Single-ply paper consists of a single layer, making it thinner and more cost-effective but less durable than multi-ply paper. Multi-ply paper features multiple layers bonded together, providing enhanced strength, absorbency, and comfort, ideal for high-usage settings. Choosing between single-ply and multi-ply paper depends on balancing budget constraints with the need for durability and user experience.
Table of Comparison
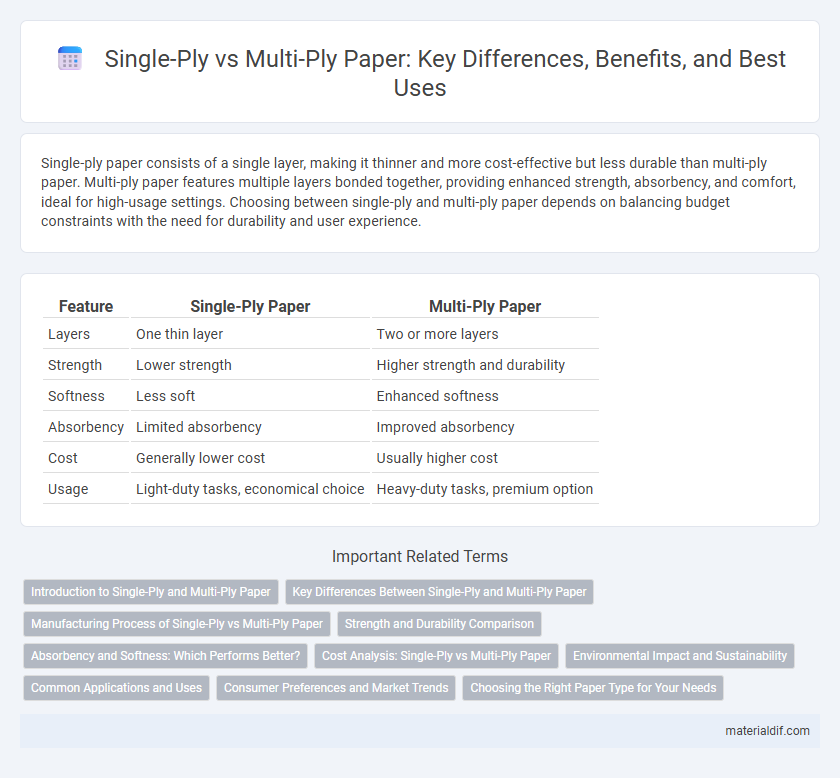
| Feature | Single-Ply Paper | Multi-Ply Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Layers | One thin layer | Two or more layers |
| Strength | Lower strength | Higher strength and durability |
| Softness | Less soft | Enhanced softness |
| Absorbency | Limited absorbency | Improved absorbency |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost |
| Usage | Light-duty tasks, economical choice | Heavy-duty tasks, premium option |
Introduction to Single-Ply and Multi-Ply Paper
Single-ply paper consists of a single layer of fibers, offering a lightweight and economical option primarily used for printing and writing purposes. Multi-ply paper features two or more bonded layers, enhancing strength, absorbency, and durability, commonly utilized in applications like tissues, napkins, and towels. Understanding the structural differences between single-ply and multi-ply paper is essential for selecting the right product based on performance requirements and cost efficiency.
Key Differences Between Single-Ply and Multi-Ply Paper
Single-ply paper consists of a single layer, offering lower thickness and reduced absorbency compared to multi-ply paper, which features two or more bonded layers enhancing durability and moisture absorption. Multi-ply paper provides superior strength and softness, making it ideal for applications requiring higher comfort and resistance. Key differences include ply count, thickness, absorbency, strength, and cost efficiency, with single-ply being more economical and multi-ply delivering premium performance.
Manufacturing Process of Single-Ply vs Multi-Ply Paper
Single-ply paper manufacturing involves a continuous process where fibers are formed into a single sheet using a paper machine, often resulting in a thinner and lighter product. Multi-ply paper production combines two or more layers of paper during the manufacturing process either by pressing and bonding separate single-ply sheets or using multilayer forming fabrics to integrate layers simultaneously, enhancing strength and absorbency. The layered structure in multi-ply paper requires precise control over adhesive application, fiber composition, and drying stages, distinguishing it from the relatively simpler single-ply production workflow.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Single-ply paper typically consists of one thin layer, making it less durable and prone to tearing under stress compared to multi-ply paper, which combines multiple layers for enhanced strength. Multi-ply paper provides superior tensile strength and increased resistance to wear and moisture, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as packaging and industrial use. The layered structure of multi-ply paper distributes stress more evenly, resulting in longer-lasting performance and reduced likelihood of damage during handling.
Absorbency and Softness: Which Performs Better?
Multi-ply paper outperforms single-ply paper in absorbency due to its multiple layers that trap more moisture, making it ideal for tasks requiring high moisture retention. Softness is generally superior in multi-ply variants, as the additional layers allow manufacturers to use finer fibers and cushioning techniques that enhance tactile comfort. Single-ply paper offers a thinner, less cushioned texture with lower absorbency, often making it less effective for heavy-duty cleaning or comfort-sensitive uses.
Cost Analysis: Single-Ply vs Multi-Ply Paper
Single-ply paper generally offers lower upfront costs due to reduced material usage and simpler manufacturing processes. Multi-ply paper, though costing more initially, provides enhanced durability and absorbency, potentially reducing overall usage and replacement frequency, which may result in long-term savings. Businesses must weigh immediate expenses against longevity and performance requirements to determine the most cost-effective choice.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Single-ply paper generally has a lower environmental impact due to reduced material use and energy consumption during production compared to multi-ply paper. Multi-ply paper, while often stronger and more durable, requires more raw materials and generates higher waste, contributing to greater deforestation and carbon emissions. Sustainable options include recycled fibers and certifications like FSC or PEFC, which help mitigate the ecological footprint of both single-ply and multi-ply papers.
Common Applications and Uses
Single-ply paper is commonly used for everyday tasks such as printing, writing, and packaging due to its lightweight and cost-effective nature. Multi-ply paper, featuring multiple layers, is preferred in applications requiring enhanced durability and absorbency, such as tissues, paper towels, and napkins in both domestic and commercial settings. The choice between single-ply and multi-ply depends on the required strength, softness, and intended use, impacting consumer preference and industrial utility.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor multi-ply paper for its superior durability and absorbency, driving significant market growth in household and personal care segments. Single-ply paper remains preferred in commercial and budget-conscious markets due to its cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits. Market trends indicate a rising demand for eco-friendly, multi-ply options that balance strength with sustainability to meet evolving consumer preferences.
Choosing the Right Paper Type for Your Needs
Single-ply paper offers a lightweight, cost-effective option ideal for everyday printing and general use, while multi-ply paper provides enhanced durability, absorbency, and strength suitable for corporate communications and heavy-duty applications. Consider factors such as print quality, thickness (measured in GSM), and the paper's intended function to select between single-ply and multi-ply options. Opting for the correct paper type ensures optimal performance, whether for professional documents, packaging, or hygiene products.
Single-Ply Paper vs Multi-Ply Paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com