Engineered quartz offers greater durability and uniformity compared to natural quartz, as it is manufactured by combining crushed quartz with resin and pigments to enhance strength and color consistency. Unlike natural quartz, which varies in appearance and requires regular sealing, engineered quartz is non-porous, making it more resistant to stains and easier to maintain. This makes engineered quartz a popular choice for kitchen and bathroom countertops where both aesthetics and functionality are important.
Table of Comparison
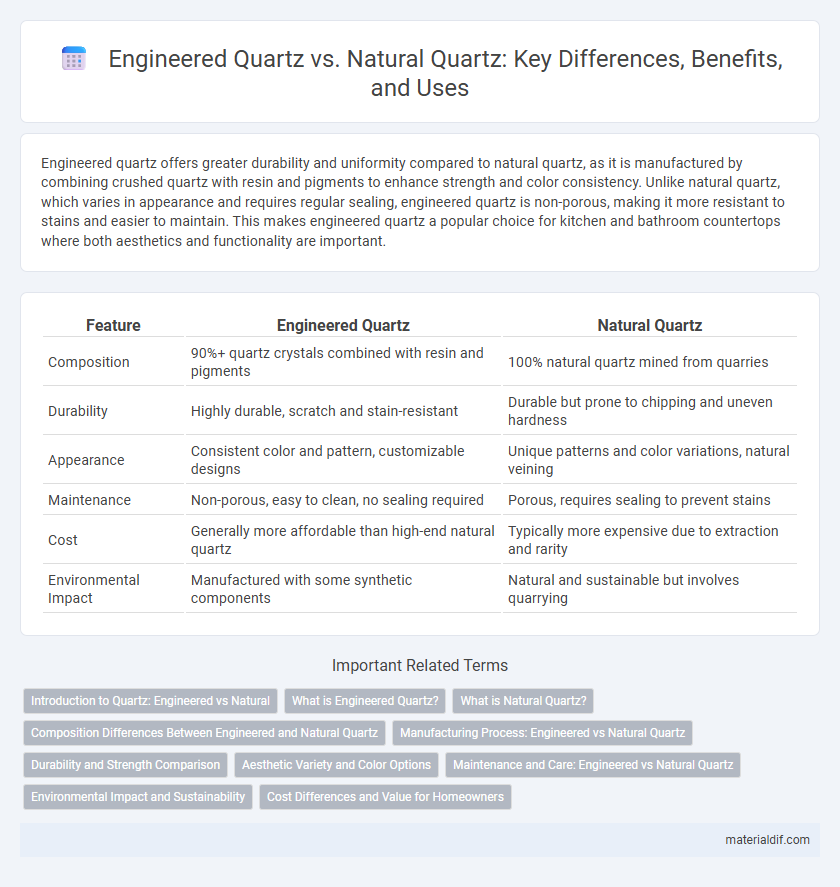
| Feature | Engineered Quartz | Natural Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 90%+ quartz crystals combined with resin and pigments | 100% natural quartz mined from quarries |
| Durability | Highly durable, scratch and stain-resistant | Durable but prone to chipping and uneven hardness |
| Appearance | Consistent color and pattern, customizable designs | Unique patterns and color variations, natural veining |
| Maintenance | Non-porous, easy to clean, no sealing required | Porous, requires sealing to prevent stains |
| Cost | Generally more affordable than high-end natural quartz | Typically more expensive due to extraction and rarity |
| Environmental Impact | Manufactured with some synthetic components | Natural and sustainable but involves quarrying |
Introduction to Quartz: Engineered vs Natural
Engineered quartz is a man-made composite material primarily composed of crushed natural quartz combined with resins and pigments, offering enhanced durability and a consistent appearance. Natural quartz, a crystalline mineral formed over millions of years, is prized for its unique patterns and natural variations, but it is less uniform and can be prone to chipping. Both materials are widely used in countertops and surfaces, with engineered quartz providing greater stain resistance and maintenance ease compared to natural quartz.
What is Engineered Quartz?
Engineered quartz is a man-made material composed of approximately 90% crushed natural quartz combined with resin and pigments to create a durable, non-porous surface. This engineered stone offers enhanced stain resistance, uniform appearance, and greater design versatility compared to natural quartz. Its consistent quality and low maintenance make it a popular choice for countertops, flooring, and wall cladding in residential and commercial spaces.
What is Natural Quartz?
Natural quartz is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of silicon dioxide, found abundantly in the Earth's crust. It forms through geological processes over millions of years, resulting in a durable and naturally occurring stone with unique color variations and patterns. Unlike engineered quartz, which is manufactured by combining crushed quartz with resins and pigments, natural quartz offers authentic mineral composition and organic aesthetics.
Composition Differences Between Engineered and Natural Quartz
Engineered quartz is composed of approximately 90-95% natural quartz crystals bound together by resins and polymers, creating a non-porous, durable surface ideal for countertops. Natural quartz, on the other hand, is a mineral primarily consisting of silicon dioxide (SiO2) found in various rock formations, exhibiting a porous structure with natural variations in texture and color. The resin content in engineered quartz enhances stain resistance and uniformity, whereas natural quartz offers unique, organic patterns and is more susceptible to chipping and staining due to its porous nature.
Manufacturing Process: Engineered vs Natural Quartz
Engineered quartz is manufactured by combining crushed natural quartz with resins and pigments, then curing the mixture under heat and pressure to create a highly durable, uniform surface. Natural quartz forms through geological processes over millions of years, resulting in heterogenous mineral compositions and textures. The controlled manufacturing process of engineered quartz allows for consistent quality and a wide range of color options compared to the variations found in natural quartz.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Engineered quartz is composed of approximately 90% natural quartz crystals combined with resins and pigments, resulting in a non-porous surface that offers superior durability and resistance to scratches and stains compared to natural quartz. Natural quartz, while inherently strong due to its crystalline structure, is more porous and susceptible to chipping, cracking, and staining because it lacks the resin-enhanced toughness of engineered variants. The high hardness rating of engineered quartz, typically around 7 on the Mohs scale, ensures enhanced longevity and performance in high-traffic areas, outperforming natural quartz in both strength and maintenance requirements.
Aesthetic Variety and Color Options
Engineered quartz offers a broader aesthetic variety and more vibrant color options compared to natural quartz, thanks to its customizable manufacturing process. While natural quartz showcases subtle, natural mineral patterns primarily in neutral tones, engineered quartz can mimic various stone looks or feature consistent patterns in an extensive palette of colors. This flexibility makes engineered quartz a preferred choice for designers seeking unique and uniform surfaces with tailored color schemes.
Maintenance and Care: Engineered vs Natural Quartz
Engineered quartz offers superior resistance to stains, scratches, and heat, making it easier to maintain with just mild soap and water, while natural quartz requires more frequent sealing and careful avoidance of harsh chemicals. Natural quartz surfaces can develop surface etching and need immediate cleaning to prevent damage from acidic substances, whereas engineered quartz is non-porous and less prone to bacterial growth. Regular wiping and avoiding abrasive scrubbers are recommended for both, but engineered quartz demands less intensive upkeep over time, ensuring longevity with minimal effort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Engineered quartz typically has a lower environmental impact compared to natural quartz due to its use of recycled materials and more efficient manufacturing processes, reducing quarrying and habitat disruption. Natural quartz extraction involves extensive mining, which can lead to land degradation and significant energy consumption, affecting local ecosystems. Sustainable practices in engineered quartz production include minimizing waste and utilizing eco-friendly resins, making it a more responsible choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Cost Differences and Value for Homeowners
Engineered quartz generally costs between $50 and $150 per square foot, while natural quartz ranges from $40 to $100 per square foot, making engineered quartz a pricier option upfront. Despite higher initial costs, engineered quartz offers superior durability, non-porous surfaces, and low maintenance, providing better long-term value for homeowners. Homeowners seeking a balance of aesthetics and functionality often find engineered quartz more cost-effective when factoring in lifespan and upkeep expenses.
Engineered Quartz vs Natural Quartz Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com