Dense-graded asphalt features tightly packed aggregate particles that create a durable, strong surface ideal for heavy traffic areas, while open-graded asphalt contains larger, more spaced aggregates allowing for enhanced drainage and reduced water accumulation. The choice between dense-graded and open-graded asphalt depends on specific project requirements such as load-bearing capacity and drainage needs. Proper selection ensures longevity, safety, and optimal performance of pavements in various environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
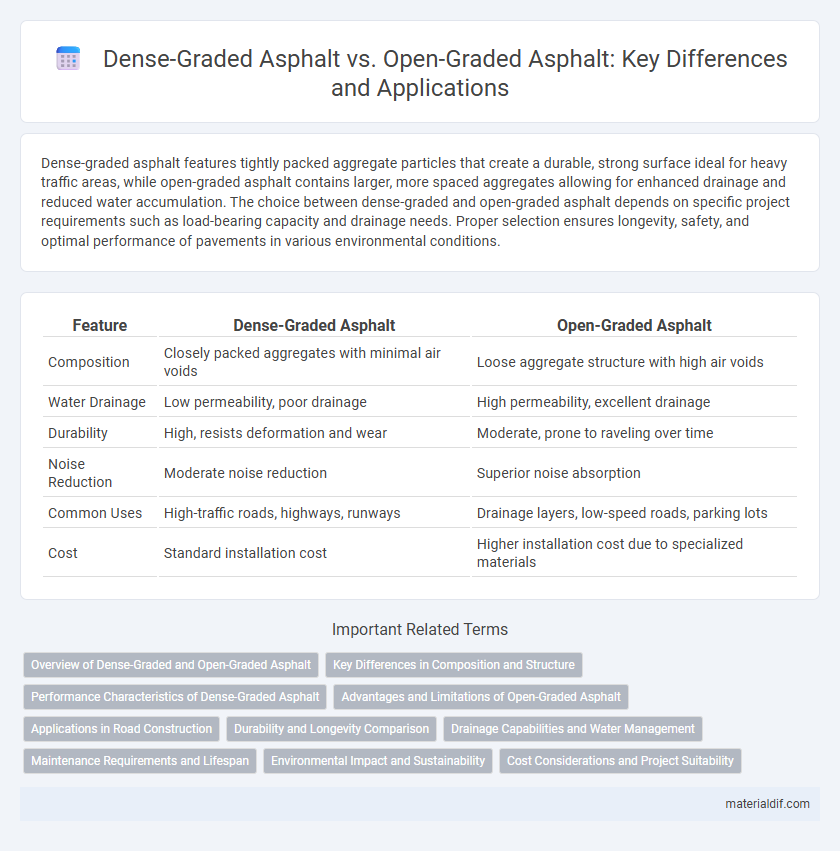
| Feature | Dense-Graded Asphalt | Open-Graded Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Closely packed aggregates with minimal air voids | Loose aggregate structure with high air voids |
| Water Drainage | Low permeability, poor drainage | High permeability, excellent drainage |
| Durability | High, resists deformation and wear | Moderate, prone to raveling over time |
| Noise Reduction | Moderate noise reduction | Superior noise absorption |
| Common Uses | High-traffic roads, highways, runways | Drainage layers, low-speed roads, parking lots |
| Cost | Standard installation cost | Higher installation cost due to specialized materials |
Overview of Dense-Graded and Open-Graded Asphalt
Dense-graded asphalt consists of a well-graded mix of aggregates that creates a compact, durable pavement surface with low air voids, enhancing resistance to deformation and water infiltration. Open-graded asphalt features a higher percentage of large aggregate particles and increased air voids, facilitating improved drainage and reducing splash and spray during wet conditions. These differences impact performance characteristics, with dense-graded asphalt favored for heavy-load areas and open-graded asphalt preferred for enhanced skid resistance and noise reduction.
Key Differences in Composition and Structure
Dense-graded asphalt features tightly packed aggregate particles with minimal air voids, resulting in a strong, durable pavement ideal for high-traffic roads. Open-graded asphalt contains larger, uniformly sized aggregates that create interconnected void spaces, enhancing permeability and reducing surface water accumulation. This structural difference influences drainage capabilities, noise reduction, and resistance to deformation under load.
Performance Characteristics of Dense-Graded Asphalt
Dense-graded asphalt exhibits superior load-bearing capacity and durability due to its tightly packed aggregate structure, which minimizes air voids and enhances resistance to deformation and rutting. This type of asphalt provides excellent surface smoothness and skid resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic roads and highways. Its dense composition also reduces water infiltration, contributing to improved pavement lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
Advantages and Limitations of Open-Graded Asphalt
Open-graded asphalt provides excellent drainage and reduces surface water accumulation, enhancing skid resistance and minimizing hydroplaning risks on pavements. It offers noise reduction benefits due to its porous structure but has limitations, including lower structural strength and higher susceptibility to clogging from debris and sediment. Maintenance requirements for open-graded asphalt are more frequent compared to dense-graded asphalt to preserve its permeability and performance.
Applications in Road Construction
Dense-graded asphalt is commonly used in high-traffic roads and highways due to its durability and smooth surface, which provides excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation. Open-graded asphalt, characterized by its high void content, is ideal for surface layers where drainage is critical, such as in rainy or snowy climates, because it effectively reduces water spray and improves skid resistance. Both types enhance pavement performance but are selected based on specific road construction needs, emphasizing structural strength for dense-graded and permeability for open-graded mixtures.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Dense-graded asphalt features tightly packed aggregates, enhancing its durability by resisting deformation and wear under heavy traffic loads, resulting in a longer service life. Open-graded asphalt offers superior drainage due to its high air void content, reducing water-related damage but generally exhibiting lower structural strength and shorter longevity. The choice between dense-graded and open-graded asphalt significantly impacts pavement durability and lifespan, with dense-graded asphalt preferred for high-load areas and open-graded asphalt used for improved water permeability and skid resistance.
Drainage Capabilities and Water Management
Dense-graded asphalt features tightly packed aggregates that limit water infiltration, providing a durable surface but less effective drainage. Open-graded asphalt contains larger aggregate particles with interconnected voids, allowing water to quickly pass through and reduce surface water accumulation. Effective water management in pavement design often leverages open-graded asphalt to minimize hydroplaning risks and improve road safety by enhancing drainage capabilities.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Dense-graded asphalt offers superior durability and requires less frequent maintenance due to its tightly packed aggregate structure, which resists water infiltration and deformation. Open-graded asphalt, with its higher void content, facilitates better drainage but demands more regular upkeep to prevent clogging and surface raveling. Lifespan-wise, dense-graded asphalt typically lasts longer under heavy traffic conditions, while open-graded asphalt is better suited for specific applications like noise reduction and stormwater management but may have a shorter service life.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dense-graded asphalt features a tightly packed aggregate structure that minimizes permeability, reducing water infiltration and runoff contamination, which helps protect surrounding ecosystems. Open-graded asphalt promotes better water drainage and reduces surface water accumulation, lowering hydroplaning risks and allowing for quicker drying, thus limiting pavement deterioration and extending lifespan. Both types contribute to sustainability by enabling the use of recycled materials and reducing urban heat island effects when properly designed and maintained.
Cost Considerations and Project Suitability
Dense-graded asphalt typically offers lower initial installation costs due to its widespread availability and simpler compaction process, making it suitable for high-traffic roads requiring durability and load-bearing capacity. Open-graded asphalt, although more expensive to install because of its specialized aggregates and drainage requirements, provides superior water permeability, reducing hydroplaning risks and is ideal for highways and areas prone to heavy rainfall. Project suitability depends on budget constraints and specific performance needs, with dense-graded preferred for cost-effective, heavy-duty paving and open-graded chosen for enhanced safety in wet conditions.
Dense-Graded Asphalt vs Open-Graded Asphalt Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com