Pea gravel consists of small, rounded stones that provide excellent drainage and a smooth surface ideal for walkways and garden paths. Crushed stone features angular, jagged edges that compact well, making it a durable choice for driveways and construction bases. Both materials offer unique benefits tailored to different landscaping and building needs depending on texture and structural requirements.
Table of Comparison
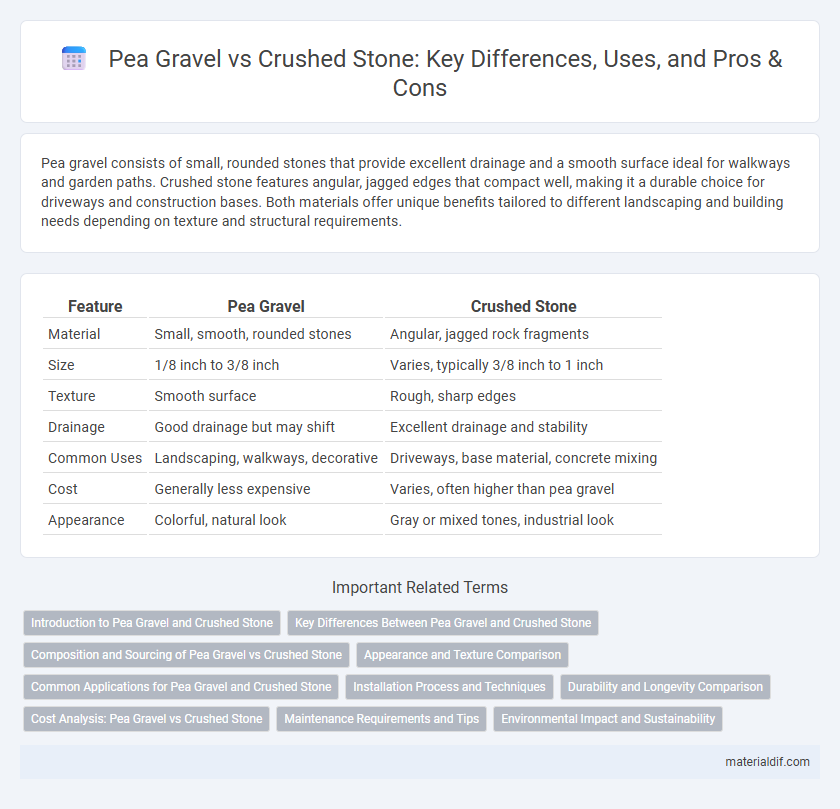
| Feature | Pea Gravel | Crushed Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Small, smooth, rounded stones | Angular, jagged rock fragments |
| Size | 1/8 inch to 3/8 inch | Varies, typically 3/8 inch to 1 inch |
| Texture | Smooth surface | Rough, sharp edges |
| Drainage | Good drainage but may shift | Excellent drainage and stability |
| Common Uses | Landscaping, walkways, decorative | Driveways, base material, concrete mixing |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Varies, often higher than pea gravel |
| Appearance | Colorful, natural look | Gray or mixed tones, industrial look |
Introduction to Pea Gravel and Crushed Stone
Pea gravel consists of small, smooth, rounded stones typically 1/8 to 3/8 inch in size, often used for landscaping, walkways, and decorative ground cover. Crushed stone is made from mechanically crushed rock fragments with angular edges, available in various sizes, commonly utilized for driveways, drainage solutions, and concrete aggregate. Both materials provide distinct aesthetic and functional benefits depending on project requirements, with pea gravel offering enhanced drainage and comfort underfoot, while crushed stone offers superior compaction and stability.
Key Differences Between Pea Gravel and Crushed Stone
Pea gravel consists of smooth, rounded stones typically ranging from 3/8 to 3/4 inch in diameter, making it ideal for decorative uses and landscaping projects that require a polished look. Crushed stone is produced by mechanically breaking larger rocks into angular pieces, often used for construction, drainage, and road base due to its interlocking stability. The key differences include texture, size uniformity, and functional applications, with pea gravel excelling in aesthetics and crushed stone providing superior structural support.
Composition and Sourcing of Pea Gravel vs Crushed Stone
Pea gravel consists of naturally rounded, smooth stones primarily composed of quartz, granite, or other durable rock types, sourced from riverbeds and natural deposits. Crushed stone is mechanically processed from larger rocks like limestone, basalt, or granite, offering angular and rough-textured fragments ideal for construction. The natural formation of pea gravel results in uniform, rounded shapes, whereas crushed stone's sourcing and crushing techniques produce varied sizes and sharper edges.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Pea gravel features smooth, rounded shapes with a polished surface, giving it a softer, more decorative appearance ideal for walkways and landscaping projects. In contrast, crushed stone consists of sharp, angular fragments with a rough texture, providing excellent compaction and stability for driveways and construction bases. The distinct textures influence drainage and mobility, with pea gravel allowing easier water flow while crushed stone offers stronger interlocking properties.
Common Applications for Pea Gravel and Crushed Stone
Pea gravel, with its smooth texture and rounded shape, is commonly used in landscaping features, garden paths, and decorative ground cover. Crushed stone, characterized by its angular edges and durability, is preferred for driveways, road bases, and concrete aggregate. Both materials provide effective drainage solutions but serve distinct functions based on their structural properties.
Installation Process and Techniques
Pea gravel installation involves spreading small, smooth stones over a prepared base, ensuring proper compaction and drainage with landscape fabric underneath to prevent weed growth. Crushed stone requires a layered approach, starting with a compacted gravel base, followed by finer aggregate layers that are carefully compacted to provide stability and prevent shifting. Both materials demand precise grading and edging techniques to maintain structural integrity and enhance longevity in landscaping or driveway projects.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Pea gravel offers smooth, rounded edges that resist chipping but may shift more under pressure, making it less durable for high-traffic areas compared to crushed stone. Crushed stone features angular, jagged edges that lock tightly together, providing superior stability and longer-lasting performance in landscaping and construction projects. The hardness and compaction ability of crushed stone contribute to its enhanced longevity, especially in driveways, walkways, and drainage systems.
Cost Analysis: Pea Gravel vs Crushed Stone
Pea gravel generally costs between $40 and $85 per ton, making it a more affordable option for decorative projects and landscaping. Crushed stone prices range from $30 to $60 per ton, often favored for construction due to its durability and strength. Labor and delivery fees vary, influencing the overall expense, with crushed stone requiring more intensive installation in some cases, potentially increasing total costs.
Maintenance Requirements and Tips
Pea gravel requires minimal maintenance as it naturally compacts and drains well, reducing the need for frequent replenishment or leveling. Crushed stone demands regular raking and occasional top-ups to prevent displacement and maintain a smooth surface. Both materials benefit from edge restraints and periodic washing to remove debris and maintain appearance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pea gravel and crushed stone differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with pea gravel generally sourced from riverbeds and considered more environmentally friendly due to minimal processing and natural water filtration benefits. Crushed stone requires extensive quarrying and crushing processes, leading to higher energy consumption and habitat disruption, making it less sustainable in comparison. Choosing pea gravel supports eco-conscious landscaping by promoting natural resource conservation and reducing carbon emissions associated with material extraction and processing.
Pea Gravel vs Crushed Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com