Hand-harvested cork ensures higher quality by preserving the bark's natural integrity, resulting in better durability and aesthetic appeal. Mechanically-harvested cork tends to damage the texture, leading to lower-grade material that may compromise performance. Choosing hand-harvested cork supports sustainable practices and superior craftsmanship essential for premium pet products.
Table of Comparison
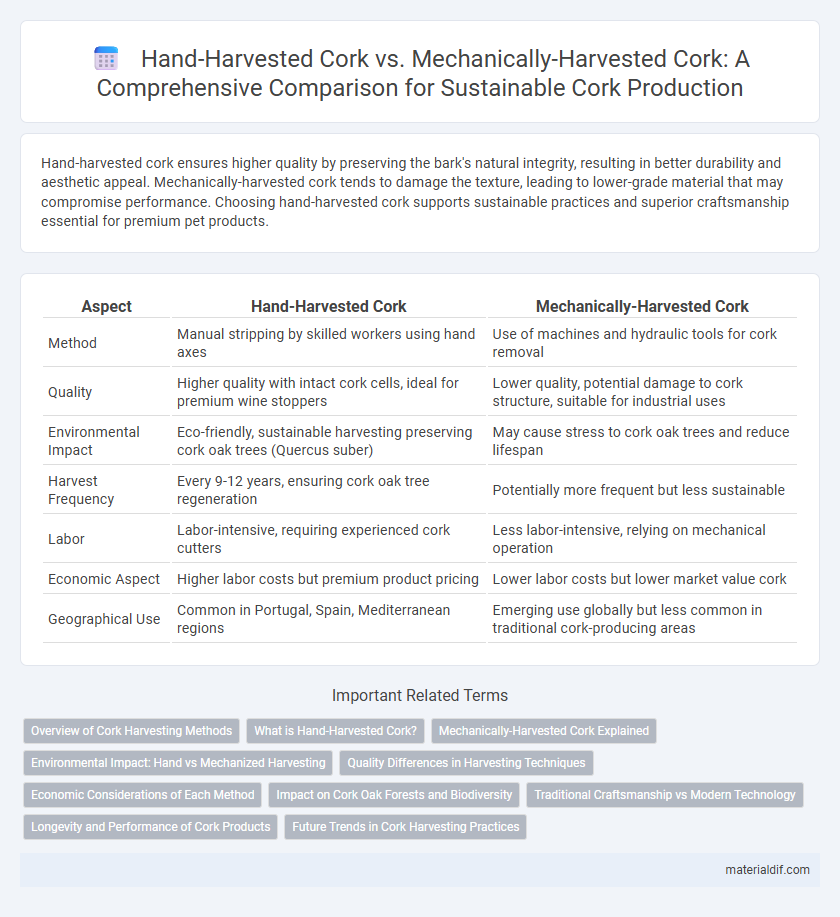
| Aspect | Hand-Harvested Cork | Mechanically-Harvested Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Manual stripping by skilled workers using hand axes | Use of machines and hydraulic tools for cork removal |
| Quality | Higher quality with intact cork cells, ideal for premium wine stoppers | Lower quality, potential damage to cork structure, suitable for industrial uses |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable harvesting preserving cork oak trees (Quercus suber) | May cause stress to cork oak trees and reduce lifespan |
| Harvest Frequency | Every 9-12 years, ensuring cork oak tree regeneration | Potentially more frequent but less sustainable |
| Labor | Labor-intensive, requiring experienced cork cutters | Less labor-intensive, relying on mechanical operation |
| Economic Aspect | Higher labor costs but premium product pricing | Lower labor costs but lower market value cork |
| Geographical Use | Common in Portugal, Spain, Mediterranean regions | Emerging use globally but less common in traditional cork-producing areas |
Overview of Cork Harvesting Methods
Hand-harvested cork involves skilled workers carefully stripping the bark from cork oak trees using specialized axes, ensuring the tree's health and sustainable regrowth over decades. Mechanically-harvested cork employs machinery to expedite bark removal but may risk damaging the tree and reducing cork quality if not managed properly. Traditional hand-harvesting remains the preferred method for premium cork products due to its precision and ecological benefits.
What is Hand-Harvested Cork?
Hand-harvested cork involves skilled workers carefully stripping the bark from cork oak trees using traditional hand tools, preserving the tree's health and ensuring high-quality material. This method, practiced mainly in Portugal and Spain, allows for selective harvesting that maintains the cork's cellular structure and durability, making it ideal for premium wine stoppers and sustainable products. Hand-harvesting supports local economies and biodiversity by promoting longer tree lifespans compared to mechanized methods.
Mechanically-Harvested Cork Explained
Mechanically-harvested cork involves the use of specialized machines designed to strip the bark from cork oak trees without harming them, significantly increasing harvesting efficiency compared to traditional hand-harvesting methods. This technology reduces labor costs and harvesting time while maintaining the cork's high quality, essential for producing premium cork products. Advances in mechanical harvesting also promote sustainable forest management by ensuring the cork oak's health and longevity after each harvest cycle.
Environmental Impact: Hand vs Mechanized Harvesting
Hand-harvested cork preserves the integrity of cork oak trees by selectively removing bark without damaging the tree, promoting long-term forest health and biodiversity. Mechanized harvesting can cause more significant damage to the bark and underlying tissues, potentially reducing the tree's lifespan and negatively impacting surrounding ecosystems. The manual method supports sustainable cork production by minimizing soil disturbance and maintaining natural habitats, whereas mechanized processes often increase carbon emissions and soil compaction.
Quality Differences in Harvesting Techniques
Hand-harvested cork maintains superior quality due to careful stripping that preserves the bark's cellular structure, resulting in a more elastic and durable material. Mechanically-harvested cork often causes microscopic damage and uneven thickness, which can compromise its insulating properties and reduce its commercial value. The traditional manual method ensures better grain consistency and fewer defects, critical for premium cork products such as wine stoppers and flooring.
Economic Considerations of Each Method
Hand-harvested cork requires skilled laborers, resulting in higher wages and increased production costs, but it yields premium quality cork with better economic value in luxury markets. Mechanically-harvested cork lowers labor expenses and boosts efficiency, making it suitable for large-scale production, although it often compromises cork quality, reducing its market price. The economic trade-off involves balancing higher initial labor investments against long-term gains in product quality and market positioning.
Impact on Cork Oak Forests and Biodiversity
Hand-harvested cork preserves the integrity of cork oak forests by carefully removing bark without damaging the trees, promoting long-term forest health and biodiversity. Mechanically-harvested cork, while efficient, risks harming the cork oaks and can disrupt habitats, leading to reduced species diversity. Sustainable manual harvesting supports the resilience of cork oak ecosystems, crucial for endangered species and carbon sequestration.
Traditional Craftsmanship vs Modern Technology
Hand-harvested cork preserves the traditional craftsmanship dating back centuries, relying on skilled laborers to carefully strip the bark without damaging the cork oak trees, ensuring sustainability and high-quality cork production. Mechanically-harvested cork leverages modern technology to increase efficiency, reduce labor costs, and scale production, although it often risks compromising the delicate tree bark and the unique texture prized in premium cork products. The balance between preserving cultural heritage and adopting innovative machinery defines the evolving landscape of the cork industry in regions like Portugal and Spain.
Longevity and Performance of Cork Products
Hand-harvested cork preserves the cellular structure of cork bark, enhancing the longevity and performance of cork products by maintaining natural elasticity and durability. Mechanically-harvested cork often results in compressed or damaged cells, which can reduce the material's resilience and lifespan in applications such as flooring and wine stoppers. Studies indicate that hand-harvested cork products exhibit superior moisture resistance and dimensional stability, contributing to sustained performance over time.
Future Trends in Cork Harvesting Practices
Future trends in cork harvesting emphasize sustainable methods, with hand-harvested cork maintaining its dominance due to the precision and minimal tree damage it ensures. Mechanically-harvested cork is undergoing innovations aimed at improving efficiency and reducing labor costs, though concerns about long-term bark health persist. Advances in technology and ecological research are driving hybrid approaches that combine manual expertise with mechanized tools to optimize yield and environmental impact in Cork oak forests.
Hand-harvested cork vs Mechanically-harvested cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com