Drainage gravel is designed with angular, coarse stones that facilitate efficient water flow, preventing puddles and soil erosion in garden beds and around foundations. Pathway gravel typically consists of smoother, rounded stones that provide a stable and comfortable walking surface, enhancing both aesthetics and safety. Choosing the right gravel depends on functional needs; drainage gravel excels in water management, while pathway gravel prioritizes walkability and appearance.
Table of Comparison
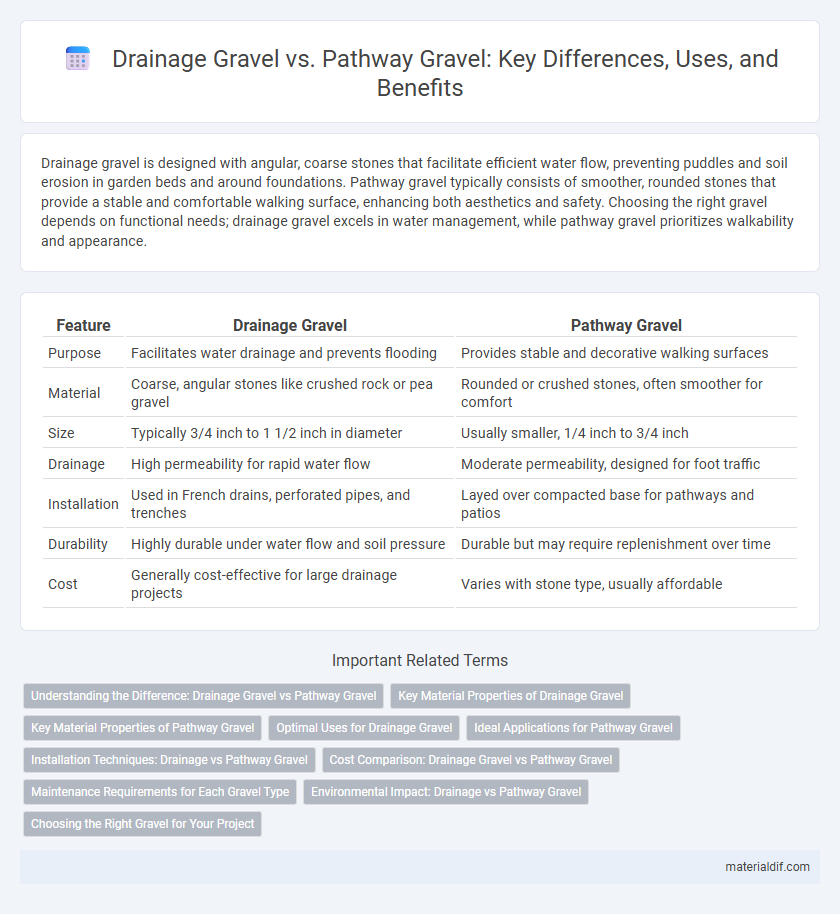
| Feature | Drainage Gravel | Pathway Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Facilitates water drainage and prevents flooding | Provides stable and decorative walking surfaces |
| Material | Coarse, angular stones like crushed rock or pea gravel | Rounded or crushed stones, often smoother for comfort |
| Size | Typically 3/4 inch to 1 1/2 inch in diameter | Usually smaller, 1/4 inch to 3/4 inch |
| Drainage | High permeability for rapid water flow | Moderate permeability, designed for foot traffic |
| Installation | Used in French drains, perforated pipes, and trenches | Layed over compacted base for pathways and patios |
| Durability | Highly durable under water flow and soil pressure | Durable but may require replenishment over time |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective for large drainage projects | Varies with stone type, usually affordable |
Understanding the Difference: Drainage Gravel vs Pathway Gravel
Drainage gravel features angular, porous stones such as crushed limestone or granite, designed to facilitate water flow and prevent flooding in landscaping or foundation applications. Pathway gravel typically consists of smaller, smoother, and more compact stones like pea gravel, providing a stable and comfortable walking surface. Choosing the appropriate type depends on function: effective drainage requires gravel with high permeability, while pathways demand gravel with good compaction and traction.
Key Material Properties of Drainage Gravel
Drainage gravel is characterized by its coarse, angular particles and high permeability, which facilitates efficient water flow and prevents soil erosion. Unlike pathway gravel, it typically exhibits low fines content to maintain effective drainage and reduce compaction. Its durability and resistance to weathering ensure long-term performance in drainage systems and landscape applications.
Key Material Properties of Pathway Gravel
Pathway gravel is characterized by its angular shape and medium-size particles, providing excellent compaction and stability for foot traffic. Its high density and durability resist displacement and erosion, making it ideal for walkways and garden paths. The material's permeability allows for efficient water drainage, preventing pooling and maintaining a dry, safe surface.
Optimal Uses for Drainage Gravel
Drainage gravel is specifically designed to facilitate water flow and prevent pooling, making it ideal for French drains, septic drain fields, and foundation drainage systems. Its angular, coarse texture enhances permeability and windrows water efficiently compared to pathway gravel, which is smoother and intended for foot traffic or aesthetic purposes. Selecting drainage gravel ensures proper soil stabilization and reduces water damage risks around structures and landscaping.
Ideal Applications for Pathway Gravel
Pathway gravel is specifically designed for foot traffic areas, featuring smaller, smoother stones that create a stable and comfortable walking surface. Ideal applications for pathway gravel include garden paths, walkways, and decorative borders where ease of movement and aesthetic appeal are essential. This type of gravel promotes drainage while maintaining firm footing, preventing muddiness and erosion along frequently used walkways.
Installation Techniques: Drainage vs Pathway Gravel
Drainage gravel installation requires a base layer of geotextile fabric to prevent soil infiltration, followed by a layer of coarse stones that facilitate water flow and prevent pooling. Pathway gravel installation involves compacting a sub-base of crushed stone before adding a finer gravel layer to create a stable, walkable surface. Proper edge restraints and consistent grading are essential in pathway gravel to maintain shape and prevent spread, while drainage gravel prioritizes permeability and rapid water dispersal.
Cost Comparison: Drainage Gravel vs Pathway Gravel
Drainage gravel typically costs between $30 to $50 per ton, due to its angular shape and specific size for water flow management, making it slightly more expensive than pathway gravel, which ranges from $25 to $40 per ton and is designed for durability and foot traffic comfort. Pathway gravel often requires more frequent replenishment because of weathering and compaction, potentially raising long-term costs despite its lower initial price. Comparing costs involves not only price per ton but also installation depth and area coverage, where drainage gravel's specialized function justifies its higher upfront investment in effective water management systems.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Gravel Type
Drainage gravel requires regular inspection and occasional removal of debris to maintain optimal water flow and prevent clogging, often necessitating periodic washing to sustain permeability. Pathway gravel demands frequent raking and replenishment to preserve a smooth walking surface and minimize displacement caused by foot traffic or weather conditions. Both types benefit from proper edging to contain gravel and reduce maintenance frequency.
Environmental Impact: Drainage vs Pathway Gravel
Drainage gravel enhances environmental sustainability by promoting excellent water permeability, reducing runoff, and preventing soil erosion, which supports groundwater recharge and minimizes flooding risks. Pathway gravel, while also permeable, often uses finer materials that can compact and limit water infiltration, potentially increasing surface runoff and localized erosion. Selecting drainage gravel over pathway gravel improves eco-friendly landscaping by optimizing natural water cycles and protecting surrounding ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Gravel for Your Project
Drainage gravel typically consists of angular, coarse stones that promote water flow and prevent pooling, making it ideal for drainage systems and areas prone to water accumulation. Pathway gravel is usually smoother and finer, providing a stable, comfortable walking surface while maintaining adequate permeability. Selecting the right gravel involves assessing project requirements such as water drainage needs, surface stability, and aesthetic preferences to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Drainage Gravel vs Pathway Gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com