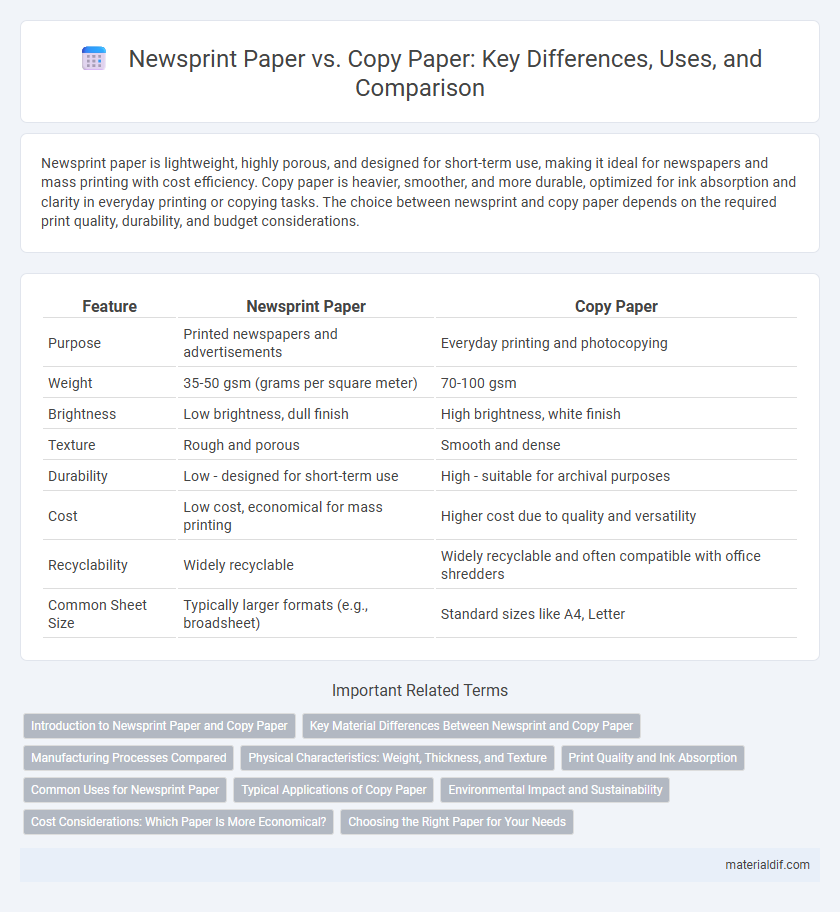
Newsprint paper is lightweight, highly porous, and designed for short-term use, making it ideal for newspapers and mass printing with cost efficiency. Copy paper is heavier, smoother, and more durable, optimized for ink absorption and clarity in everyday printing or copying tasks. The choice between newsprint and copy paper depends on the required print quality, durability, and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Newsprint Paper | Copy Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Printed newspapers and advertisements | Everyday printing and photocopying |
| Weight | 35-50 gsm (grams per square meter) | 70-100 gsm |
| Brightness | Low brightness, dull finish | High brightness, white finish |
| Texture | Rough and porous | Smooth and dense |
| Durability | Low - designed for short-term use | High - suitable for archival purposes |
| Cost | Low cost, economical for mass printing | Higher cost due to quality and versatility |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Widely recyclable and often compatible with office shredders |
| Common Sheet Size | Typically larger formats (e.g., broadsheet) | Standard sizes like A4, Letter |
Introduction to Newsprint Paper and Copy Paper
Newsprint paper is a low-cost, lightweight paper primarily used for printing newspapers, characterized by its high lignin content and lower brightness, making it less durable and more prone to yellowing over time. Copy paper, also known as copier or office paper, features a higher brightness and smoother finish, designed for inkjet and laser printers to produce sharp text and images. The fundamental differences in weight, brightness, and durability determine their specific applications in printing and document reproduction.
Key Material Differences Between Newsprint and Copy Paper
Newsprint paper is made primarily from mechanical pulp with lower brightness and opacity, resulting in a more porous texture ideal for high-speed newspaper printing. Copy paper consists of chemical pulp with higher brightness, opacity, and smoothness, providing superior print quality and durability suited for office printers and copiers. The fiber composition and processing methods directly influence their respective weight, surface finish, and ink absorption properties.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Newsprint paper is produced using a mechanical pulping process that retains most of the wood fibers, resulting in a lower cost and a rougher texture ideal for newspaper printing. Copy paper undergoes chemical pulping, removing lignin to create a smoother, brighter surface suitable for ink absorption and sharp text reproduction. The manufacturing differences also influence durability and weight, with copy paper typically being heavier and more resilient than newsprint.
Physical Characteristics: Weight, Thickness, and Texture
Newsprint paper typically has a lower basis weight, ranging from 45 to 55 gsm, making it lighter and thinner compared to copy paper, which generally weighs between 75 and 90 gsm. The thickness of newsprint ranges around 40 to 50 microns, offering a more porous and coarse texture, while copy paper features a smoother surface and thickness of approximately 90 to 110 microns, enhancing print quality and durability. These physical differences influence print clarity, ink absorption, and suitability for various printing applications.
Print Quality and Ink Absorption
Newsprint paper typically features lower print quality due to its rough texture and high absorbency, which causes ink to spread and results in less sharp images and text. Copy paper, designed with a smoother surface and optimized coating, offers superior print clarity and precise ink absorption, preventing smudging and bleed-through. The enhanced ink retention on copy paper enables vibrant colors and crisp details, making it ideal for professional documents and high-resolution printing.
Common Uses for Newsprint Paper
Newsprint paper is primarily used for printing newspapers, flyers, and other mass-distributed publications due to its low cost and lightweight properties. Its uncoated surface makes it ideal for fast production and high-speed printing processes, although it is less durable and has lower brightness compared to copy paper. Common uses include daily news distribution, promotional leaflets, and packaging materials for temporary or disposable products.
Typical Applications of Copy Paper
Copy paper is predominantly used in office environments for printing documents, reports, and correspondence due to its smooth finish and consistent weight, typically ranging from 20 to 24 pounds. It excels in high-speed laser and inkjet printers, ensuring crisp text and sharp images across various media types such as flyers, forms, and presentations. Unlike newsprint paper, copy paper offers superior brightness and opacity, reducing show-through and enhancing readability for professional and administrative applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Newsprint paper, typically made from recycled fibers and unbleached pulp, has a lower environmental impact compared to copy paper due to its reduced energy consumption and fewer chemical processes during production. Copy paper often requires virgin fibers and bleaching agents, leading to higher resource depletion and increased carbon emissions. Choosing newsprint paper supports sustainability by promoting recycling and minimizing deforestation and pollution associated with paper manufacturing.
Cost Considerations: Which Paper Is More Economical?
Newsprint paper is significantly cheaper than copy paper due to its low manufacturing costs and use of lower-grade pulp, making it ideal for high-volume, short-term printing like newspapers. Copy paper, produced with higher-quality fibers and added brightness treatments, carries a higher price but offers superior durability and print clarity for office documents. For budget-focused bulk printing, newsprint provides the most economical choice, whereas copy paper suits professional presentations and formal communications despite its greater cost.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Needs
Newsprint paper is lightweight, inexpensive, and ideal for printing newspapers and large-volume flyers, offering a rough texture and lower brightness suitable for short-term use. Copy paper is heavier, brighter, and smoother, designed for inkjet and laser printers, providing high-quality printing for documents and everyday office use. Selecting the right paper depends on factors like print quality, durability, and budget, with newsprint favored for cost-effective mass distribution and copy paper preferred for sharp text and long-lasting records.
Newsprint paper vs Copy paper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com