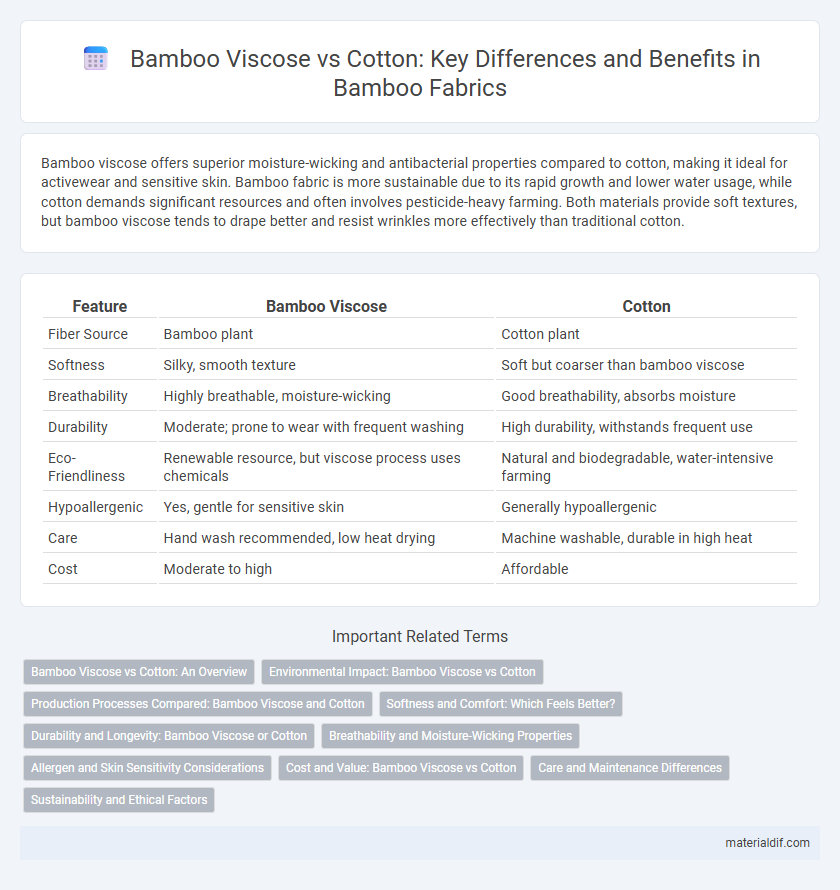
Bamboo viscose offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties compared to cotton, making it ideal for activewear and sensitive skin. Bamboo fabric is more sustainable due to its rapid growth and lower water usage, while cotton demands significant resources and often involves pesticide-heavy farming. Both materials provide soft textures, but bamboo viscose tends to drape better and resist wrinkles more effectively than traditional cotton.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Viscose | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Source | Bamboo plant | Cotton plant |
| Softness | Silky, smooth texture | Soft but coarser than bamboo viscose |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Good breathability, absorbs moisture |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to wear with frequent washing | High durability, withstands frequent use |
| Eco-Friendliness | Renewable resource, but viscose process uses chemicals | Natural and biodegradable, water-intensive farming |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, gentle for sensitive skin | Generally hypoallergenic |
| Care | Hand wash recommended, low heat drying | Machine washable, durable in high heat |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable |
Bamboo Viscose vs Cotton: An Overview
Bamboo viscose fibers are derived from bamboo pulp through a chemical process, creating a soft, breathable fabric often compared to cotton for comfort and moisture-wicking properties. Unlike conventional cotton, which requires significant water and pesticide use, bamboo viscose production can be more sustainable, though it depends on the processing method's environmental impact. Both fabrics are hypoallergenic and biodegradable, but bamboo viscose typically offers better antibacterial qualities and a smoother texture suitable for sensitive skin.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo Viscose vs Cotton
Bamboo viscose production uses significantly less water and pesticides compared to conventional cotton farming, reducing its overall environmental impact. However, the chemical processing involved in bamboo viscose manufacturing can cause pollution if not managed properly. Sustainable practices in both materials are essential, but bamboo viscose offers a greener alternative in terms of resource consumption and land use.
Production Processes Compared: Bamboo Viscose and Cotton
Bamboo viscose production involves chemically treating bamboo fibers with solvents to dissolve and regenerate cellulose, resulting in a soft fabric with a lower environmental footprint compared to conventional methods. Cotton cultivation demands significant water, pesticides, and land resources, contributing to higher environmental stress. While bamboo viscose uses chemical processes that require energy and safe waste management, cotton's agricultural inputs make its production more resource-intensive overall.
Softness and Comfort: Which Feels Better?
Bamboo viscose is known for its exceptional softness, often compared to the feel of silk, making it a superior choice for comfort-sensitive fabrics. Its natural moisture-wicking properties keep skin dry and cool, enhancing overall comfort compared to traditional cotton. Cotton offers breathability and durability, but bamboo viscose excels in softness and temperature regulation, providing a more luxurious and comfortable feel.
Durability and Longevity: Bamboo Viscose or Cotton
Bamboo viscose fibers exhibit superior durability compared to cotton due to their natural strength and resistance to abrasion, which extends the lifespan of textiles. Unlike cotton, bamboo viscose maintains its structural integrity after multiple washes, reducing fabric thinning and pilling. This resilience makes bamboo viscose an ideal choice for long-lasting, sustainable clothing and home textiles.
Breathability and Moisture-Wicking Properties
Bamboo viscose outperforms cotton in breathability due to its naturally porous fiber structure, allowing better air circulation that keeps the skin cool and dry. Its superior moisture-wicking properties efficiently draw sweat away from the body, enhancing comfort during physical activity or hot weather. Cotton, while breathable, tends to retain moisture longer, often leading to a damp and less comfortable feel.
Allergen and Skin Sensitivity Considerations
Bamboo viscose is naturally hypoallergenic and antibacterial, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies. Its smooth fibers reduce irritation compared to cotton, which can sometimes cause allergic reactions due to pesticide residues or fiber roughness. Bamboo viscose also maintains better moisture-wicking properties, helping prevent skin irritation and promoting comfort for sensitive skin.
Cost and Value: Bamboo Viscose vs Cotton
Bamboo viscose often costs more than cotton due to its eco-friendly production process and sustainable sourcing, offering higher long-term value through biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties. Cotton, while generally more affordable upfront, requires intensive water and pesticide use, which can reduce its environmental value. Consumers seeking durable, hypoallergenic fabric with minimal ecological impact often find bamboo viscose provides a superior cost-to-value ratio despite the price difference.
Care and Maintenance Differences
Bamboo viscose requires gentle washing in cold water and air drying to maintain its softness, while cotton is more durable and can withstand higher temperatures in both washing and drying. Bamboo viscose is prone to shrinking and losing shape if exposed to heat, whereas cotton fibers are more resilient to repeated laundering. Proper care of bamboo viscose involves avoiding harsh detergents and bleach, which can damage the fabric, unlike cotton which tolerates a wider range of cleaning products.
Sustainability and Ethical Factors
Bamboo viscose offers significant sustainability advantages over conventional cotton, using less water and requiring fewer pesticides, which reduces environmental impact and promotes ethical farming practices. The rapid growth rate of bamboo allows for efficient land use and faster regeneration, making it a renewable resource compared to the longer cultivation cycles of cotton. Ethically, bamboo harvesting supports reduced chemical exposure for workers and lower greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with eco-friendly and socially responsible textile production standards.
Bamboo viscose vs cotton Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com