Polyester yarns are the fundamental building blocks used in textile manufacturing, offering strength, durability, and resistance to shrinkage and wrinkles. Polyester fabrics, created by weaving or knitting these yarns, provide versatile applications ranging from apparel to home furnishings, exhibiting excellent moisture-wicking and quick-drying properties. The performance and quality of the final polyester fabric heavily depend on the characteristics and processing of the polyester yarns used.
Table of Comparison
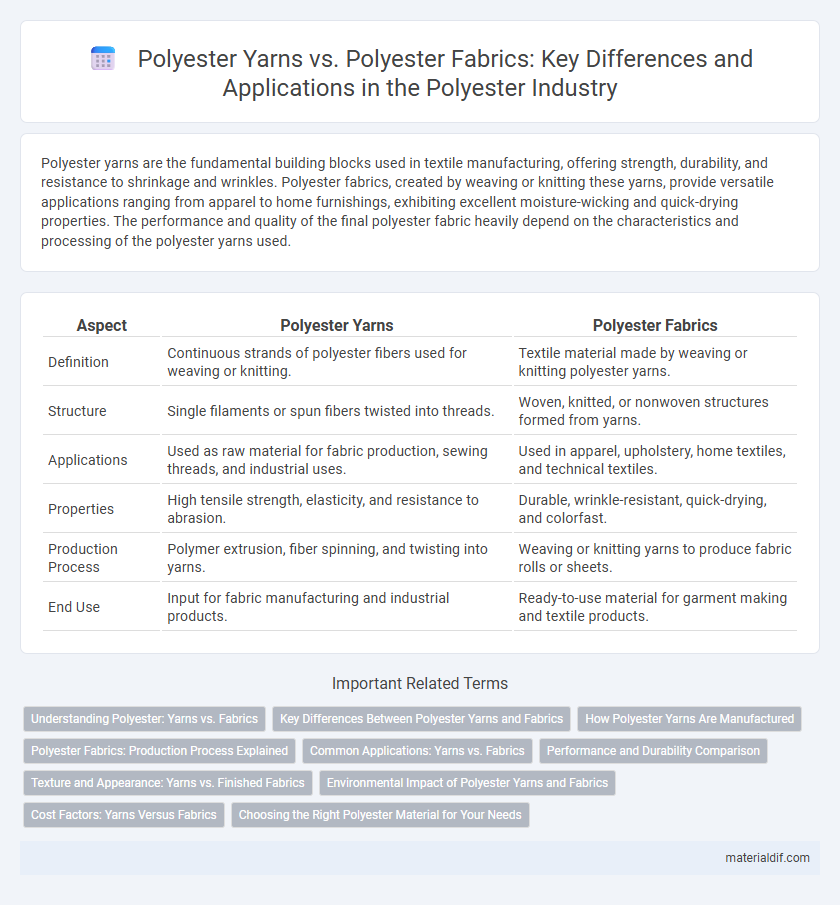
| Aspect | Polyester Yarns | Polyester Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous strands of polyester fibers used for weaving or knitting. | Textile material made by weaving or knitting polyester yarns. |
| Structure | Single filaments or spun fibers twisted into threads. | Woven, knitted, or nonwoven structures formed from yarns. |
| Applications | Used as raw material for fabric production, sewing threads, and industrial uses. | Used in apparel, upholstery, home textiles, and technical textiles. |
| Properties | High tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. | Durable, wrinkle-resistant, quick-drying, and colorfast. |
| Production Process | Polymer extrusion, fiber spinning, and twisting into yarns. | Weaving or knitting yarns to produce fabric rolls or sheets. |
| End Use | Input for fabric manufacturing and industrial products. | Ready-to-use material for garment making and textile products. |
Understanding Polyester: Yarns vs. Fabrics
Polyester yarns serve as the foundational fibers spun from synthetic polymers, specifically polyethylene terephthalate, known for their strength, durability, and resistance to shrinking and stretching. Polyester fabrics, on the other hand, are woven or knitted textiles created from these yarns, offering versatile applications in apparel, upholstery, and industrial uses due to their lightweight, wrinkle-resistant, and moisture-wicking properties. Understanding the distinction between yarns and fabrics enhances insight into polyester's manufacturing process, quality control, and end-use performance in the textile industry.
Key Differences Between Polyester Yarns and Fabrics
Polyester yarns are continuous strands of synthetic fibers spun together for weaving or knitting, providing strength and elasticity at the fiber level. In contrast, polyester fabrics are finished textiles created by interlacing polyester yarns through weaving or knitting processes, resulting in varied textures, weights, and applications. The key differences lie in their form and function: yarns serve as the raw material for fabric production, while fabrics are the end products used in apparel, upholstery, and industrial applications.
How Polyester Yarns Are Manufactured
Polyester yarns are produced through a process called melt spinning, where polymer chips are melted and extruded through spinnerets to form fine filaments. These filaments are then cooled, drawn to align the molecular chains for strength, and wound onto spools before being spun into yarns. The quality of polyester yarns directly affects the durability, texture, and performance of the final polyester fabrics used in textiles.
Polyester Fabrics: Production Process Explained
Polyester fabrics are produced through a complex process that begins with polymerization, where purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and monoethylene glycol (MEG) react to form polyethylene terephthalate (PET) chips. These chips are then melted and extruded into fine filaments through spinnerets, solidified by cooling, and drawn to enhance strength and flexibility. The fibers undergo texturizing and weaving or knitting to create various textured polyester fabrics suitable for diverse applications in apparel, upholstery, and industrial use.
Common Applications: Yarns vs. Fabrics
Polyester yarns are widely used in textile manufacturing sectors for weaving and knitting into various fabrics, serving as the foundational element in garments, upholstery, and industrial textiles. Polyester fabrics, derived from these yarns, are prevalent in apparel, home furnishings, and outdoor gear due to their durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. The common applications of polyester yarns focus on producing versatile fabric types, while polyester fabrics are directly utilized in finished products such as sportswear, curtains, and automotive interiors.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Polyester yarns exhibit high tensile strength and excellent elasticity, contributing to superior durability when used in various textile applications. Polyester fabrics, woven or knit from these yarns, offer enhanced abrasion resistance and moisture-wicking properties, improving overall performance in activewear and industrial uses. The synergistic combination of polyester yarn characteristics and fabric construction results in materials that maintain shape, resist shrinking, and provide long-lasting wear.
Texture and Appearance: Yarns vs. Finished Fabrics
Polyester yarns exhibit a smooth and uniform texture that influences the final fabric's hand feel and drape. Finished polyester fabrics showcase variations in texture, ranging from soft and silky to matte and textured, depending on the weave, knit, or finishing treatments applied. The appearance of polyester fabrics is enhanced by the yarn's characteristics, with luster and color vibrancy becoming more pronounced after processing into fabric form.
Environmental Impact of Polyester Yarns and Fabrics
Polyester yarns, derived from synthetic fibers, contribute significantly to microplastic pollution during manufacturing and washing, posing environmental challenges. Polyester fabrics, produced through further processing of these yarns, exhibit high durability but often resist biodegradation, lingering in landfills for decades. Innovations in recycling and sustainable production methods aim to mitigate the ecological footprint of both polyester yarns and fabrics in the textile industry.
Cost Factors: Yarns Versus Fabrics
Polyester yarns generally incur lower costs compared to polyester fabrics due to fewer processing stages and reduced labor requirements. Fabric production demands additional weaving or knitting, dyeing, and finishing processes that significantly increase overall expenses. The price disparity reflects the complexity of converting yarns into finished fabrics, impacting material selection in textile manufacturing and product pricing.
Choosing the Right Polyester Material for Your Needs
Polyester yarns offer versatility in texture and strength, ideal for customizing fabric properties such as durability and elasticity. Polyester fabrics, woven or knitted from these yarns, provide finished materials suited for specific applications like apparel, upholstery, or industrial use. Selecting the right polyester material depends on factors such as intended use, required durability, breathability, and cost-effectiveness.
Polyester Yarns vs Polyester Fabrics Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com