Round gravel features smooth, rounded edges formed by natural erosion, making it ideal for drainage and decorative uses where aesthetics and water flow are important. Angular gravel has sharp, jagged edges that interlock well, providing superior stability and strength in construction and road base applications. Choosing between round and angular gravel depends on the specific project requirements for drainage, compaction, and visual appeal.
Table of Comparison
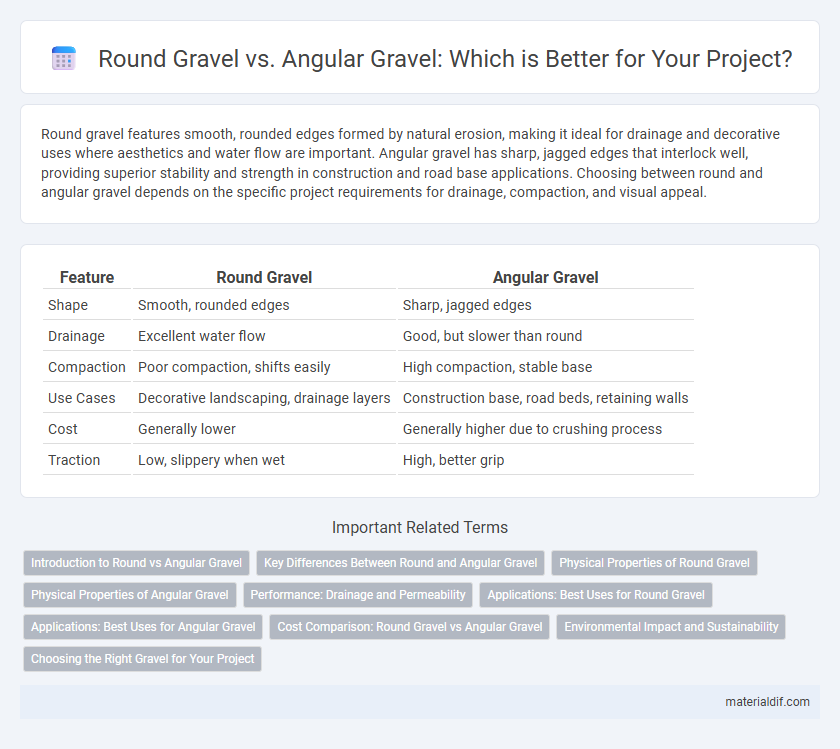
| Feature | Round Gravel | Angular Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Smooth, rounded edges | Sharp, jagged edges |
| Drainage | Excellent water flow | Good, but slower than round |
| Compaction | Poor compaction, shifts easily | High compaction, stable base |
| Use Cases | Decorative landscaping, drainage layers | Construction base, road beds, retaining walls |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher due to crushing process |
| Traction | Low, slippery when wet | High, better grip |
Introduction to Round vs Angular Gravel
Round gravel features smooth, rounded edges formed by natural weathering and water transport, making it ideal for drainage systems and decorative landscaping due to its ease of compaction and aesthetic appeal. Angular gravel has sharp, jagged edges created by mechanical crushing, offering superior interlocking properties that enhance stability and load-bearing capacity, commonly used in construction and road bases. Understanding the differences in texture and shape between round and angular gravel is essential for selecting the appropriate type based on application requirements.
Key Differences Between Round and Angular Gravel
Round gravel features smooth, rounded edges formed through natural weathering and water erosion, offering superior drainage and easier compaction in construction projects. Angular gravel has sharp, jagged edges created by mechanical crushing, providing enhanced interlock and stability, ideal for driveways and concrete mix. The choice between round and angular gravel significantly affects soil compaction, drainage efficiency, and load-bearing capacity in landscaping and building applications.
Physical Properties of Round Gravel
Round gravel exhibits smooth, rounded edges due to natural weathering and erosion processes, resulting in lower surface area and less interlocking ability compared to angular gravel. These physical properties contribute to improved water drainage and easier compaction, making round gravel ideal for applications like drainage systems and landscaping. Its decreased friction makes it less stable under load, which can affect structural integrity in construction projects requiring high shear strength.
Physical Properties of Angular Gravel
Angular gravel features sharp edges and rough surfaces that increase interlocking and stability in construction applications. Its irregular shape enhances load-bearing capacity and reduces shifting, making it ideal for road bases and drainage systems. Compared to round gravel, angular gravel compacts more tightly, providing superior resistance to movement under pressure.
Performance: Drainage and Permeability
Round gravel exhibits superior drainage and permeability due to its smooth, rounded particles that create larger voids between stones, allowing water to flow freely. Angular gravel, with its sharp, irregular edges, compacts tightly and reduces void spaces, leading to slower water drainage and lower permeability. For applications requiring efficient water runoff and minimal retention, round gravel outperforms angular gravel in maintaining optimal drainage conditions.
Applications: Best Uses for Round Gravel
Round gravel is ideal for drainage systems, landscaping, and pathways due to its smooth, rounded edges that promote water flow and reduce compaction. It is commonly used in French drains, driveways, and decorative garden beds, providing a stable yet permeable surface. The smooth texture makes it less abrasive, suitable for playgrounds and erosion control while maintaining aesthetics.
Applications: Best Uses for Angular Gravel
Angular gravel is ideal for construction projects requiring strong interlocking capabilities, such as concrete mixing, road base stabilization, and drainage systems. Its sharp edges provide superior traction and compaction compared to round gravel, making it essential for heavy-duty applications like retaining walls and railroad ballast. Landscapers favor angular gravel for pathways and decorative borders due to its enhanced stability and resistance to shifting.
Cost Comparison: Round Gravel vs Angular Gravel
Round gravel typically costs less than angular gravel due to simpler extraction and processing methods, which reduce overall production expenses. Angular gravel, with its sharper edges and higher crushing requirements, often demands more labor and energy, leading to increased costs. Budget-conscious projects usually prefer round gravel for its affordability, while angular gravel is chosen for applications needing better compaction and stability despite higher prices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Round gravel typically results from natural weathering processes, making it more environmentally sustainable due to less processing and lower energy consumption during extraction. Angular gravel, often crushed for specific industrial uses, requires intensive mining and crushing, increasing carbon emissions and habitat disruption. Choosing round gravel supports ecological balance by minimizing environmental footprint and promoting sustainable resource usage.
Choosing the Right Gravel for Your Project
Round gravel offers smooth, rounded edges ideal for landscaping and drainage projects, promoting excellent water flow and ease of movement. Angular gravel features sharp, jagged edges that create tight interlocks, providing superior stability and strength for construction foundations and road bases. Selecting the right gravel depends on project requirements, with round gravel best for aesthetic and drainage purposes, while angular gravel suits structural integrity and load-bearing applications.
Round Gravel vs Angular Gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com