Class 5 gravel consists of smaller, finer particles ideal for leveling and creating a solid base for paving, while Class 2 gravel contains larger, more angular stones suited for heavy-duty construction projects requiring excellent drainage and stability. The finer texture of Class 5 gravel makes it perfect for compacting and providing a smooth surface, whereas Class 2 gravel's coarser composition ensures durability and strength under high traffic loads. Selecting between Class 5 and Class 2 gravel depends on the specific application, with Class 5 preferred for finishing layers and Class 2 chosen for foundational support.
Table of Comparison
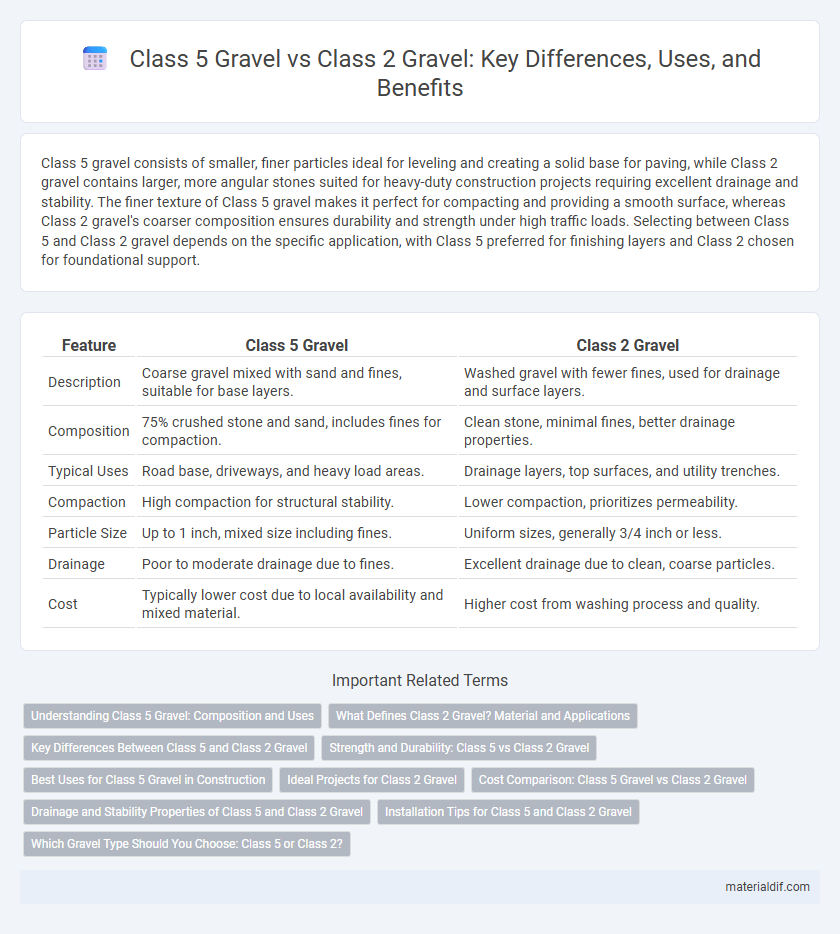
| Feature | Class 5 Gravel | Class 2 Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Coarse gravel mixed with sand and fines, suitable for base layers. | Washed gravel with fewer fines, used for drainage and surface layers. |
| Composition | 75% crushed stone and sand, includes fines for compaction. | Clean stone, minimal fines, better drainage properties. |
| Typical Uses | Road base, driveways, and heavy load areas. | Drainage layers, top surfaces, and utility trenches. |
| Compaction | High compaction for structural stability. | Lower compaction, prioritizes permeability. |
| Particle Size | Up to 1 inch, mixed size including fines. | Uniform sizes, generally 3/4 inch or less. |
| Drainage | Poor to moderate drainage due to fines. | Excellent drainage due to clean, coarse particles. |
| Cost | Typically lower cost due to local availability and mixed material. | Higher cost from washing process and quality. |
Understanding Class 5 Gravel: Composition and Uses
Class 5 gravel features a mix of crushed stone and fines, creating a compactable base ideal for driveways and road construction. Its composition typically includes angular particles that interlock well, providing strong structural support and excellent drainage properties. This contrasts with Class 2 gravel, which contains fewer fines and is better suited for surface layering and less load-bearing applications.
What Defines Class 2 Gravel? Material and Applications
Class 2 gravel typically consists of a blend of coarse and fine aggregate materials, including crushed rock, sand, and smaller gravel particles, providing excellent compaction properties. This material is commonly used for base layers in road construction, driveway foundations, and as a stable subbase for heavy-duty paving projects due to its ability to distribute loads effectively. Compared to Class 5 gravel, which is primarily used for drainage and top layers, Class 2 gravel offers superior strength and durability for structural support.
Key Differences Between Class 5 and Class 2 Gravel
Class 5 gravel consists of finely crushed rock mixed with milling dust, typically used for sub-base layers in road construction due to its excellent compaction and drainage properties. Class 2 gravel contains larger, more uniform crushed rock pieces, offering high strength and stability suitable for structural base layers and heavy load-bearing applications. Key differences lie in particle size distribution, compaction ability, and intended structural use, with Class 5 optimized for foundational sub-layers and Class 2 for more load-demanding surfaces.
Strength and Durability: Class 5 vs Class 2 Gravel
Class 5 gravel offers moderate strength and durability, suitable for light-duty driveways and pathways, whereas Class 2 gravel provides higher compaction and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for road bases and heavier traffic areas. The angular shape and better gradation of Class 2 gravel enhance its interlocking properties, resulting in superior stability and resistance to shifting under pressure. For projects requiring long-term durability and structural integrity, Class 2 gravel outperforms Class 5 in strength.
Best Uses for Class 5 Gravel in Construction
Class 5 gravel is a versatile, well-graded aggregate commonly used for base layers in driveways, roads, and walkways due to its excellent compaction and drainage properties. It typically contains a mix of sand, gravel, and fines, providing a stable foundation that supports heavy loads and reduces settling in construction projects. This makes Class 5 gravel ideal for foundational work, including concrete slabs and pavement sub-bases, where durability and load distribution are critical.
Ideal Projects for Class 2 Gravel
Class 2 gravel is ideal for road base and foundation projects due to its superior compaction and stability properties compared to Class 5 gravel. Its well-graded mix of crushed stone and finer materials ensures excellent load-bearing capacity and drainage, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like driveways, highways, and commercial building pads. Class 2 gravel provides a durable, long-lasting base that resists shifting and erosion under heavy traffic and weather conditions.
Cost Comparison: Class 5 Gravel vs Class 2 Gravel
Class 5 gravel is generally less expensive than Class 2 gravel due to its coarser composition and lower processing requirements. Class 2 gravel, characterized by a blend of fine particles and larger aggregates, commands a higher price because of its superior compaction and stability properties. When budgeting for road construction or landscaping, the cost difference between these gravels directly impacts the overall project expenditure.
Drainage and Stability Properties of Class 5 and Class 2 Gravel
Class 5 gravel provides superior drainage due to its coarse aggregate mix, allowing water to flow freely and preventing pooling or erosion. Class 2 gravel combines smaller, more compact particles that enhance stability by creating a dense, solid base ideal for driving surfaces. The choice between Class 5 and Class 2 gravel depends on project requirements prioritizing either optimal drainage or structural stability.
Installation Tips for Class 5 and Class 2 Gravel
Class 5 gravel, commonly used for driveways and base layers, compacts well and requires proper grading and moisture control during installation to ensure stability and prevent shifting. Class 2 gravel, favored for drainage and road base applications, demands careful layering and thorough compaction to enhance load-bearing capacity and reduce water retention. Both gravel types benefit from a well-prepared subgrade to maximize durability and performance over time.
Which Gravel Type Should You Choose: Class 5 or Class 2?
Class 5 gravel features larger, coarse particles ideal for drainage and base layers in construction, while Class 2 gravel consists of a mix of coarse and fine crushed stone suitable for driveways and walkways requiring a compacted surface. Selecting Class 5 gravel is best for projects needing superior drainage and stability, whereas Class 2 gravel provides a smooth, solid surface perfect for areas with moderate traffic. Evaluating project requirements like load-bearing capacity and surface finish guides the optimal choice between Class 5 or Class 2 gravel.
Class 5 Gravel vs Class 2 Gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com