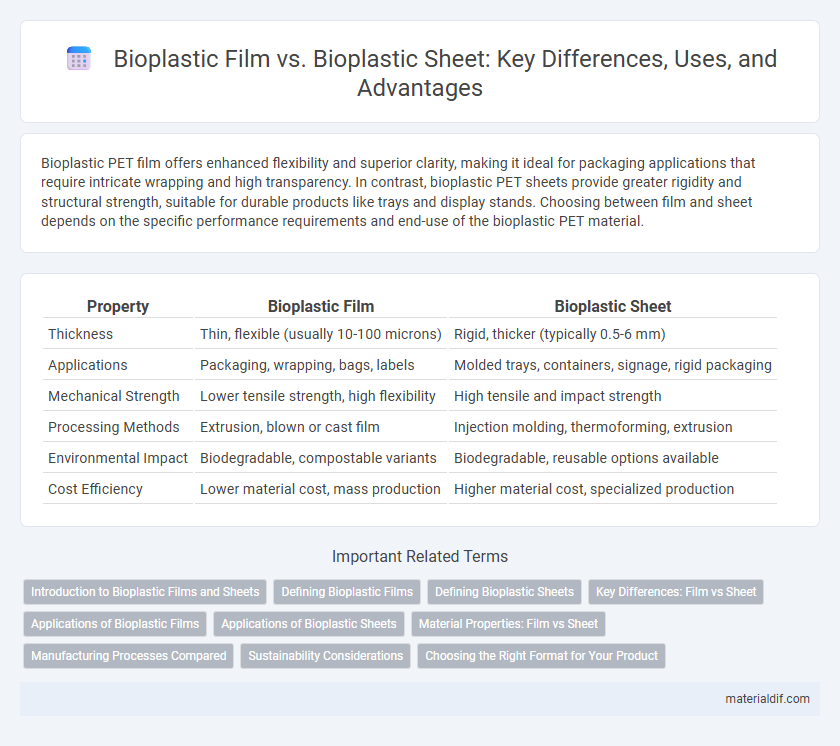
Bioplastic PET film offers enhanced flexibility and superior clarity, making it ideal for packaging applications that require intricate wrapping and high transparency. In contrast, bioplastic PET sheets provide greater rigidity and structural strength, suitable for durable products like trays and display stands. Choosing between film and sheet depends on the specific performance requirements and end-use of the bioplastic PET material.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bioplastic Film | Bioplastic Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Thin, flexible (usually 10-100 microns) | Rigid, thicker (typically 0.5-6 mm) |
| Applications | Packaging, wrapping, bags, labels | Molded trays, containers, signage, rigid packaging |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength, high flexibility | High tensile and impact strength |
| Processing Methods | Extrusion, blown or cast film | Injection molding, thermoforming, extrusion |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable variants | Biodegradable, reusable options available |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower material cost, mass production | Higher material cost, specialized production |
Introduction to Bioplastic Films and Sheets
Bioplastic films and sheets serve distinct purposes in sustainable packaging and manufacturing, with films typically used for flexible applications like wrapping and bags, while sheets provide rigid structures for containers and trays. Composed from biodegradable polymers such as polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), bioplastic films offer transparency, flexibility, and moisture barrier properties suitable for food packaging. Bioplastic sheets combine durability and moldability, making them ideal for eco-friendly alternatives in automotive parts, consumer goods, and medical device housings.
Defining Bioplastic Films
Bioplastic films are thin, flexible layers typically used for packaging, offering biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional plastics. These films are engineered for properties like water resistance, gas permeability, and mechanical strength, making them suitable for food wrapping and agricultural applications. Unlike bioplastic sheets, which are thicker and used for molded products, films emphasize flexibility and transparency.
Defining Bioplastic Sheets
Bioplastic sheets are solid, flat materials produced from renewable biomass sources such as cornstarch, sugarcane, or cellulose, designed for applications requiring rigidity and structural integrity. Unlike bioplastic films, which are thin, flexible, and used primarily for packaging and wrapping, sheets provide durability and can be thermoformed or cut for producing containers, trays, and other molded products. The biodegradability and compostability of bioplastic sheets depend on their polymer composition, with PLA, PHA, and cellulose-based variants offering environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional plastic sheets.
Key Differences: Film vs Sheet
Film and sheet bioplastics differ primarily in thickness and application versatility, with films typically under 0.5 mm used for flexible packaging like bags and wraps, while sheets exceed 0.5 mm and serve in rigid applications such as trays and containers. The production process varies as films are often produced by extrusion or casting to achieve thin, pliable materials, whereas sheets are manufactured through thermoforming or compression molding for structural strength. Mechanical properties also differ; films emphasize tensile strength and flexibility for durability in wrapping, while sheets prioritize rigidity and impact resistance to maintain shape and protect contents.
Applications of Bioplastic Films
Bioplastic films are widely used in packaging applications due to their flexibility, transparency, and biodegradability, making them ideal for food wraps, agricultural mulch films, and medical packaging. Their ability to provide moisture barriers and extend shelf life supports sustainable alternatives to conventional plastic films. These films also find applications in lamination and disposable items, contributing significantly to eco-friendly product cycles.
Applications of Bioplastic Sheets
Bioplastic sheets offer versatile applications across packaging, automotive interiors, and consumer goods due to their rigidity and durability. Their ability to be thermoformed into trays, containers, and protective casings enhances product protection while reducing environmental impact. Industries favor bioplastic sheets for sustainable alternatives in manufacturing eco-friendly household items and electronic housings.
Material Properties: Film vs Sheet
Bioplastic films typically exhibit higher flexibility, transparency, and tensile strength, making them ideal for packaging applications requiring durability and clarity. Bioplastic sheets possess greater rigidity, thickness, and impact resistance, suitable for structural uses and thermoforming processes. Material density and moisture barrier properties vary between film and sheet, influencing their performance in food preservation and industrial applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Film bioplastics are typically produced through blown or cast film extrusion, offering flexibility and thin profiles ideal for packaging, while bioplastic sheets are manufactured via compression molding or thermoforming, resulting in thicker, rigid materials suitable for structural applications. The film extrusion process involves rapid cooling to achieve uniform thickness and clarity, whereas sheet production emphasizes controlled heating and pressure to enhance dimensional stability and mechanical strength. Manufacturing parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cooling rates are optimized differently to cater to the distinct functional requirements of bioplastic films versus sheets.
Sustainability Considerations
Bioplastic films offer higher biodegradability and lower carbon footprints due to their thin material layers, enhancing waste reduction in single-use packaging. Sheets provide increased durability for reuse and mechanical recycling, supporting circular economy models through longer product lifecycles. Choosing between film and sheet formats depends on end-of-life scenarios and environmental impact assessments tailored to application-specific sustainability goals.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Product
Selecting the appropriate bioplastic format between film and sheet depends on the product's intended application and performance requirements. Bioplastic films offer superior flexibility and are ideal for packaging that demands lightweight, moisture-resistant properties, while bioplastic sheets provide rigidity and structural strength suited for durable items like trays and containers. Evaluating factors such as thickness, tensile strength, and environmental impact ensures the chosen format aligns with sustainability goals and functional needs.
Film vs Sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com