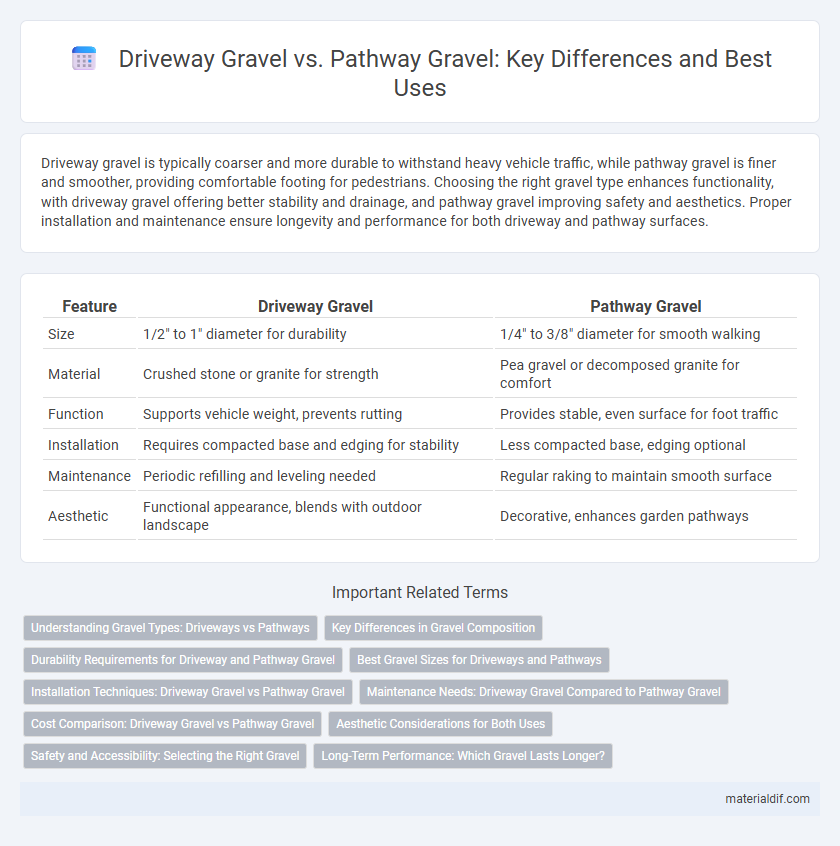
Driveway gravel is typically coarser and more durable to withstand heavy vehicle traffic, while pathway gravel is finer and smoother, providing comfortable footing for pedestrians. Choosing the right gravel type enhances functionality, with driveway gravel offering better stability and drainage, and pathway gravel improving safety and aesthetics. Proper installation and maintenance ensure longevity and performance for both driveway and pathway surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Driveway Gravel | Pathway Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 1/2" to 1" diameter for durability | 1/4" to 3/8" diameter for smooth walking |
| Material | Crushed stone or granite for strength | Pea gravel or decomposed granite for comfort |
| Function | Supports vehicle weight, prevents rutting | Provides stable, even surface for foot traffic |
| Installation | Requires compacted base and edging for stability | Less compacted base, edging optional |
| Maintenance | Periodic refilling and leveling needed | Regular raking to maintain smooth surface |
| Aesthetic | Functional appearance, blends with outdoor landscape | Decorative, enhances garden pathways |
Understanding Gravel Types: Driveways vs Pathways
Driveway gravel typically consists of larger, more durable stones such as crushed limestone or granite, providing stability and preventing rutting under vehicle weight. Pathway gravel is finer and smoother like pea gravel or decomposed granite, offering comfort underfoot and better drainage for pedestrian use. Selecting the right gravel type ensures longevity and functionality tailored to the specific demands of driveways and pathways.
Key Differences in Gravel Composition
Driveway gravel typically consists of larger, angular crushed stone that provides better compaction and stability for vehicle weight, often ranging from 3/4 inch to 1.5 inches in size. Pathway gravel tends to be finer and smoother, such as pea gravel or decomposed granite, which offers a comfortable walking surface and better drainage. The key difference lies in the gravel size and texture, with driveway gravel prioritizing durability and load-bearing capacity, while pathway gravel emphasizes aesthetics and foot traffic comfort.
Durability Requirements for Driveway and Pathway Gravel
Driveway gravel requires higher durability to withstand heavy vehicle loads and frequent traffic, often using crushed stone or granite for optimal strength. Pathway gravel prioritizes comfort and aesthetic appeal, typically utilizing softer, rounded stones or pea gravel that resist compaction but endure moderate foot traffic. Selecting the right gravel type ensures longevity and proper functionality tailored to the specific demands of driveways versus pathways.
Best Gravel Sizes for Driveways and Pathways
Driveway gravel requires larger, more angular stones typically between 3/4 to 1 1/2 inches to provide stability and support heavy vehicle traffic, while pathway gravel benefits from smaller, smoother sizes like 3/8 to 3/4 inches to ensure comfort and ease of walking. The angularity of driveway gravel improves interlocking and reduces shifting, crucial for load-bearing surfaces, whereas finer pathway gravel enhances drainage and reduces dust. Choosing the correct gravel size optimizes durability and functionality specific to either driveways or pedestrian pathways.
Installation Techniques: Driveway Gravel vs Pathway Gravel
Driveway gravel installation requires a thicker base layer, often 4 to 6 inches of crushed stone, compacted to support vehicle weight and prevent rutting. Pathway gravel generally involves a thinner base, around 2 to 3 inches, providing easier drainage and comfort for foot traffic. Proper edging and geotextile fabric placement are essential in both applications to maintain gravel stability and reduce weed growth.
Maintenance Needs: Driveway Gravel Compared to Pathway Gravel
Driveway gravel typically requires more frequent maintenance than pathway gravel due to heavier vehicle traffic causing displacement and compaction. Regular replenishing and grading are necessary to prevent potholes and ruts, ensuring a smooth driving surface. Pathway gravel experiences lighter foot traffic, resulting in less frequent maintenance and primarily requiring occasional raking to maintain even coverage.
Cost Comparison: Driveway Gravel vs Pathway Gravel
Driveway gravel typically costs between $50 and $100 per ton, reflecting its heavier, more durable composition designed to support vehicle weight, compared to pathway gravel which ranges from $30 to $70 per ton due to its lighter materials suited for foot traffic. The installation cost for driveway gravel may be higher as it often requires additional base preparation and compaction to ensure long-term stability. Pathway gravel offers a more budget-friendly option with lower material and labor expenses, ideal for decorative or light-use walkways.
Aesthetic Considerations for Both Uses
Driveway gravel typically features larger, more durable stones like crushed granite or quartz, providing a rugged texture that masks tire marks and supports vehicle weight, contributing to a functional yet polished appearance. Pathway gravel, often composed of finer materials such as pea gravel or decomposed granite, emphasizes smoother textures and consistent colors, enhancing walkability and creating inviting, visually cohesive garden paths. Different gravel types and sizes directly influence the overall aesthetic, ensuring that driveways convey strength and durability while pathways evoke charm and elegance.
Safety and Accessibility: Selecting the Right Gravel
Driveway gravel should consist of larger, angular stones like crushed limestone or granite to provide stability and prevent wheel slipping, enhancing vehicle safety. Pathway gravel typically features smaller, smoother stones such as pea gravel, ensuring comfortable walking surfaces and reducing tripping hazards for pedestrians. Properly choosing the right gravel type improves accessibility by balancing traction needs for vehicles with foot traffic comfort.
Long-Term Performance: Which Gravel Lasts Longer?
Driveway gravel typically consists of larger, more durable stones like crushed granite or limestone, providing superior compaction and resistance to heavy vehicle traffic, which contributes to its long-term performance. Pathway gravel often uses smaller, smoother stones such as pea gravel or decomposed granite, which offer better walkability but may shift or erode faster under foot traffic and weather conditions. For extended durability, driveway gravel outperforms pathway gravel due to its ability to maintain structure and minimize displacement over time.
Driveway gravel vs Pathway gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com