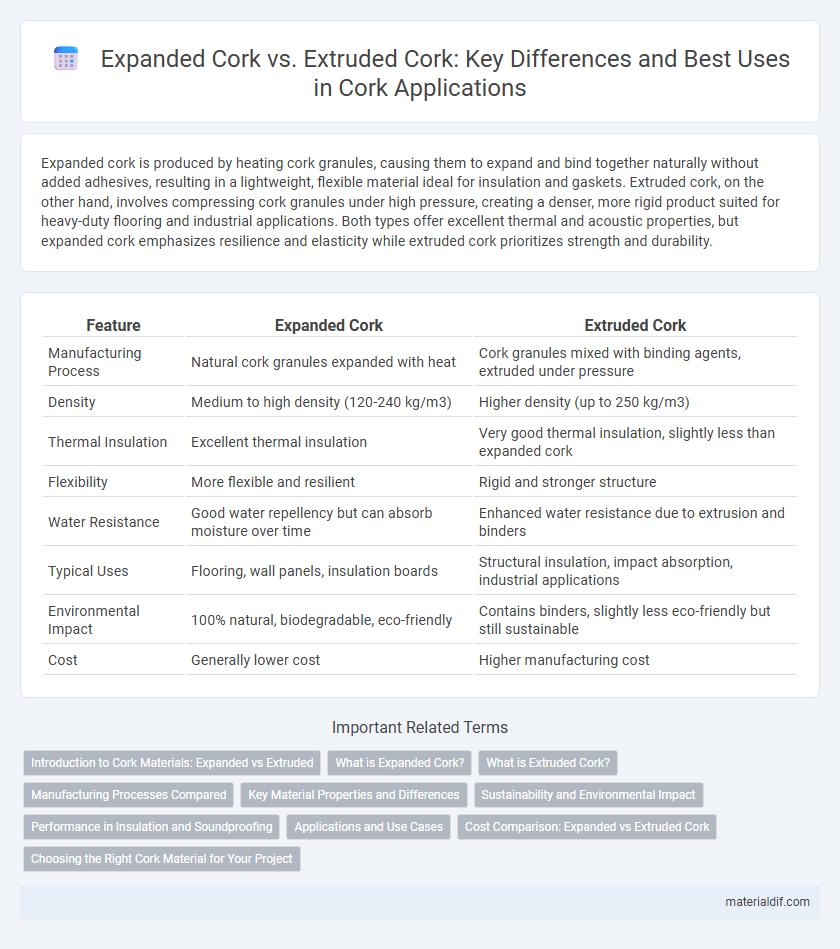
Expanded cork is produced by heating cork granules, causing them to expand and bind together naturally without added adhesives, resulting in a lightweight, flexible material ideal for insulation and gaskets. Extruded cork, on the other hand, involves compressing cork granules under high pressure, creating a denser, more rigid product suited for heavy-duty flooring and industrial applications. Both types offer excellent thermal and acoustic properties, but expanded cork emphasizes resilience and elasticity while extruded cork prioritizes strength and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Expanded Cork | Extruded Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Natural cork granules expanded with heat | Cork granules mixed with binding agents, extruded under pressure |
| Density | Medium to high density (120-240 kg/m3) | Higher density (up to 250 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent thermal insulation | Very good thermal insulation, slightly less than expanded cork |
| Flexibility | More flexible and resilient | Rigid and stronger structure |
| Water Resistance | Good water repellency but can absorb moisture over time | Enhanced water resistance due to extrusion and binders |
| Typical Uses | Flooring, wall panels, insulation boards | Structural insulation, impact absorption, industrial applications |
| Environmental Impact | 100% natural, biodegradable, eco-friendly | Contains binders, slightly less eco-friendly but still sustainable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
Introduction to Cork Materials: Expanded vs Extruded
Expanded cork is produced by heating cork granules until they expand and naturally bind, resulting in a lightweight, flexible material ideal for insulation and acoustic applications. Extruded cork involves combining cork granules with natural resin binders and compressing them through an extrusion process, yielding a denser, more uniform product with enhanced mechanical strength suitable for flooring and industrial uses. Both materials leverage cork's natural properties but differ in manufacturing methods that influence their performance and application range.
What is Expanded Cork?
Expanded cork is a natural, lightweight material produced by heating cork granules until they expand and bond together without any additives, resulting in a versatile and highly sustainable product. It offers excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties, making it ideal for construction and design applications. Unlike extruded cork, expanded cork retains the cellular structure of cork, preserving its elasticity and resilience.
What is Extruded Cork?
Extruded cork is a manufactured cork product created by grinding natural cork granules and binding them with resin before shaping under high pressure through an extrusion process. This method produces a dense, uniform material ideal for sealing, insulation, and vibration damping applications due to its consistent texture and enhanced mechanical properties. Compared to expanded cork, extruded cork offers improved structural integrity and dimensional stability, making it suitable for industrial and construction uses.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Expanded cork is produced by heating natural cork granules until they expand and fuse without additives, resulting in a lightweight, flexible material with natural cellular structure. Extruded cork undergoes a process where cork powder is mixed with a binder and then mechanically forced through a mold, creating a denser, more uniform panel often used for insulation. The manufacturing process of expanded cork emphasizes thermal expansion of granules, while extruded cork relies on compression and binding agents to achieve its shape and performance characteristics.
Key Material Properties and Differences
Expanded cork is a natural, lightweight material made by heating cork granules, resulting in a porous structure with excellent thermal insulation and sound absorption properties. Extruded cork undergoes additional mechanical compression, creating a denser and more rigid material with higher compressive strength, making it suitable for structural applications. While expanded cork excels in flexibility and impact resistance, extruded cork provides superior durability and moisture resistance, influencing their specific uses in construction and design.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Expanded cork is produced by heating raw cork granules, creating a natural, biodegradable insulation material with no chemical additives, making it highly sustainable and environmentally friendly. Extruded cork involves compressing cork powder with organic binders, which can introduce synthetic components and reduce biodegradability, impacting its ecological footprint. Both materials offer thermal insulation benefits, but expanded cork generally provides a lower environmental impact due to its minimal processing and 100% natural composition.
Performance in Insulation and Soundproofing
Expanded cork offers superior insulation performance due to its cellular structure that traps air effectively, providing excellent thermal resistance and energy efficiency. Extruded cork, while denser and more uniform, delivers enhanced soundproofing qualities by absorbing and dampening noise vibrations more efficiently. Both materials excel in sustainability and durability but serve different performance needs in building applications.
Applications and Use Cases
Expanded cork offers superior thermal insulation and is commonly used in flooring underlays, wall insulation, and soundproofing panels for residential and commercial buildings. Extruded cork, known for its higher density and durability, is ideal for industrial applications such as gaskets, seals, and vibration dampening in automotive and machinery sectors. Both materials provide eco-friendly solutions, with expanded cork excelling in lightweight, flexible applications and extruded cork favored where mechanical strength and resistance to compression are critical.
Cost Comparison: Expanded vs Extruded Cork
Expanded cork generally costs less than extruded cork due to its simpler manufacturing process and use of natural, less processed materials. Extruded cork involves additional heat and pressure treatments, raising production costs and resulting in a higher price per cubic meter. Buyers often choose expanded cork for budget-friendly insulation solutions, while extruded cork is preferred for applications requiring higher density and durability despite the increased cost.
Choosing the Right Cork Material for Your Project
Expanded cork offers excellent thermal insulation and is lightweight, making it ideal for eco-friendly construction projects requiring soundproofing and moisture resistance. Extruded cork provides higher density, durability, and compressive strength, suitable for heavy-duty applications like flooring underlays and industrial uses. Selecting the right cork material depends on project-specific demands for insulation performance, mechanical load, and environmental exposure.
Expanded Cork vs Extruded Cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com