Vitrified porcelain undergoes a high-temperature firing process that makes it dense, non-porous, and highly durable, ideal for heavy-traffic areas and moisture-prone environments. Non-vitrified porcelain, while still strong, is more porous and requires sealing to prevent water absorption and staining. Choosing vitrified porcelain ensures superior resistance to wear, making it the preferred option for both indoor and outdoor applications where longevity is crucial.
Table of Comparison
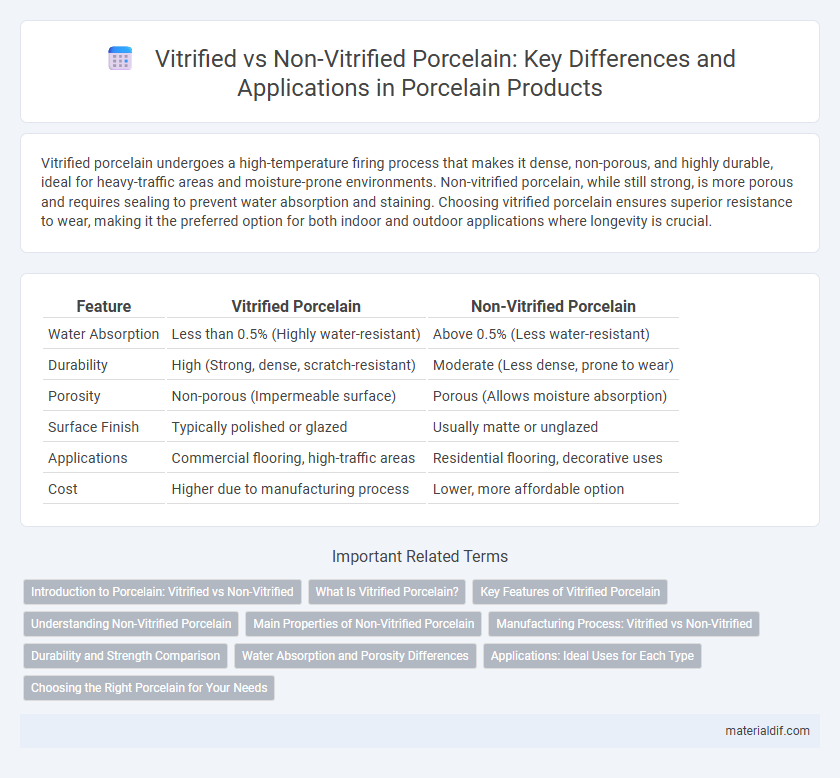
| Feature | Vitrified Porcelain | Non-Vitrified Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Water Absorption | Less than 0.5% (Highly water-resistant) | Above 0.5% (Less water-resistant) |
| Durability | High (Strong, dense, scratch-resistant) | Moderate (Less dense, prone to wear) |
| Porosity | Non-porous (Impermeable surface) | Porous (Allows moisture absorption) |
| Surface Finish | Typically polished or glazed | Usually matte or unglazed |
| Applications | Commercial flooring, high-traffic areas | Residential flooring, decorative uses |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing process | Lower, more affordable option |
Introduction to Porcelain: Vitrified vs Non-Vitrified
Vitrified porcelain is characterized by its low porosity and high density, achieved through intense firing processes that fuse the particles, resulting in superior strength and water resistance. Non-vitrified porcelain, while still durable, remains more porous due to lower firing temperatures, making it less resistant to moisture absorption and staining. These fundamental differences influence their applications in flooring, wall cladding, and sanitary ware, where vitrified porcelain is preferred for high-traffic, moisture-prone environments.
What Is Vitrified Porcelain?
Vitrified porcelain is a type of ceramic material characterized by its non-porous, glass-like surface resulting from a high-temperature firing process that fuses the clay particles together. This vitrification enhances durability, making the porcelain resistant to water absorption, staining, and freezing, which is ideal for both indoor and outdoor use. Unlike non-vitrified porcelain, which remains porous and less dense, vitrified porcelain offers superior strength and longevity for applications such as flooring, countertops, and tiles.
Key Features of Vitrified Porcelain
Vitrified porcelain is characterized by its low porosity, high strength, and resistance to water absorption, making it ideal for heavy-duty flooring and wall applications. The vitrification process fuses the particles, creating a dense, glass-like surface that enhances durability and stain resistance compared to non-vitrified porcelain. Key features include superior hardness, minimal shrinkage during firing, and enhanced resistance to chemicals and weathering, ensuring long-lasting performance in both residential and commercial environments.
Understanding Non-Vitrified Porcelain
Non-vitrified porcelain is characterized by its porous nature and incomplete glass-like transformation during firing, resulting in lower density and higher water absorption compared to vitrified porcelain. This type of porcelain is often used in decorative applications where moisture resistance is less critical, offering a more matte finish and easier craftsmanship flexibility. Its permeability and lower strength limit its use in high-traffic flooring or outdoor environments, distinguishing it from vitrified porcelain's durability and resistance to stains and frost.
Main Properties of Non-Vitrified Porcelain
Non-vitrified porcelain is characterized by its porous structure, lower density, and reduced water absorption compared to vitrified porcelain, making it less durable for high-traffic areas. It typically exhibits a matte finish with a softer surface texture and limited resistance to stains and chemicals. Commonly used in decorative applications and low-traffic interiors, non-vitrified porcelain requires regular maintenance to preserve its appearance.
Manufacturing Process: Vitrified vs Non-Vitrified
Vitrified porcelain undergoes a high-temperature firing process, typically above 1200degC, which causes the raw materials to fuse into a glass-like, non-porous structure, enhancing durability and water resistance. Non-vitrified porcelain is fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and less dense material that absorbs moisture more readily and tends to be less strong. The vitrification process significantly impacts the tile's mechanical properties, making vitrified porcelain ideal for high-traffic and outdoor applications, while non-vitrified is often used for indoor, decorative purposes.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Vitrified porcelain exhibits superior durability and strength due to its low porosity and enhanced resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Non-vitrified porcelain, with higher porosity, absorbs more water, reducing its strength and making it more susceptible to chipping and cracking under stress. The vitrification process results in a denser, harder material that significantly outperforms non-vitrified porcelain in terms of long-term structural integrity.
Water Absorption and Porosity Differences
Vitrified porcelain exhibits extremely low water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, due to its dense, glass-like structure created through high-temperature firing. Non-vitrified porcelain has higher porosity, resulting in greater water absorption, often exceeding 3%, which makes it more susceptible to moisture-related damage. The reduced porosity in vitrified porcelain enhances durability and stain resistance, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Applications: Ideal Uses for Each Type
Vitrified porcelain, characterized by its low porosity and high density, is ideal for high-traffic commercial flooring, outdoor patios, and kitchen countertops due to its superior durability and resistance to water and stains. Non-vitrified porcelain, with its higher porosity and matte finish, is better suited for decorative wall tiles, indoor residential bathrooms, and areas where slip resistance is prioritized. Selecting the appropriate type ensures optimal performance tailored to environmental exposure and functional demands.
Choosing the Right Porcelain for Your Needs
Vitrified porcelain offers superior density and low porosity, making it highly resistant to moisture, stains, and wear, ideal for high-traffic areas and outdoor installations. Non-vitrified porcelain, with its more porous surface, suits decorative applications or indoor use where water resistance is less critical. Selecting the right porcelain depends on durability requirements, exposure to elements, and desired aesthetic, ensuring longevity and performance in your specific environment.
Vitrified porcelain vs Non-vitrified porcelain Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com