Bamboo particleboard offers greater durability and eco-friendliness compared to MDF due to its natural bamboo fibers, which provide enhanced strength and moisture resistance. MDF, made from wood fibers and resin, is generally less resistant to water and more prone to swelling and warping over time. Choosing bamboo particleboard supports sustainable forestry practices while delivering superior performance in furniture and interior applications.
Table of Comparison
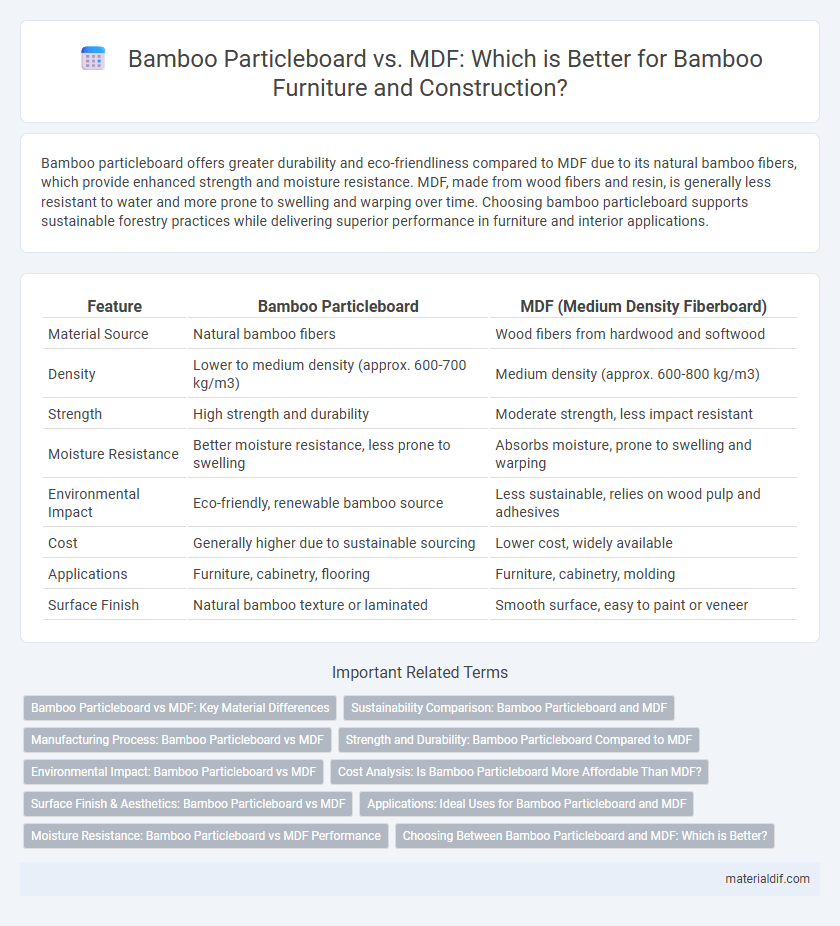
| Feature | Bamboo Particleboard | MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural bamboo fibers | Wood fibers from hardwood and softwood |
| Density | Lower to medium density (approx. 600-700 kg/m3) | Medium density (approx. 600-800 kg/m3) |
| Strength | High strength and durability | Moderate strength, less impact resistant |
| Moisture Resistance | Better moisture resistance, less prone to swelling | Absorbs moisture, prone to swelling and warping |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable bamboo source | Less sustainable, relies on wood pulp and adhesives |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable sourcing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Furniture, cabinetry, flooring | Furniture, cabinetry, molding |
| Surface Finish | Natural bamboo texture or laminated | Smooth surface, easy to paint or veneer |
Bamboo Particleboard vs MDF: Key Material Differences
Bamboo particleboard features natural bamboo fibers bonded with resin, offering higher durability and moisture resistance compared to MDF, which is made from compressed wood fibers and resins. Bamboo particleboard typically exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced eco-friendliness due to bamboo's rapid renewability. MDF provides a smoother surface ideal for painting but lacks the structural robustness and water resistance found in bamboo particleboard.
Sustainability Comparison: Bamboo Particleboard and MDF
Bamboo particleboard is significantly more sustainable than MDF due to its rapid renewability and lower environmental impact during production. Bamboo grows up to three times faster than hardwood trees used for MDF, requiring less water and no pesticides, which reduces carbon emissions and deforestation risks. In contrast, MDF relies on slower-growing wood fibers and often involves formaldehyde-based adhesives, contributing to higher toxicity and lower eco-friendliness.
Manufacturing Process: Bamboo Particleboard vs MDF
Bamboo particleboard is manufactured by compressing bamboo particles with resin under heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, sustainable panel with natural bamboo fibers enhancing strength. MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) is produced by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into fine fibers, which are then combined with wax and adhesive and pressed into panels, yielding a smooth surface ideal for detailed finishing. The bamboo particleboard manufacturing process emphasizes rapid growth and renewability of bamboo, offering ecological advantages over the wood-based MDF process that relies on tree pulp fibers.
Strength and Durability: Bamboo Particleboard Compared to MDF
Bamboo particleboard exhibits superior strength and durability compared to MDF due to its dense fibrous structure and natural lignin composition, which enhances resistance to impact and moisture. The high tensile strength of bamboo fibers gives bamboo particleboard increased load-bearing capacity, making it more suitable for heavy-duty applications. Unlike MDF, bamboo particleboard resists warping and swelling, ensuring longer lifespan in humid environments.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo Particleboard vs MDF
Bamboo particleboard offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to MDF due to bamboo's rapid growth rate and renewable nature, which reduces deforestation and carbon emissions. Bamboo particleboard production typically involves fewer harmful chemicals and lower formaldehyde emissions than traditional MDF, enhancing indoor air quality and sustainability. The biodegradability and carbon sequestration capabilities of bamboo further strengthen its environmental advantages over conventional wood fiber MDF.
Cost Analysis: Is Bamboo Particleboard More Affordable Than MDF?
Bamboo particleboard generally offers a more affordable alternative to MDF due to the rapid growth and renewability of bamboo, which reduces raw material costs. Manufacturing bamboo particleboard also consumes less energy compared to MDF, further lowering overall production expenses. While MDF might have slightly higher material costs, its consistent density and workability can justify its price in specific applications.
Surface Finish & Aesthetics: Bamboo Particleboard vs MDF
Bamboo particleboard offers a natural, textured surface with visible bamboo fibers that enhance its organic aesthetics, making it ideal for eco-friendly designs. MDF provides a smooth, uniform finish that accepts paint and veneers effortlessly, allowing versatile customization in furniture and cabinetry. Both materials differ significantly in surface appeal, with bamboo particleboard emphasizing natural beauty and MDF prioritizing a sleek, consistent look.
Applications: Ideal Uses for Bamboo Particleboard and MDF
Bamboo particleboard offers excellent durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for furniture, cabinetry, and interior wall panels in humid environments. MDF excels in smooth surface finishes and precise machining, suited for decorative molding, painted furniture, and intricate cabinetry designs. Both materials serve well in eco-friendly building projects, with bamboo particleboard favored for structural support and MDF preferred for aesthetic detailing.
Moisture Resistance: Bamboo Particleboard vs MDF Performance
Bamboo particleboard exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to MDF due to its natural density and fibrous structure, which limits water absorption and swelling. MDF tends to absorb more moisture, leading to quicker deterioration and warping in humid environments. This makes bamboo particleboard a preferred choice for applications requiring enhanced durability against moisture exposure.
Choosing Between Bamboo Particleboard and MDF: Which is Better?
Bamboo particleboard offers superior durability and eco-friendliness compared to MDF, as it is made from fast-growing bamboo fibers that provide higher strength and resistance to moisture. MDF, or medium-density fiberboard, is smoother and easier to paint but is generally less durable and more prone to water damage than bamboo particleboard. When choosing between bamboo particleboard and MDF, consider the intended use, moisture exposure, and environmental impact to select the best material for cabinetry, furniture, or flooring.
Bamboo particleboard vs MDF Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com